Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prevention of Bacterial Diseases
I Laboratory Identification of Bacteria
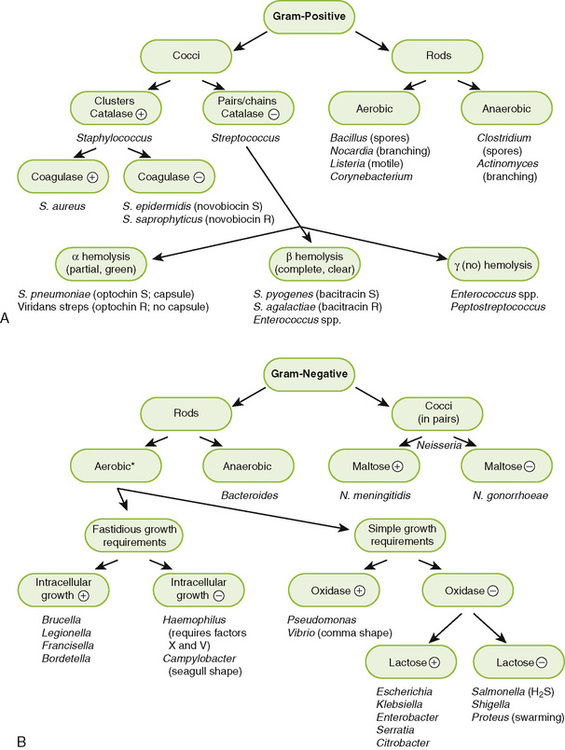
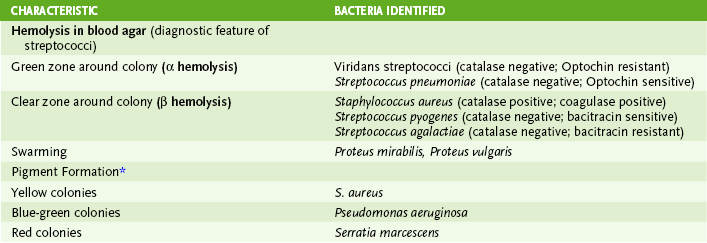
• Most medically important bacteria can be classified as gram-positive or gram-negative and further identified based on their shape and various metabolic properties as summarized in Figure 8-1.
• Step 1: treat smear with crystal violet primary stain.
• Step 2: add iodine solution, which precipitates primary stain within the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall.
• Step 3: rinse with solvent that dissolves the outer membrane and washes out the crystal violet from the thin peptidoglycan layer of gram-negative bacteria but not from the thick peptidoglycan layer of gram-positive bacteria.
• Step 4: counterstain with red safranin, which is taken up by gram-negative organisms, allowing them to be visualized.
• Purple (positive reaction): organisms with thick peptidoglycan cell wall
• Red (negative reaction): organisms with thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane
• Gram-variable or gram-resistant: modified cell wall old cultures or cells treated with β-lactam antibiotics in which the peptidoglycan is weakened—therefore, poor or no color retention; modified cell wall (Box 8-1)
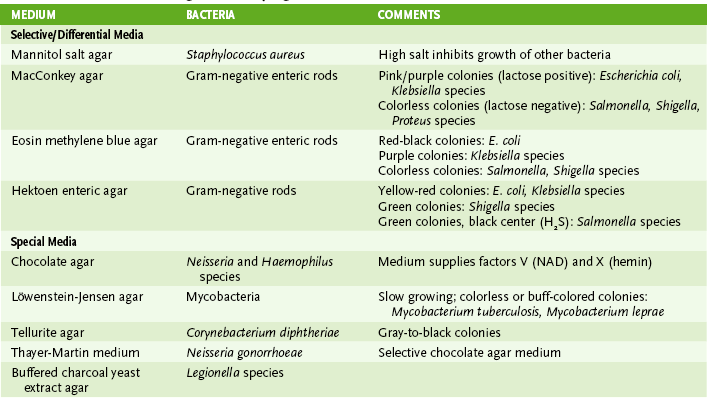
B Growth and isolation of bacteria
• Most bacteria will grow on blood agar or other nonselective media.
• Selective medium inhibits growth of some bacteria (e.g., EMB agar inhibits gram-positive bacteria).
• Differential medium incorporates an identifying test.
a. MacConkey agar is both selective (inhibits gram-positive bacteria) and differential (tests for lactose use).
• Special medium incorporates particular metabolites or provides specific culture conditions required by certain bacteria.
1. Metabolic tests for fermentation of various sugars and production of byproducts (e.g., acid or gases)
• Lactose fermentation differentiates the more and less pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae.
a. Lactose fermenting includes more benign Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species.
b. Nonlactose fermenting includes more pathogenic Shigella and Salmonella species.
• Glucose and maltose fermentation differentiate Neisseria species.
D Immunologic tests (see Chapter 3)
1. Detection of surface antigens is useful in identifying some bacteria and distinguishing between strains (serotypes) of a species that have one or more unique antigens.
2. For example, serotypes of Escherichia coli possess different O antigens. The O157:H7 serotype are enterohemorrhagic E. coli strains.
E Antibiotic sensitivity assays
• Quantitative determination of drug concentration that inhibits growth or kills an organism in culture
• Semiquantitative method used to evaluate sensitivity of an organism to achievable blood levels of an antibiotic
• Is not useful for infections of central nervous system or bone
• Diffusion of antibiotic from impregnated disk inhibits growth of susceptible bacteria plated on agar.
• Diameter of zone of growth inhibition surrounding disk is basis for rating an organism as sensitive, intermediate, or resistant to tested antibiotic.
3. E-test uses a graduated diffusion method to give MIC values for bacteria grown on agar plates.
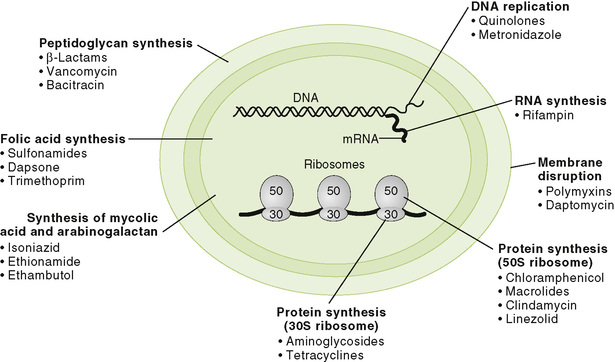
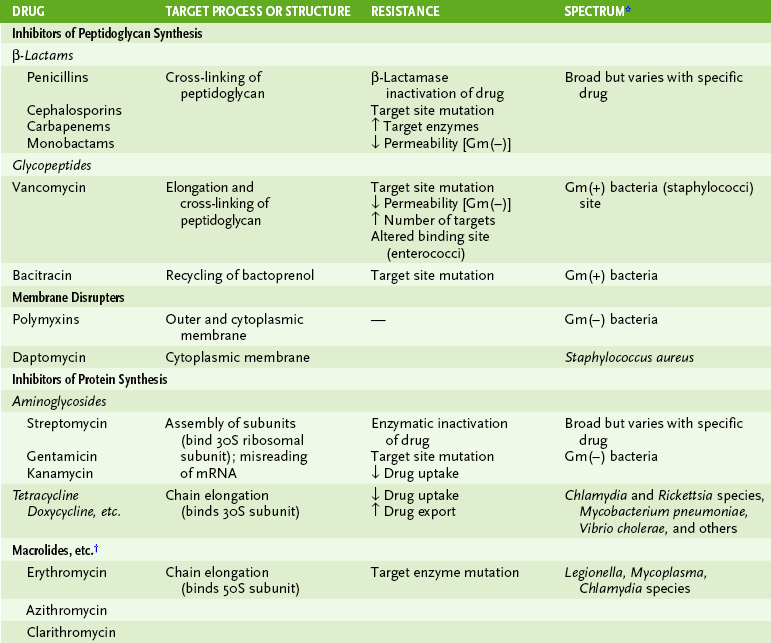
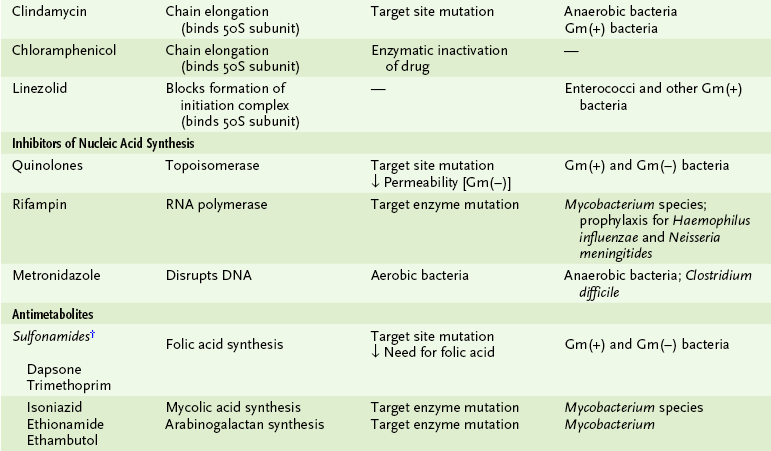
1. Most antimicrobials are inhibitors of essential enzymes or disrupters of membranes (Fig. 8-2; Table 8-3).
TABLE 8-3
Properties of Common Antibiotics
Gm(-), gram negative; Gm(+), gram positive.
*Only a general guide to spectrum of these drugs.
†Refers to ketolides and azalides.
‡Sulfonamides are analogs of PABA, a substrate for dihydropteroate synthase. Dapsone also inhibits this enzyme. Trimethoprim inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, another enzyme in the pathway synthesizing folic acid.
2. Antibiotic resistance can arise by several different mechanisms (Box 8-2; see Table 8-3).
B Inhibitors of peptidoglycan synthesis
• Continued degradation of peptidoglycan in the absence of synthesis prevents growth and eventually leads to cell lysis.
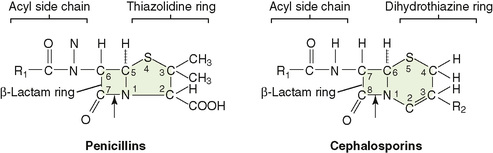
1. Penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems inhibit the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains (Fig. 8-3).
• These drugs, which only act on growing cells, contain a β-lactam ring essential for their activity.
• Smaller and more hydrophilic β-lactam drugs can enter gram-negative bacteria through porin channels in the outer membrane, but bulky or hydrophobic drugs are excluded.
• β-Lactamase, an enzyme that cleaves the β-lactam ring, inactivates these drugs.
a. Many bacteria carry the β-lactamase gene on plasmids, allowing for easy spread of resistance through a bacterial population and even to related strains.
b. Effectiveness of β-lactamase–susceptible antibiotics is increased by coadministration of penicillin analogs (e.g., sulbactam) that inhibit the β-lactamase.
2. Vancomycin inhibits elongation of peptidoglycan chains and their cross-linking.
• “Grabs” onto the D-ala-D-ala of the peptidoglycan precursor
• Is effective against gram-positive bacteria but too bulky to pass through the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
3. Bacitracin prevents reuse of the bactoprenol carrier that functions in assembly of peptidoglycan from smaller precursors.
C Peptide antibiotic disrupters of bacterial membranes
1. Polymyxins and daptomycin have cyclic peptides and a fatty acyl side chain.
2. Polymyxins (colistin) are especially effective against gram-negative bacteria, disrupting both the outer membrane and the cytoplasmic membrane.
3. Polymyxins are used in most topical antibiotic ointments.
D Inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis
1. Quinolones inhibit bacterial topoisomerase, which is essential for maintaining the proper DNA structure for transcription and replication.
• Resistance arises from mutation in topoisomerase, preventing binding of drug, or in porin, reducing entry of drug into gram-negative bacteria.
• Broad-spectrum drugs, especially for gram-negative organisms: ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin
• Extended-spectrum drugs for gram-positive organisms (pneumococci): moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin
2. Rifampin inhibits synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA; transcription) by binding to the bacterial RNA polymerase.
E Inhibitors of protein synthesis
1. Several groups of antibiotics prevent initiation of protein synthesis or peptide bond formation (i.e., chain elongation), or they cause misreading of the mRNA (see Table 8-3).
2. Resistance results from enzymatic inactivation of the antibiotic or its target site, mutation of the target site, or altered transport of the drug.
1. Refers to treatment with antibody usually in the form of gammaglobulin from immune serum
2. Confers immediate, relatively short-term protection
3. Used in treatment of tetanus, botulism, rabies, and diphtheria
4. Used for prevention of hepatitis A and B, varicella, and other virus infections
1. Refers to treatment with various types of agents that can induce an immune response (Table 8-4)
TABLE 8-4
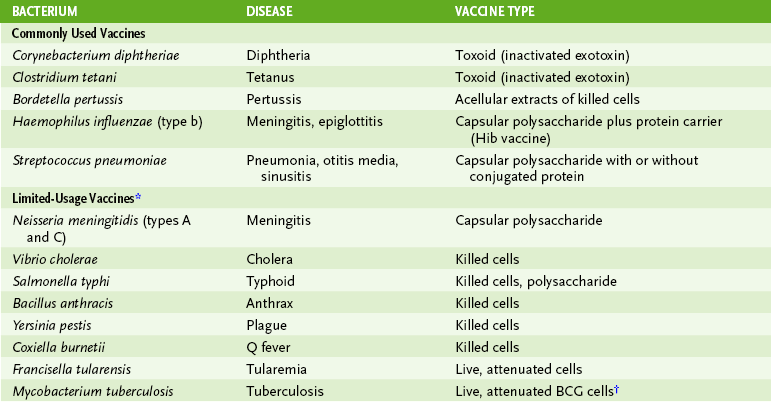
*These vaccines are usually administered only to those at high risk for exposure to the indicated organisms.
†Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is an avirulent strain of Mycobacterium bovis. This vaccine is not recommended in the United States.