Kim, JH, et al. Differential diagnosis of periampullary carcinomas at MR imaging. Radiographics. 2002; 22(6):1335–1352.
Korman, MU. Radiologic evaluation and staging of small intestine neoplasms. Eur J Radiol. 2002; 42(3):193–205.
Iki, K, et al. Primary adenocarcinoma of the duodenum demonstrated by ultrasonography. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36(3):195–199.
Ishida, H, et al. Duodenal carcinoma: sonographic findings. Abdom Imaging. 2001; 26(5):469–473.
Nagi, B, et al. Primary small bowel tumors: a radiologic-pathologic correlation. Abdom Imaging. 2001; 26(5):474–480.
Gore, R, et al. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology, 2nd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2000. [1980-1992].
Buckley, JA, et al. CT evaluation of small bowel neoplasms: spectrum of disease. Radiographics. 1998; 18(2):379–392.
Neugut, AI, et al. The epidemiology of cancer of the small bowel. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998; 7(3):243–251.
Arber, N, et al. Molecular genetics of small bowel cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1997; 6(9):745–748.
Buckley, JA, et al. Small bowel cancer. Imaging features and staging. Radiol Clin North Am. 1997; 35(2):381–402.
Buckley, JA, et al. The accuracy of CT staging of small bowel adenocarcinoma: CT/pathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997; 21(6):986–991.
Gore, RM. Small bowel cancer. Clinical and pathologic features. Radiol Clin North Am. 1997; 35(2):351–360.
Maglinte, DT, et al. Small bowel cancer. Radiologic diagnosis. Radiol Clin North Am. 1997; 35(2):361–380.
Laurent, F, et al. CT of small-bowel neoplasms. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1995; 16(2):102–111.
 .
.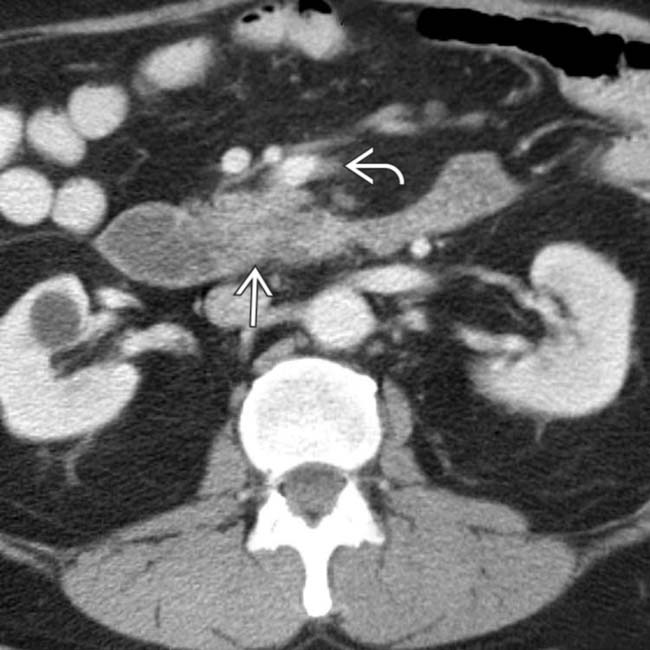
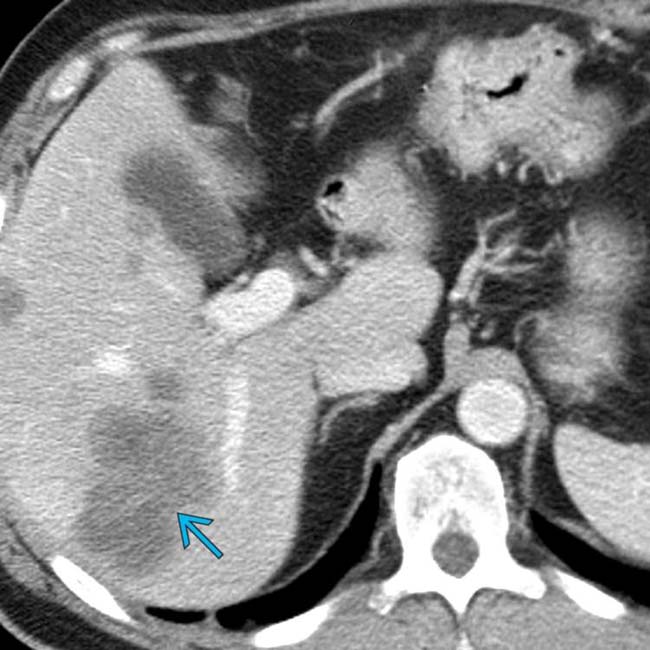
 . There is also a subtle extension of tumor along the superior mesenteric vessels
. There is also a subtle extension of tumor along the superior mesenteric vessels  .
.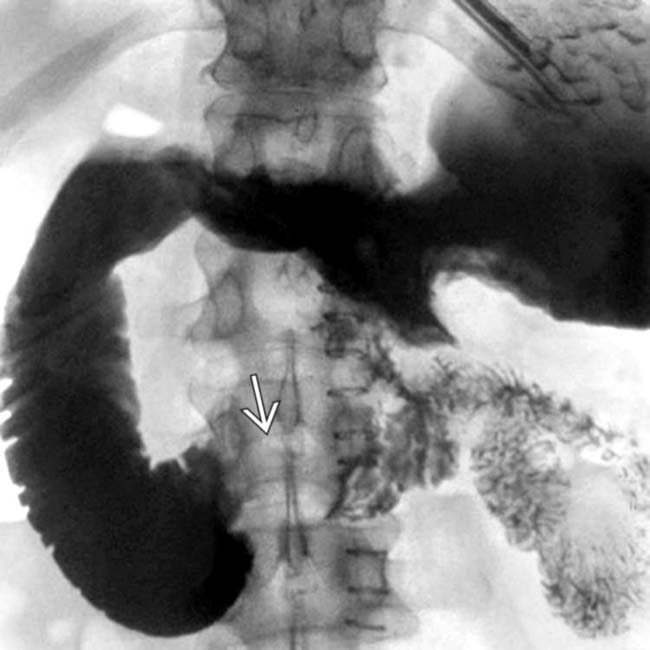
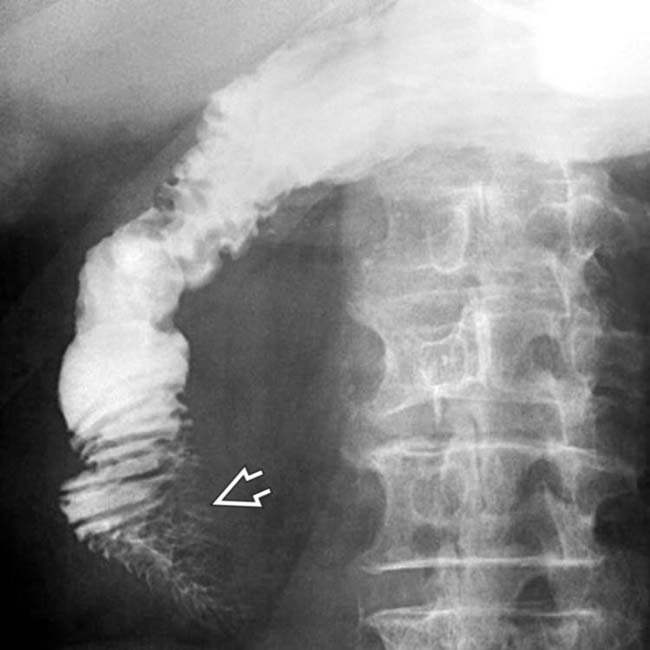
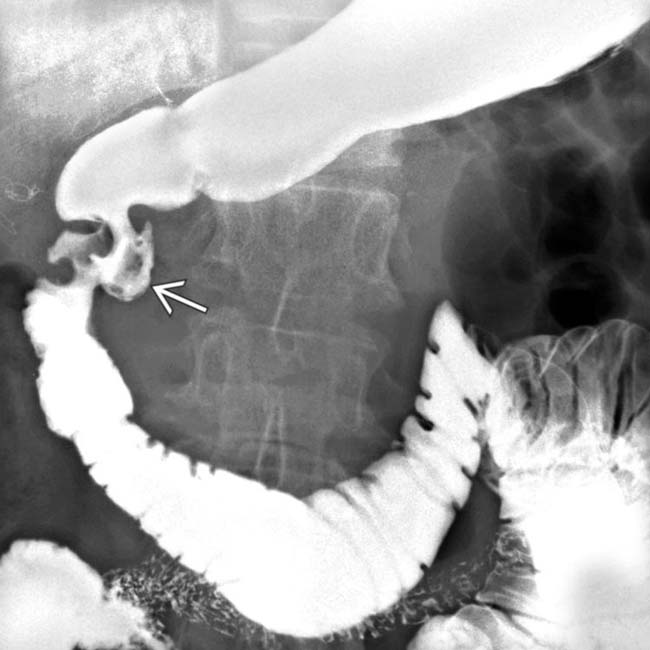
 more clearly. Note the “shoulder” or abrupt transition to tumor at its proximal extent. The lumen of the more proximal duodenum is dilated.
more clearly. Note the “shoulder” or abrupt transition to tumor at its proximal extent. The lumen of the more proximal duodenum is dilated.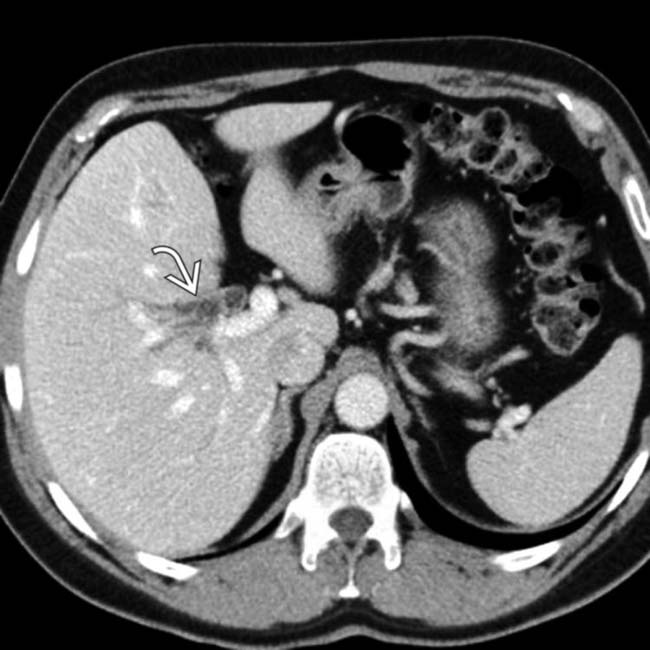
 .
.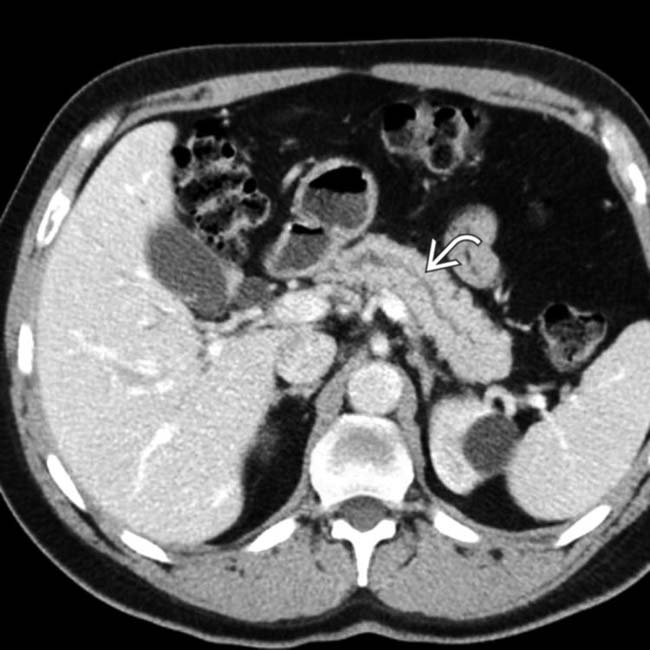
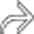 is also dilated. The findings, to this point, suggest a malignant obstructing neoplasm at or near the ampulla of Vater.
is also dilated. The findings, to this point, suggest a malignant obstructing neoplasm at or near the ampulla of Vater.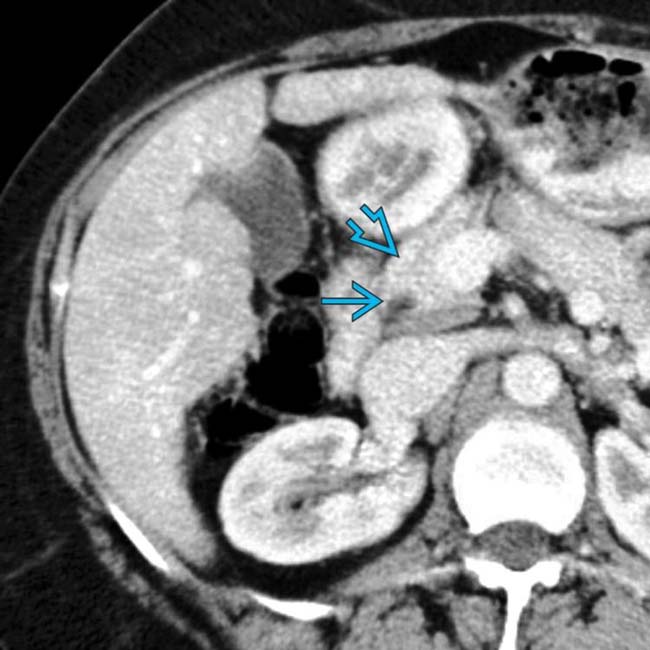
 is normal, while the distal common bile duct
is normal, while the distal common bile duct  remains dilated.
remains dilated.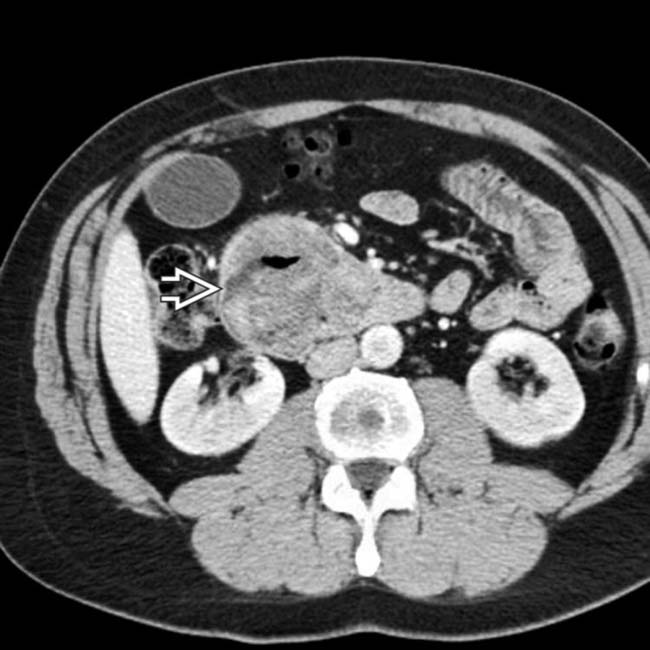
 present within the lumen of the 2nd and 3rd portions of the duodenum that obstructed the ducts at the site of a relatively low-lying ampulla. Endoscopy confirmed a duodenal carcinoma arising in a villous adenoma.
present within the lumen of the 2nd and 3rd portions of the duodenum that obstructed the ducts at the site of a relatively low-lying ampulla. Endoscopy confirmed a duodenal carcinoma arising in a villous adenoma.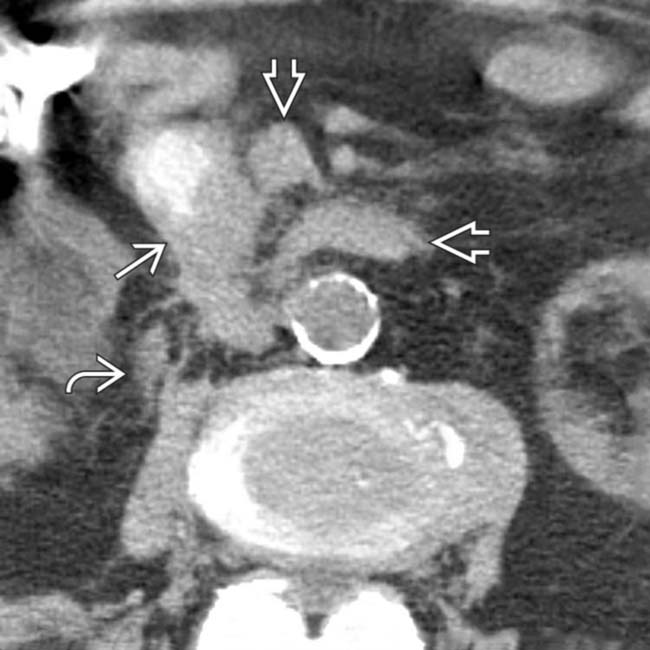
 . There is extensive tumor infiltration of the adjacent fat planes
. There is extensive tumor infiltration of the adjacent fat planes  and regional lymphadenopathy
and regional lymphadenopathy  .
.
 , the primary duodenal carcinoma.
, the primary duodenal carcinoma.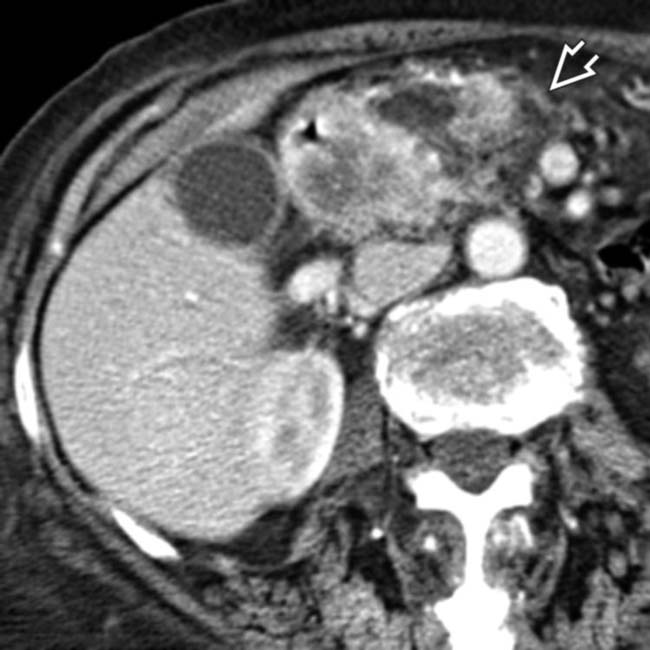
 .
.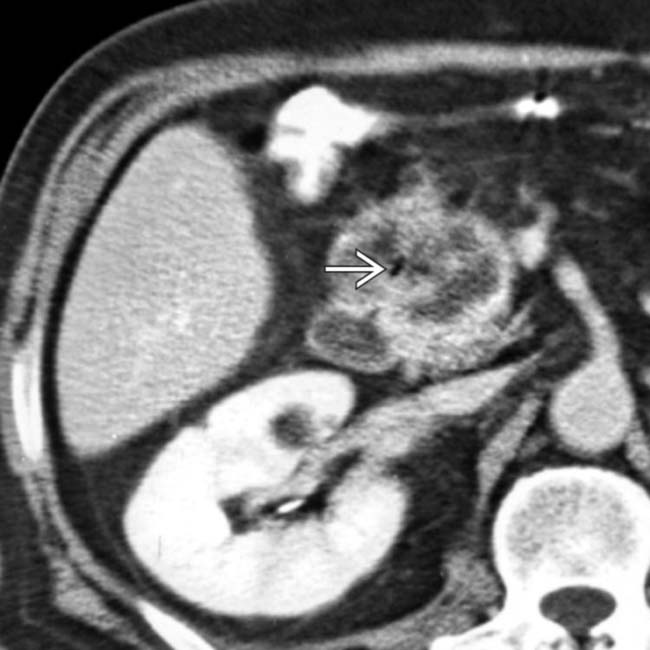
 , which shows the mass to be arising within the duodenum rather than the pancreas.
, which shows the mass to be arising within the duodenum rather than the pancreas.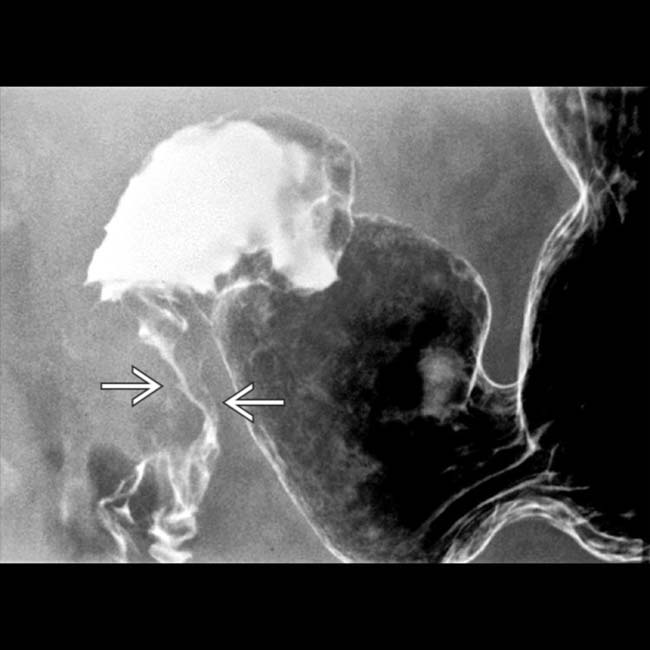
 , representing duodenal carcinoma. (Courtesy H. Harvin, MD.)
, representing duodenal carcinoma. (Courtesy H. Harvin, MD.)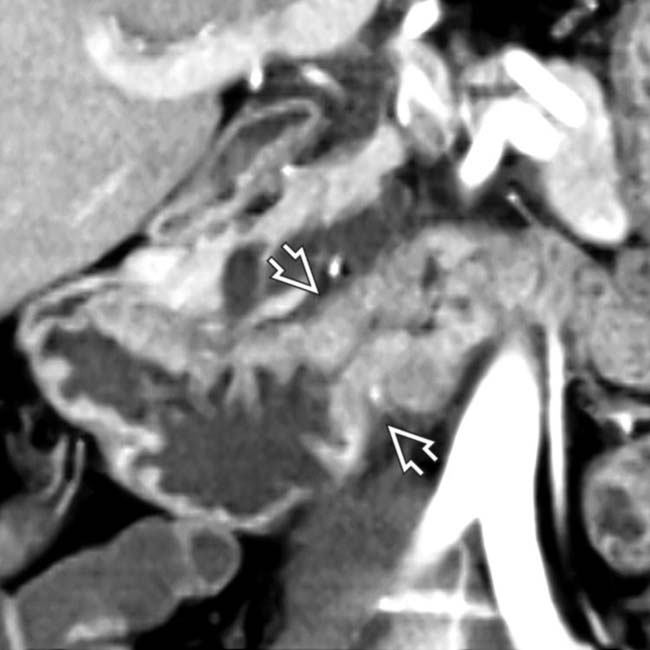
 .
.
 and biliary stent
and biliary stent  for palliation of obstruction.
for palliation of obstruction.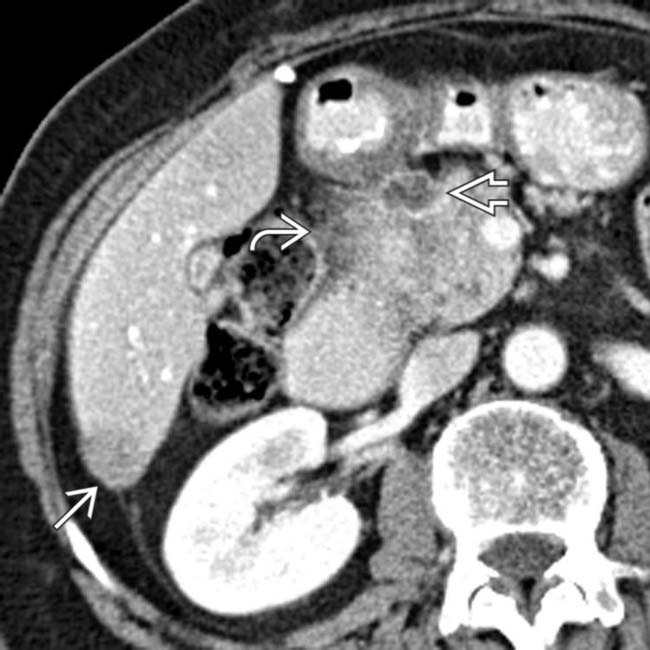
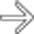
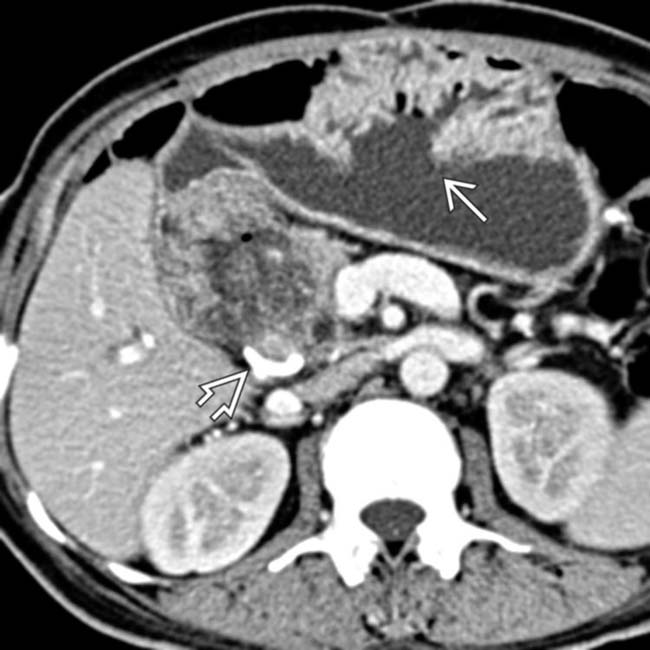
 , a low-density lymph node
, a low-density lymph node  , and liver metastasis
, and liver metastasis 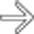 in a patient with duodenal carcinoma.
in a patient with duodenal carcinoma.





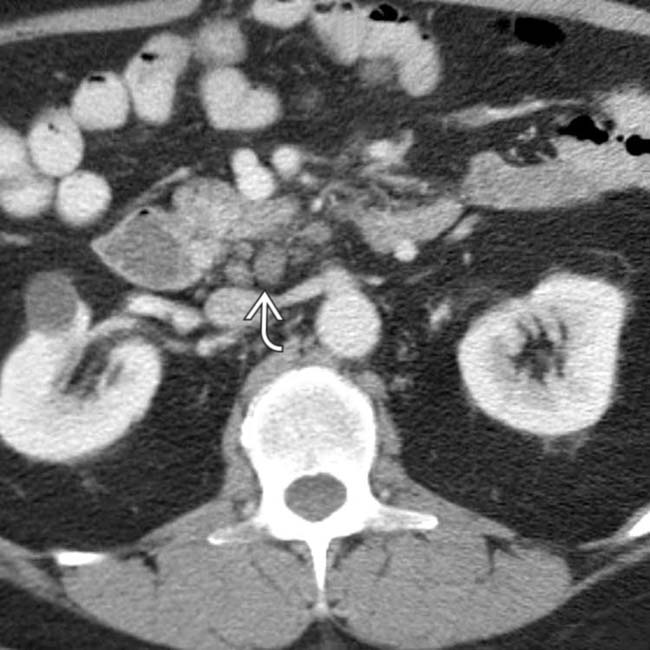
 .
.
































































 , which proved to be duodenal carcinoma.
, which proved to be duodenal carcinoma. 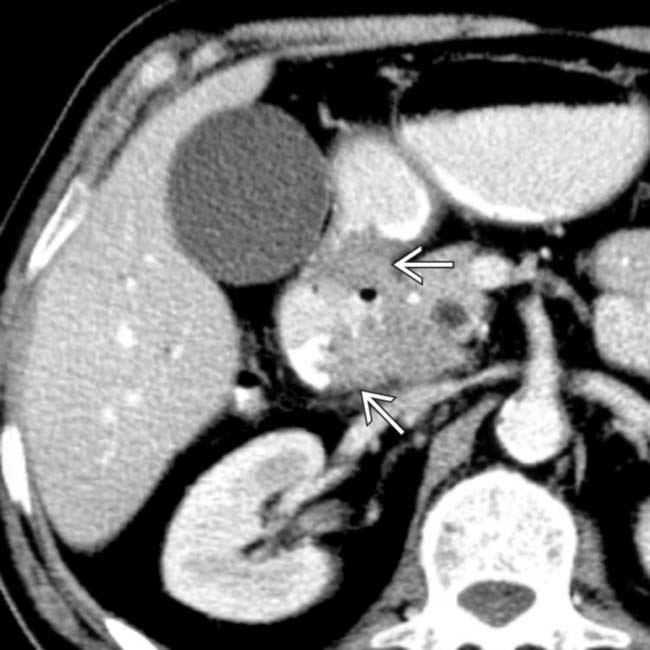
 along the medial border of the 2nd portion of the duodenum, which proved to be duodenal carcinoma.
along the medial border of the 2nd portion of the duodenum, which proved to be duodenal carcinoma. 


