1.Nisa, AU, et al. Dubin-Johnson syndrome. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008; 18(3):188–189.
2.Mor-Cohen, R, et al. Age estimates of ancestral mutations causing factor VII deficiency and Dubin-Johnson syndrome in Iranian and Moroccan Jews are consistent with ancient Jewish migrations. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007; 18(2):139–144.
3.Jedlitschky, G, et al. Structure and function of the MRP2 (ABCC2) protein and its role in drug disposition. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2006; 2(3):351–366.
4.Lee, JH, et al. Neonatal Dubin-Johnson syndrome: long-term follow-up and MRP2 mutations study. Pediatr Res. 2006; 59(4 Pt 1):584–589.
5.Rastogi, A, et al. Dubin-Johnson syndrome–a clinicopathologic study of twenty cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2006; 49(4):500–504.
6.Sobaniec-Lotowska, ME, et al. Ultrastructure of Kupffer cells and hepatocytes in the Dubin-Johnson syndrome: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12(6):987–989.
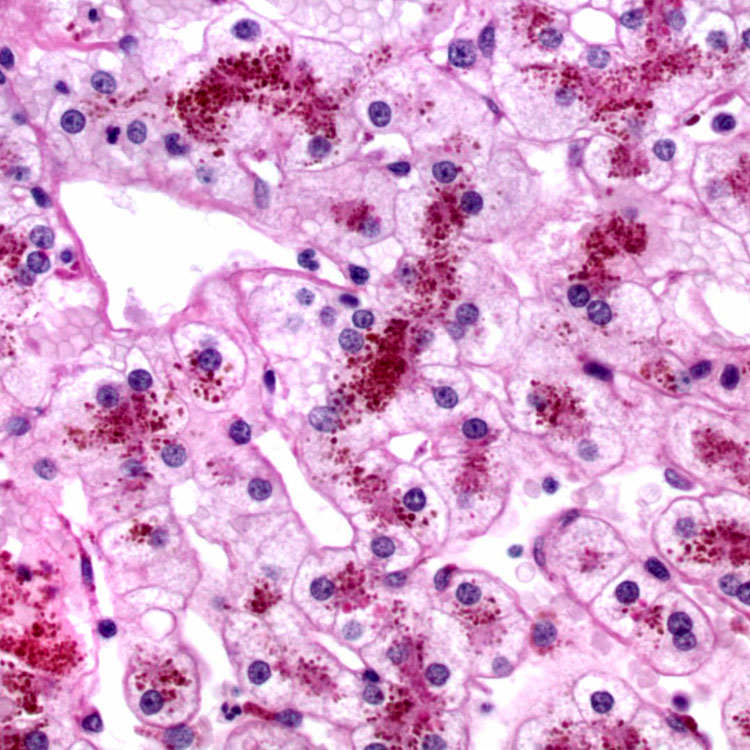
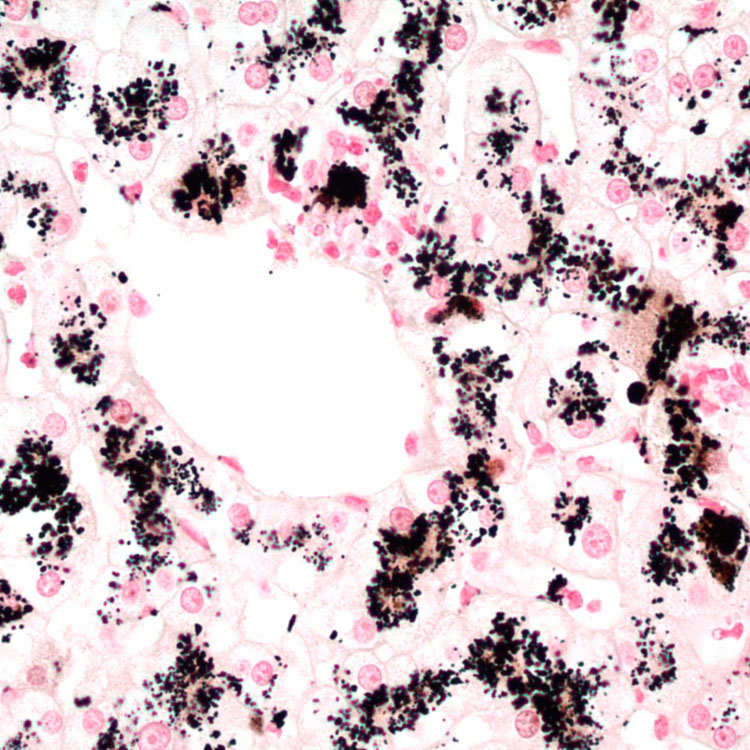
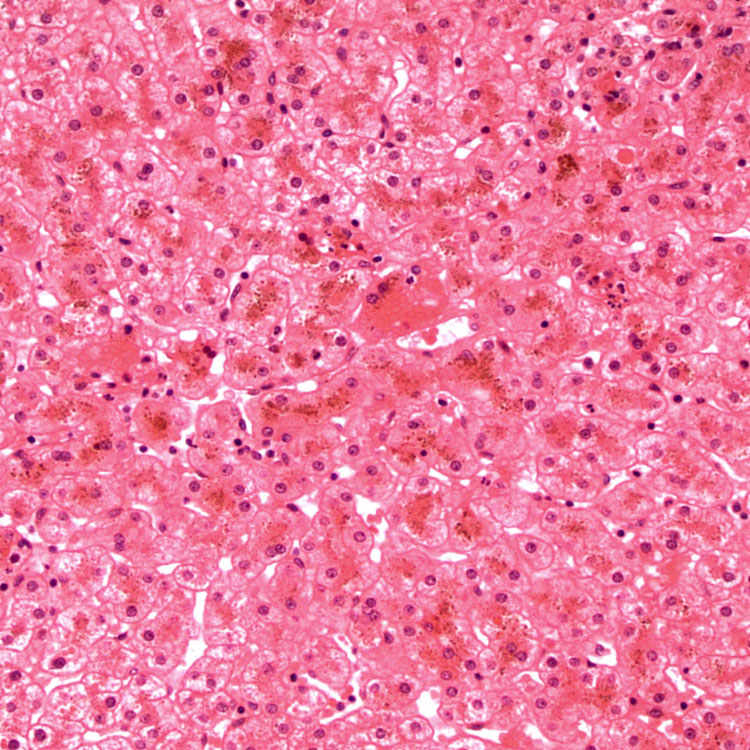
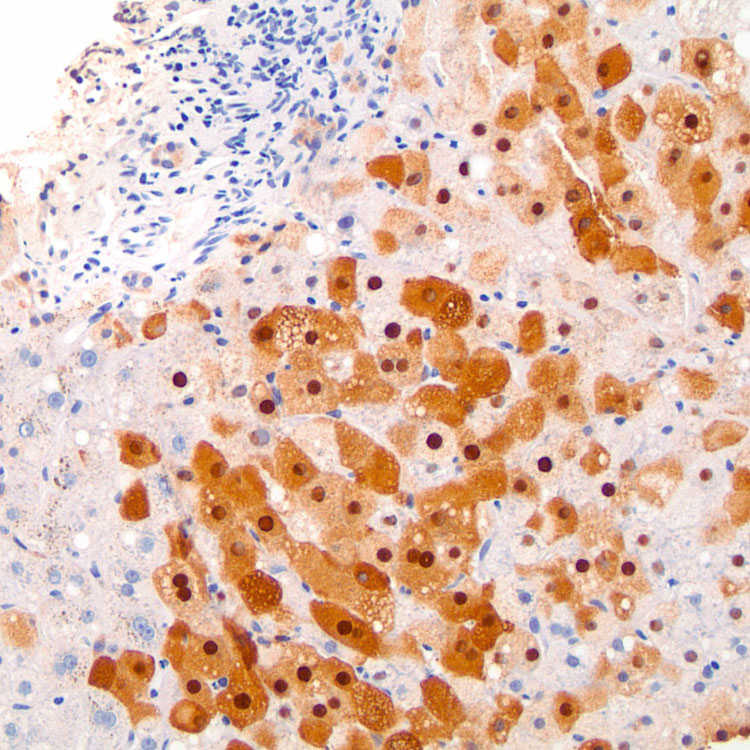
 corresponding to the pigment within centrizonal hepatocytes.
corresponding to the pigment within centrizonal hepatocytes.