Dematiaceous (Melanized) Molds
1. Describe the dematiaceous fungi, including natural habitat, transmission, and diseases with signs and symptoms.
2. Identify the site where mycetomas are frequently located and the population or populations at risk of infection.
3. Compare and contrast Exophiala jeanselmei and Exophiala dermatitidis, including test methods to distinguish between the two.
4. Describe the microscopic and morphologic features of Pseudallescheria boydii, including its sexual and asexual forms.
5. Differentiate the diagnostic microscopic features of the molds included in this chapter.
Epidemiology and Pathogenesis
Superficial Infections (Tinea Nigra and Black Piedra)
Mycetoma
Two types of mycetomas have been described. Actinomycotic (bacterial) mycetomas are caused by the aerobic actinomycetes, including Nocardia, Actinomadura, and Streptomyces spp. (The aerobic Actinomycetes are described in detail in Chapter 19.) Eumycotic (fungal) mycetomas are caused by a heterogeneous group of fungi that have septate hyphae. Eumycotic mycetomas are subcategorized as white grain mycetomas or black grain mycetomas, a distinction determined by the pigmentation of the infecting agent’s hyphae.
Pathogenesis and Spectrum of Disease
The spectrum of disease caused by the dematiaceous fungi ranges from superficial infections (e.g., skin and hair) to emergent, rapidly progressive, and often fatal disease (e.g., brain abscess). The following list, which is not comprehensive, provides the common etiologic agents of diseases that may be caused by dematiaceous fungi (Table 61-1).
TABLE 61-1
| Organism | Disease | Site | Tissue Form |
| Slow-Growing Species | |||
| Cladosporium spp. | Chromoblastomycosis | Subcutaneous | Sclerotic bodies |
| Phaeohyphomycosis | Brain, subcutaneous | Septate hyphae | |
| Ochroconis gallopava | Phaeohyphomycosis | Brain, subcutaneous, lungs | Septate hyphae |
| Exophiala dermatitidis | Phaeohyphomycosis | Brain, eye, subcutaneous, and dissemination | Hyphal fragments and budding yeast |
| Pneumonial | Lungs | ||
| Hortaea jeanselmei | Mycetoma phaeomycotic cyst | Subcutaneous | Hyphal fragments and budding yeasts |
| Hortaea werneckii | Tinea nigra | Skin | Hyphal fragments and budding yeast |
| Fonsecaea spp. | Chromoblastomycosis | Subcutaneous | Sclerotic bodies |
| Phaeohyphomycosis | Brain | Septate hyphae | |
| Cavitary lung disease | Lungs | Septate hyphae | |
| Phialophora spp. | Chromoblastomycosis | Subcutaneous | Sclerotic bodies |
| Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous | Septate hyphae | |
| Septic arthritis | Joints | Septate hyphae | |
| Piedraia hortae | Black piedra | Hair | Asci-containing nodules cemented to hair shafts |
| Madurella mycetomatis | Mycetoma | Subcutaneous | Hyphal fragments |
| Rapid-Growing Species | |||
| Alternaria spp. | Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous | Septate hyphae |
| Sinusitis | Sinuses | Septate hyphae, possibly fungus ball | |
| Nasal septal erosion | Nasal septum | Septate hyphae | |
| Ulcers and onychomycosis | Skin, nails | Septate hyphae | |
| Bipolaris spp. | Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous, brain, eye, bones | Septate hyphae |
| Sinusitis, fungus ball | Sinuses | Septate hyphae, possibly fungus ball | |
| Curvularia spp. | Sinusitis | Sinuses | Septate hyphae; possibly fungus ball |
| Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous, heart valves, eye, and lungs | Septate hyphae | |
| Drechslera spp. | Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous and brain | Septate hyphae |
| Sinusitis | Sinuses | Septate hyphae | |
| Exserohilum spp. | Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous | Septate hyphae |
| Pseudallescheria boydii | Mycetoma | Subcutaneous | Granules of hyaline hyphae |
| Phaeohyphomycosis | Subcutaneous, skin, joints, bones, brain, lungs | Septate, hyaline hyphae | |
| Cladophialophora bantiana | Phaeohyphomycosis | Brain | Septate hyphae |
 Bacterial: Nocardia, Actinomadura, and Streptomyces spp.
Bacterial: Nocardia, Actinomadura, and Streptomyces spp.
 White grain mycetoma: P. boydii and Acremonium and Fusarium spp.
White grain mycetoma: P. boydii and Acremonium and Fusarium spp.
 Black grain mycetoma: Madurella mycetomatis, Exophiala jeanselmei, and Curvularia spp.
Black grain mycetoma: Madurella mycetomatis, Exophiala jeanselmei, and Curvularia spp.
• Chromoblastomycosis: Cladosporium/Cladophialophora, Phialophora, and Fonsecaea spp.
• Phaeohyphomycosis: E. jeanselmei; Exophiala dermatitidis; and Curvularia, Bipolaris, Alternaria, and Exserohilum spp.
• Sinusitis: Alternaria, Bipolaris, Exserohilum, and Curvularia spp.
• Mycotic keratitis and endophthalmitis: E. dermatitidis and Bipolaris and Curvularia spp.
• Brain abscess: Cladophialophora bantiana, E. dermatitidis, and Bipolaris spp.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Specimen Collection and Transport
See General Considerations for the Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Infections in Chapter 59.
Direct Detection Method
Stains
Cultivation
Superficial Infections.
H. werneckii, the causative agent of tinea nigra, may be recovered on common fungal media but grows very slowly. Initial colonies of H. werneckii may be olive to black, shiny, and yeastlike (Figure 61-2), and usually grow within 2 to 3 weeks. As the cultures age, colonies become filamentous, with velvety gray aerial hyphae. P. hortae, the causative agent of black piedra, is easily cultured on any fungal culture medium lacking cycloheximide. Colonies of this organism are also very slow growing, appear dark brown to black, and also produce aerial mycelium. Some isolates may produce a red to brown diffusible pigment.
Approach to Identification
Superficial Infections
Mycetoma
White Grain Mycetoma: Pseudallescheria boydii and Acremonium spp.
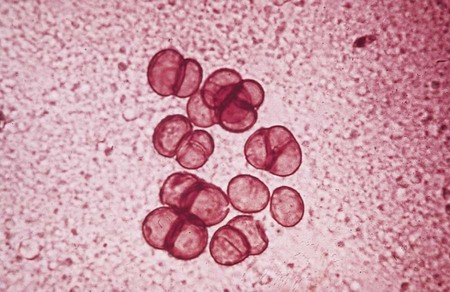
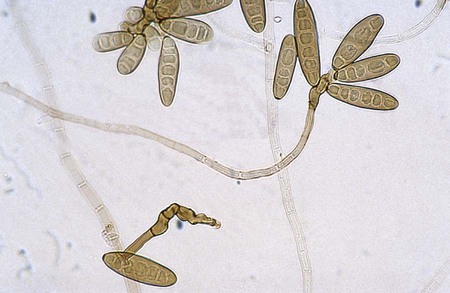
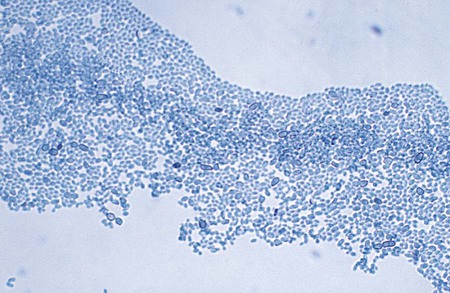
P. boydii is an example of an organism that exhibits both asexual and sexual reproduction. The teleomorphic, or sexual, form of this fungus, which is evidenced by the production of cleistothecia, is P. boydii; if asexual reproductive structures alone are observed, the organism may be called Scedosporium apiospermum. The asexually produced conidia of P. boydii/S. apiospermum are golden brown, elliptical to pyriform, and single celled and are borne singly from the tips of long or short conidiophores (annellophores) (see Figure 59-2). This anamorph (a fungus that disseminates reproductive structures without meiosis) predominates in cultures from clinical specimens. Another anamorphic form, the Graphium stage of P. boydii, may be seen less commonly. It consists of clusters of conidiophores with conidia produced at the ends; it has also been referred to as coremia (see Figure 59-3). The teleomorphic (sexual) form of the organism produces brown to black cleistothecia, which are pseudoparenychatous, saclike structures containing asci and ascospores. When the latter are fully developed, the large (50 to 200 µm), thick-walled cleistothecia rupture, releasing the asci and ascospores (see Figure 59-1). Ascospores are oval and delicately pointed at each end. Isolates of P. boydii may be induced to form cleistothecia by culturing on plain water agar; however, they are seldom found on primary recovery of a culture from a clinical specimen. Recognition of P. boydii is important, because the organism is resistant to amphotericin B, an antifungal agent commonly used for systemic infections.
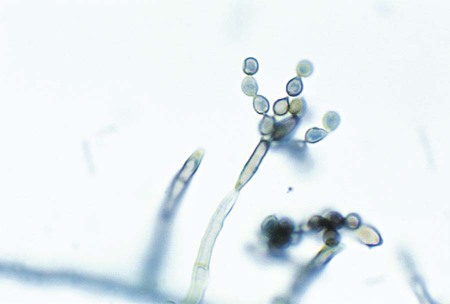
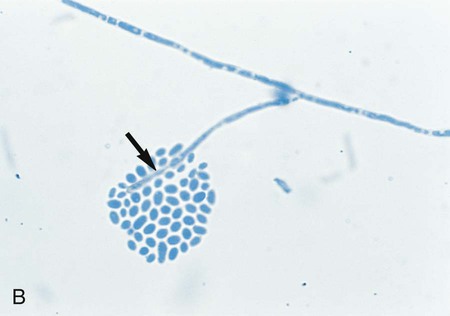
Acremonium spp. develops hyaline hyphae and produces simple, unbranched, erect conidiophores. Single-celled conidia are produced loosely or in gelatinous masses at the tip of the conidiophore (see Figure 59-17). Intercalary and terminal chlamydoconidia may also be produced.
Chromoblastomycosis: Cladosporium, Phialophora, and Fonsecaea spp.
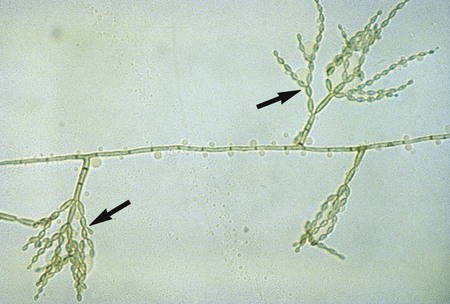
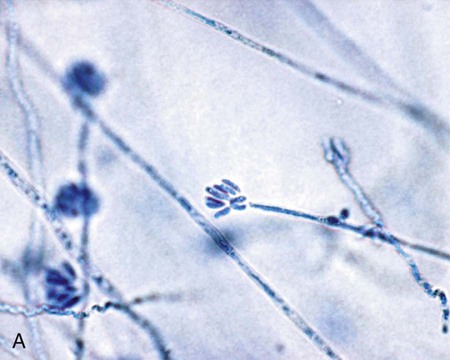
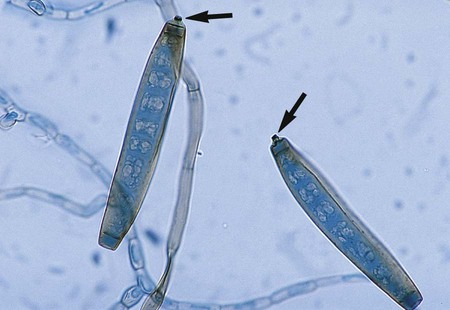
The genus Phialophora includes species that produce short, flask-shaped to tubular phialides, each having a well-developed collarette. Clusters of conidia are produced by the phialides through an apical pore and often remain aggregated near the opening in a gelatinous mass. Phialophora spp. produce colonies that are wooly and olive-brown to brownish gray; some strains may appear to have concentric zones of color. Microscopically, hyphae are dematiaceous, and sporulation is common. Phialophora richardsiae produces phialides with distinct flattened or saucerlike collarettes (Figure 61-3). In contrast, Phialophora verrucosa produces deeper, more cup- or flask-shaped phialides. Pleomorphic phialides may also be seen with these species; however, all produce either or both hyaline elliptical conidia or brown elliptical conidia within the phialides.
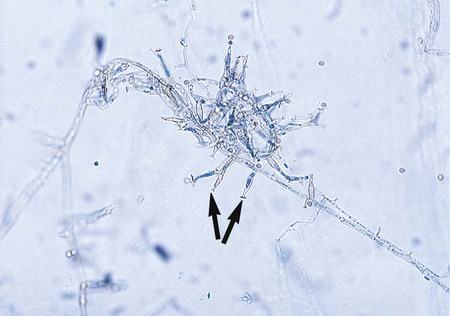
• Cladosporium (Cladosporium carrionii): Cladosporium type of sporulation with long chains of elliptical conidia (2-3 × 4-5 µm) borne from erect, tall, branching conidiophores (Figure 61-4).
• Phialophora spp.: P. verrucosa produces phialides, each with a distinct cup- or flask-shaped collarette (Figure 61-5); P. richardsiae produces phialides with a flattened collarette (see Figure 61-3). Conidia are produced endogenously and occur in clusters at the tip of the phialide.
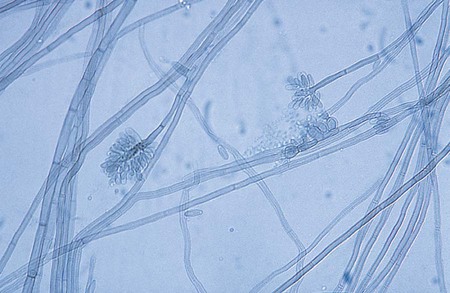
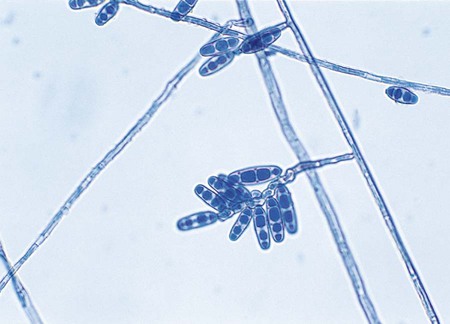
• Fonsecaea spp.: Conidial heads with sympodial arrangement of conidia are seen, with primary conidia giving rise to secondary conidia (Figure 61-6). Cladosporium-type, Phialophora-type, and/or Rhinocladiella-type sporulation may also occur.
Phaeohyphomycosis: Alternaria, Bipolaris, Cladosporium, Curvularia, Drechslera, Exophiala, Exserohilum, and Phialophora spp.
Alternaria spp.
Microscopically hyphae are septate and golden brown pigmented; conidiophores are simple but sometimes branched. Conidiophores bear a chain of large, brown conidia resembling a drumstick and contain both horizontal and longitudinal septa (Figure 61-7). Observing chains of conidia sometimes is difficult, because they may be dislodged as the culture mount is prepared.
Bipolaris spp.
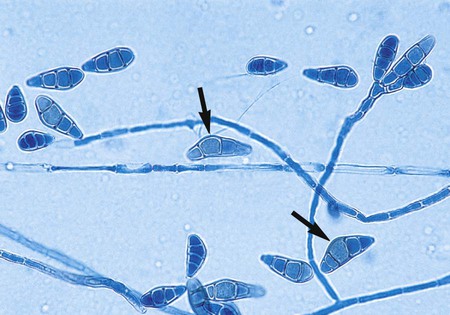
Hyphae are dematiaceous and septate. Conidiophores, however, are characteristically bent (geniculate) at the locations where conidia are attached; conidia are arranged sympodially and are oblong to fusoid. The hilum protrudes slightly (Figure 61-8). Germ tubes are formed at one or both ends, parallel to the long axis of the conidium, when the fungus is incubated in water at 25°C for up to 24 hours (i.e., from both poles, thus the name Bipolaris).
Cladosporium spp.
Microscopically hyphae are septate and brown. Conidiophores are long, branched, and give rise to branching chains of darkly pigmented, budding conidia. Conidia usually are single celled and exhibit prominent attachment scars (dysjunctors). The cells that produce the branch points are often referred to as shield cells (Figure 61-9). This organism frequently fails to reveal chains of conidia on wet mounts, because conidia are so easily dislodged.
Curvularia spp.
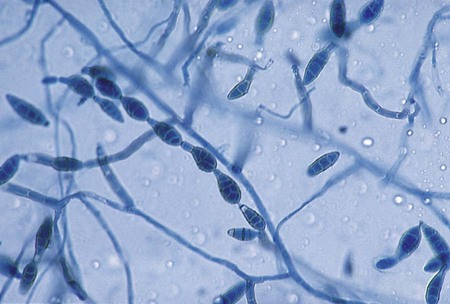
Microscopically hyphae are dematiaceous and septate. Conidiophores are geniculate (i.e., bent where conidia are attached). Conidia are arranged sympodially and are golden brown, multicelled, and curved, with a central swollen cell (Figure 61-10). The end cells are lighter in color than the swollen cell.
Drechslera spp.
Microscopically the hyphae are septate and darkly pigmented, and conidiophores are geniculate. Conidia are produced sympodially (Figure 61-11). However, sporulation is generally sparse with this organism and is not commonly seen. The conidia of Drechslera spp. are impossible to differentiate from those of Bipolaris spp. based on morphologic criteria alone. The germ tube test may be used to differentiate these organisms. Conidia are placed in a drop of water, a coverslip is applied, and the organism is observed after an incubation period of at least 24 hours. Any of the cells of the conidia belonging to Drechslera spp. may germinate, and these may grow perpendicular to the long axis of the conidium. In contrast, only the end cells of the conidia belonging to Bipolaris spp. germinate, and these grow predominantly parallel to the longitudinal axis of the conidium.
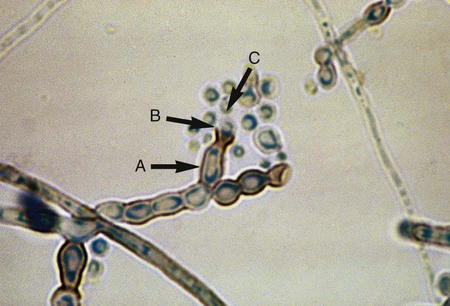
Exophiala spp.
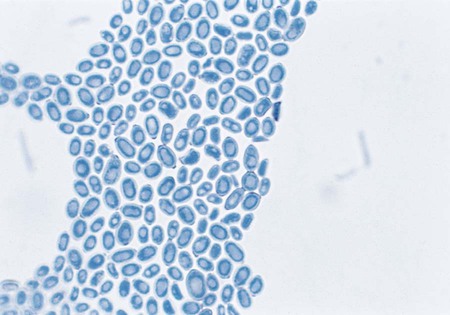
Only the Exophiala species E. jeanselmei and E. dermatitidis are considered here; although other species exist, they are recovered far less commonly in the clinical laboratory. The microscopic features of young colonies of Exophilia sp. exhibit dematiaceous, yeastlike cells (Figure 61-12). Although these may appear to be budding, close inspection may disclose that the daughter cells are produced by annellides rather than true buds. The microscopic features of young colonies of Exophilia sp. exhibit dematiaceous, yeastlike cells. Felt-like, filamentous colonies produce dematiaceous hyphae and conidiophores that are cylindrical and have a tapered tip. Annellations may be visible at the tip, and clusters of oval to round conidia are apparent (Figure 61-13). Potassium nitrate is utilized by E. jeanselmei but not by E. dermatitidis. Temperature studies are also useful for differentiating the most common Exophiala species. Both E. jeanselmei and E. dermatitidis grow at 37°C, but only E. dermatitidis can grow at 40° to 42°C.
Exserohilum spp.
Hyphae are septate and dematiaceous. Conidiophores are geniculate, and conidia are produced sympodially. Conidia are elongate, ellipsoid to fusoid, and exhibit a prominent hilum that is truncated and protruding (Figure 61-14). The conidia are multicellular, have perpendicular septa, and usually contain five to nine septa.