Chapter 34 DNA Repair
SOURCES OF DNA DAMAGE
DNA damage comes from two sources: the intrinsic metabolism of the cell and environmental insult.
DNA REPAIR
Because DNA damage is continual, DNA repair systems are found in all organisms to reverse or remove these altered bases. Many plants and animals (but not humans) have an enzyme called photolyase that is able to absorb visible light and use the energy to directly split apart the fused bases in a CPD or 6–4 photoproduct, restoring the native DNA sequence. Humans rely on a complex of DNA repair enzymes that recognize distortions in the DNA, such as those caused by CPD or 8oGua, and remove them by cutting out the single strand of DNA. Special enzymes called endonucleases (e.g. T4 endonuclease V, UV endonuclease) specifically target only CPD and the OGG1 glycosylase binds only to 8oGua. Once the damaged bases have been removed, the gap in the DNA is restored by adding in undamaged bases, using the opposite strand as a template.
MEASURING DNA REPAIR
• The comet assay
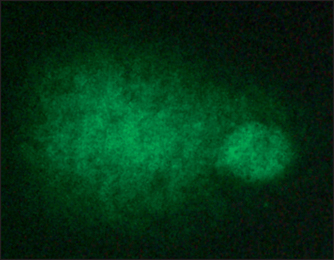
Cultured mammalian cells are seeded onto glass slides and placed in an electric field. The DNA, which is ordinarily tightly wound, cannot leave the nucleus. But if the DNA contains breaks in the double helix, then the stands can unwind and stream out of the nucleus toward the cathode (positive charged pole). When the DNA is stained and examined under the microscope, the nuclei appear to be ‘comets’ with a ball-shaped head and strands trailing out into a tail Fig. 34.1.
• Antibody-based assays
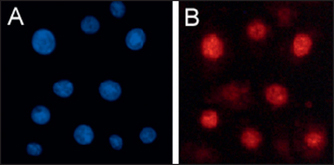
Several antibodies raised against specific types of DNA damage (e.g. anti-CPD, anti-8oGua or anti-O6meGua) have been developed to directly measure the appearance and removal of DNA lesions. Cultured cells may be stained with these antibodies, and counterstained for the DNA of the nucleus, and then examined under the microscope for the amount of antibody binding as a measure of the extent of DNA damage. Figure 34.2A shows UV-irradiated cells stained for the nucleus (blue); Figure 34.2B shows the same cells also stained for CPD (red). In other assays the DNA is purified from the cells, or from skin, and bound to a filter membrane, which is then probed with the damage-specific antibodies. A reduction in the amount of antibody binding after treating the cells, artificial or natural skin with a cosmeceutical ingredient (always compared to an untreated control) is a direct measure of DNA repair.
Brash D. Sunlight and the onset of skin cancer. Trends in Genetics. 1997;13:410–414.
Brennan M, Bhatti H, Nerusu KC, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in UV-irradiated human skin. Photochemistry and Photobiology. 2003;78:43–48.
Fisher G, Datta S, Talwar H, et al. Molecular basis of sun-induced premature ageing and retinoid antagonism. Nature. 1996;379:335–339.
Obayashi K, Kurihara K, Okano Y, et al. L-ergothioneine scavenges superoxide and singlet oxygen and suppresses TNF-α and MMP-1 expression in UV-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. Journal of Cosmetic Science. 2005;56:17–27.
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz L, Unsal-Kacmaz K, et al. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2004;73:39–85.
Stege H, Roza L, Vink A, et al. Enzyme plus light therapy to repair DNA damage in ultraviolet-B-irradiated human skin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. 2000;97:1790–1795.
van Zeeland A, Mullenders L, Vrieling H. Gene and sequence specificity of DNA damage induction and repair: consequences for mutagenesis. Mutation Research. 2001;485:15–21.
Wolf P, Maier H, Müllegger R, et al. Topical treatment with liposomes containing T4 endonuclease V protects human skin in vivo from ultraviolet-induced upregulation of interleukin-10 and tumor necrosis factor-α. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2000;114:149–156.
Yarosh D, Tsimis J, Green L, et al. Enhanced unscheduled DNA synthesis in UV-irradiated human skin explants treated with T4N5 liposomes. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1991;97:147–150.
Yarosh D, Klein J, O’Connor A, et al. Effect of topically applied T4 endonuclease V in liposomes on skin cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum: a randomized study. Lancet. 2001;357:926–929.