Dental radiography – general patient considerations including control of infection
General guidelines on patient care
• For intraoral radiography the patient should be positioned comfortably in the dental chair, ideally with the occlusal plane horizontal and parallel to the floor. For most projections the head should be supported against the chair to minimize unwanted movement. This upright positioning is assumed in subsequent chapters when describing radiographic techniques. However, some clinicians elect to X-ray their patients in the supine position along with most other dental surgery procedures. All techniques need to be modified accordingly, but it can sometimes be more difficult to assess angulations and achieve accurate alignment of film and tubehead with the patient lying down.
• For extraoral views the patient should be reassured about the large, possibly frightening or unfriendly-looking equipment, before being positioned within the machine. This is of particular importance with children.
• The procedure should be explained to the patients in terms they can understand, including warning them not to move during the investigation.
• Spectacles, dentures or orthodontic appliances should be removed. Jewellery including earrings may also need to be removed for certain projections.
• A protective lead thyroid collar, if deemed appropriate for the investigation being carried out, should be placed on the patient (see Ch. 7).
• The exposure factors on the control panel should be selected before positioning the intraoral image receptor and X-ray tubehead, in order to reduce the time of any discomfort associated with the investigation.
• Intraoral image receptor should be positioned carefully to avoid trauma to the soft tissues taking particular care where tissues curve, e.g. the anterior hard palate, lingual to the mandibular incisor teeth and distolingual to the mandibular molars.
• The radiographic investigation should be carried out as accurately and as quickly as possible, to avoid having to retake the radiograph and to lessen patient discomfort.
• The patient should always be watched throughout the exposure to check that he/she has obeyed instructions and has not moved.
Specific requirements when X-raying children and patients with disabilities
These two groups of patients can present particular problems during radiography, including:
As a result of these difficulties, the following additional guidelines should be considered:
• Only radiographic investigations appropriate to the limitations imposed by the patient’s age, cooperation or disability should be attempted.
• Select intraoral image receptor of appropriate size, modifying standard techniques as necessary.
• Utilize assistant(s) to help hold the image receptor and/or steady and reassure the patient. This can be accomplished by using an accompanying relative, rather than repeatedly using a member of staff.
NOTE: Radiation protection regulations usually require that during an exposure a designated controlled area or exclusion zone must exist around the X-ray set and theoretically only the patient is allowed in this area (see Ch. 7). Therefore, if assistance is needed and this requirement cannot be fulfilled, a radiation protection adviser (RPA) or a medical physics expert must advise on the appropriate protective measures for the assistant.
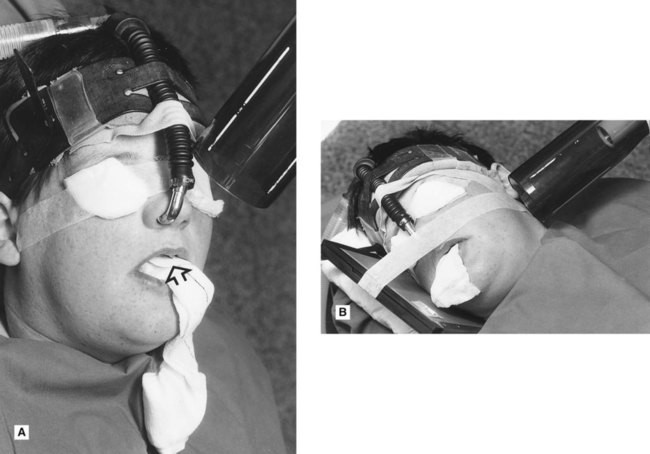
• Perform any necessary radiography under general anaesthesia, if an uncooperative patient is having their dental treatment in this manner (see Fig. 8.1). Radiographs taken are usually restricted to oblique laterals and periapicals although bitewings can be taken.
• Avoid panoramic radiography because of the need for the patient to remain still for approximately 18 seconds (see Ch. 15). Oblique lateral radiographs should be regarded as the extraoral views of choice.
• Use the paralleling technique, if possible, for periapical radiography because with this technique the relative positions of the image receptor, teeth and X-ray beam are maintained, irrespective of the position of the patient’s head (see Ch. 9).
Control of infection
Main infections of concern
• Infective hepatitis caused by hepatitis B (HBV) or hepatitis C (HCV) viruses. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that of the 2 billion people that have been infected with HBV, more than 350 million have chronic (lifelong) infections. In the developing world, 8–10% of people in the general population become chronically infected. HBV is thought to be 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. WHO estimates that 3% of the world’s population has been infected with HCV
• Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV disease and AIDS caused by HIV)
• Tuberculosis (TB). The incidence of all forms of TB is rising
• Cold sores caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV). HCWs are at risk of getting herpetic whitlow, a painful finger infection, although this has reduced since the adoption of the use of gloves
• Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), e.g. Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD).
A thorough medical history should therefore be obtained from all patients. However, the medical history and examination may not identify asymptomatic carriers of infectious diseases.
Infection control measures
• All staff should be trained in infection control procedures and their compliance monitored.
• All clinical staff should be vaccinated against hepatitis B and have their response to this vaccine checked.
• Open wounds on the hands should be covered with waterproof dressings.
• Protective non-sterile, non-powdered medical gloves (e.g. latex or nitrile) should be worn for all radiographic procedures and changed after every patient.
• Eye protection – either safety glasses or visors (see Fig. 8.2) should be worn but masks are not usually necessary for radiography.
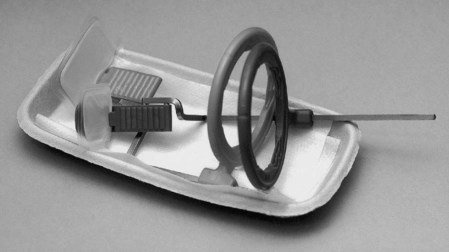
• All required image receptors and holders should be placed on disposable trays to avoid contamination of work surfaces (see Fig. 8.3).
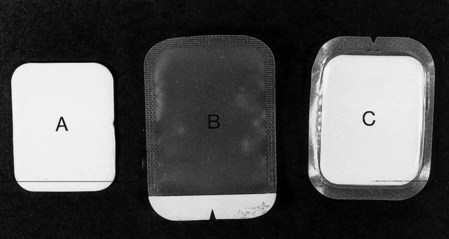
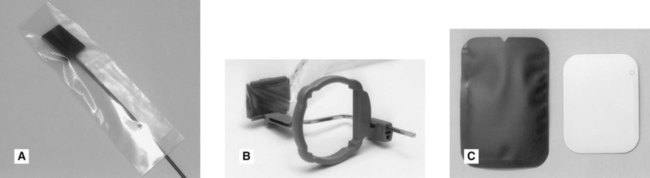
• To prevent salivary contamination of film packets, they should be placed in small barrier envelopes or preferably purchased pre-packed in such envelopes, before use (see Fig. 8.4). After being used in the mouth, the film packet should be emptied out of the barrier envelope onto a clean surface after which it can be handled safely.
• Digital radiography sensors must also be placed inside appropriate barrier envelopes (see Fig. 8.5).
• Film packets must only be introduced into daylight-loading processors using clean hands or washed gloves. Powdered gloves may cause artefacts on the films.
• Contaminated disposable trays, barrier envelopes and image receptor packaging should be discarded directly into suitable clinical waste disposal bags.
• All holders/bite blocks/bite pegs should be decontaminated and sterilized in an autoclave as set out in national guidance, for example in the UK the Department of Health’s document HTM01-05 Decontamination in Primary Care Dental Practices updated in 2012.
• Disposable holders should be discarded as clinical waste.
• X-ray equipment, including the tubehead, control panel, timer switch and cassettes which have been touched during the radiographic procedure should be wiped after each patient with a suitable surface disinfectant, e.g. Mikrozid®.
• Alternatively, all pieces of equipment can be covered, for example with cling film or dedicated barrier sleeves, which can be replaced after every patient (see Fig. 8.6).
• Soiled gloves and cleaning swabs should be placed in suitable disposal bags and sealed for incineration.