Faster to perform, less operator dependent, more sensitive and specific
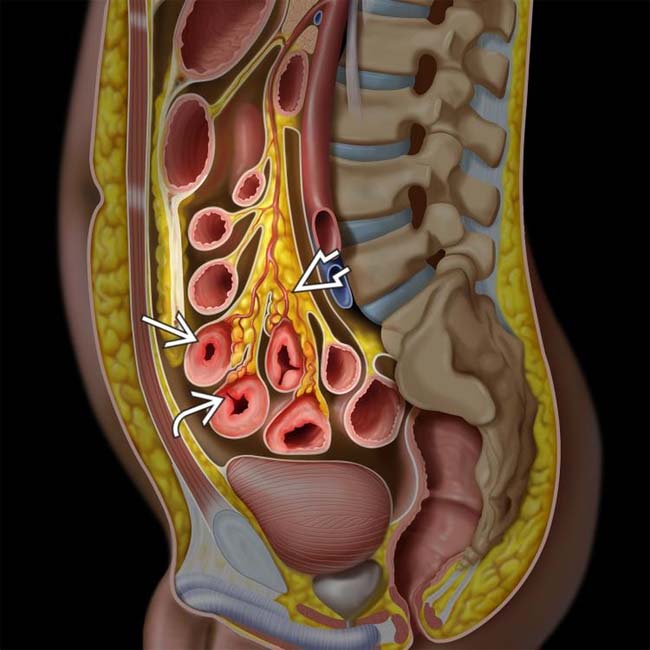
 , transmural inflammation with deep ulcers
, transmural inflammation with deep ulcers  , mesenteric vessel engorgement, and fibrofatty proliferation
, mesenteric vessel engorgement, and fibrofatty proliferation  .
.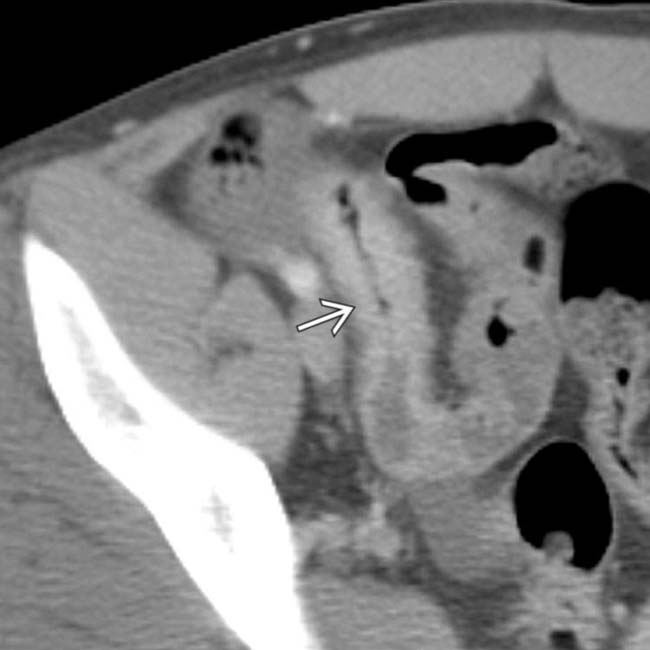
 .
.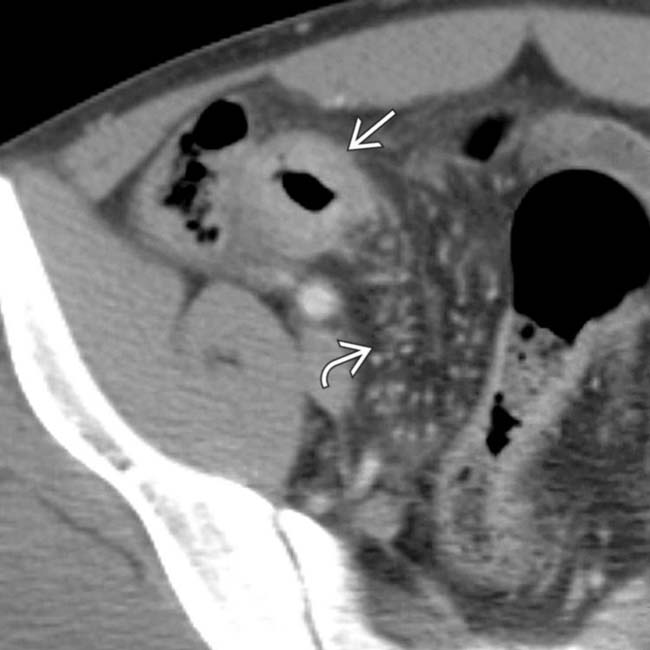
 , as well as local mesenteric fibrofatty proliferation and engorged vasa recta
, as well as local mesenteric fibrofatty proliferation and engorged vasa recta  .
.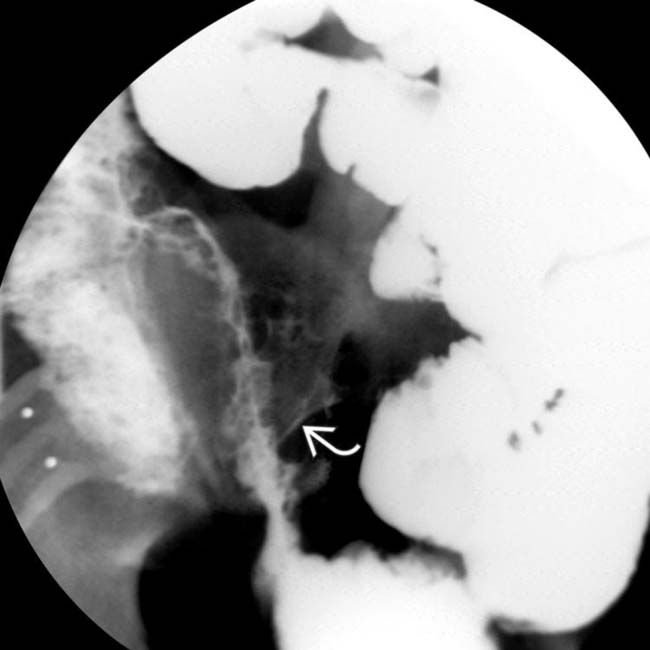
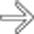
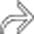 are opacified. Traditional barium studies remain valuable for evaluation of strictures, fistulas, and sinus tracts.
are opacified. Traditional barium studies remain valuable for evaluation of strictures, fistulas, and sinus tracts.IMAGING
General Features
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Ulcerative Colitis (“Backwash” Ileitis)
 .
.
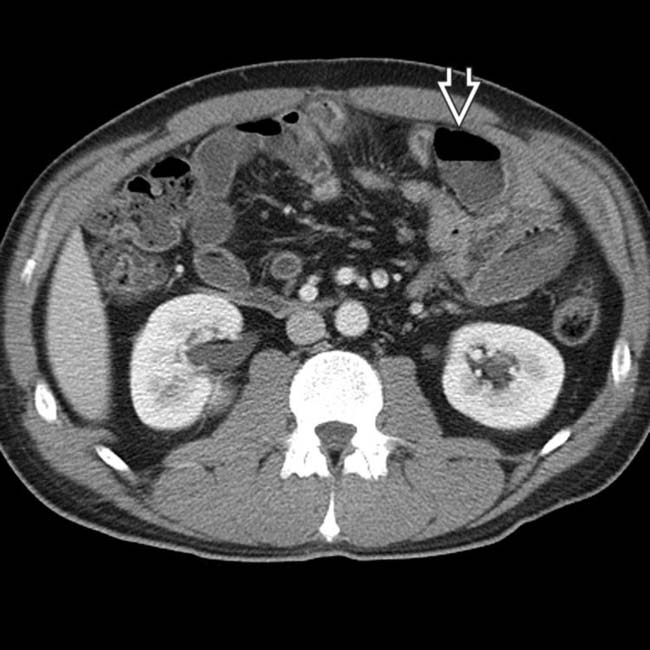
 , along with clusters of mildly enlarged mesenteric nodes
, along with clusters of mildly enlarged mesenteric nodes  .
.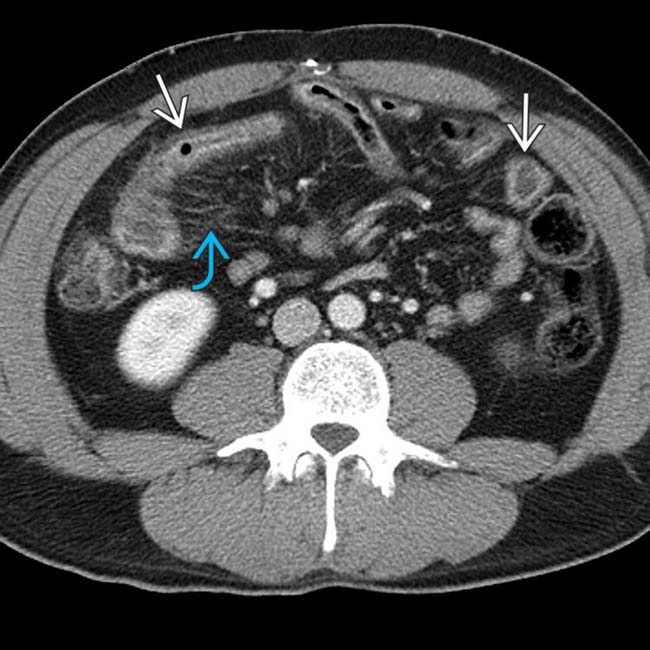
 that were separated by normal segments of bowel, the classic “skip lesions” of Crohn disease. Note the engorged vasa recta
that were separated by normal segments of bowel, the classic “skip lesions” of Crohn disease. Note the engorged vasa recta  supplying the more distal segment of inflamed bowel.
supplying the more distal segment of inflamed bowel.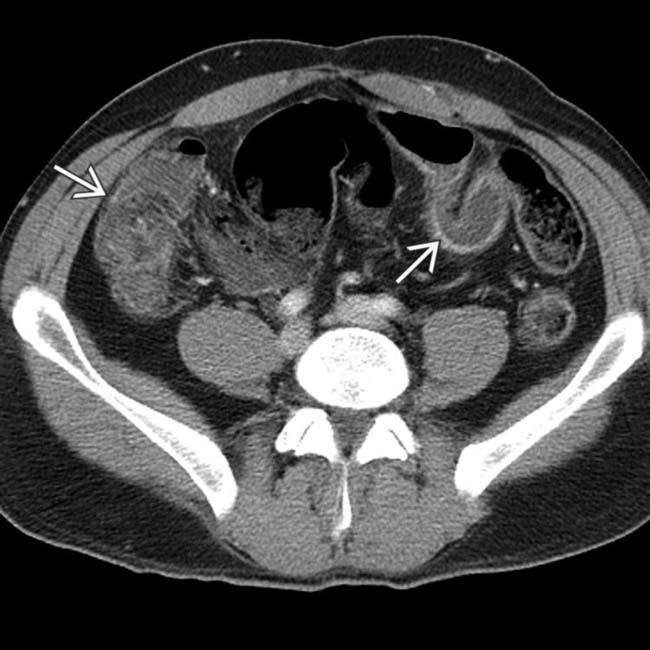
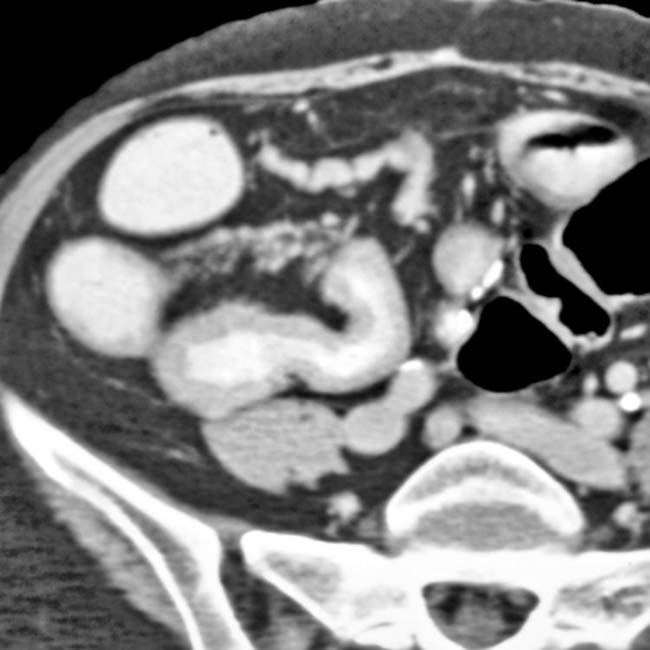
 with mucosal enhancement, wall thickening, and luminal narrowing.
with mucosal enhancement, wall thickening, and luminal narrowing.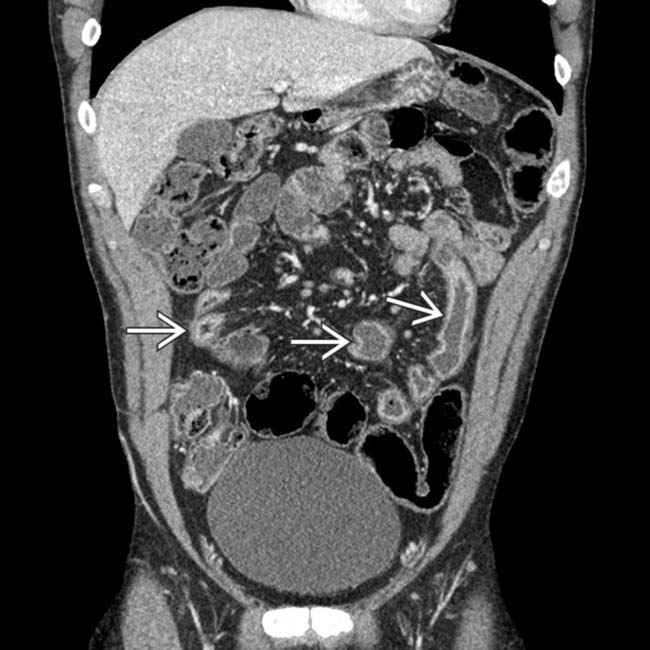
 along with mesenteric lymphadenopathy and prominent vessels.
along with mesenteric lymphadenopathy and prominent vessels.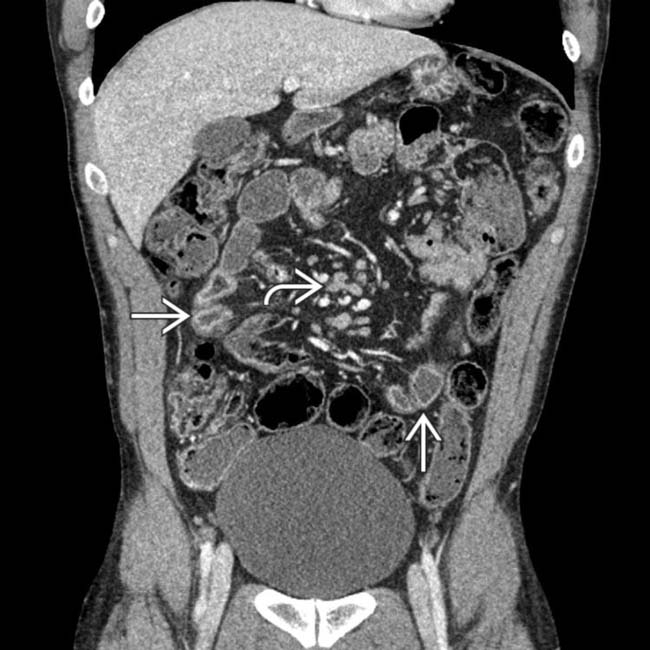
 and mesenteric lymphadenopathy
and mesenteric lymphadenopathy  . The diagnosis of Crohn disease was confirmed on colonoscopy with biopsy of the terminal ileum.
. The diagnosis of Crohn disease was confirmed on colonoscopy with biopsy of the terminal ileum.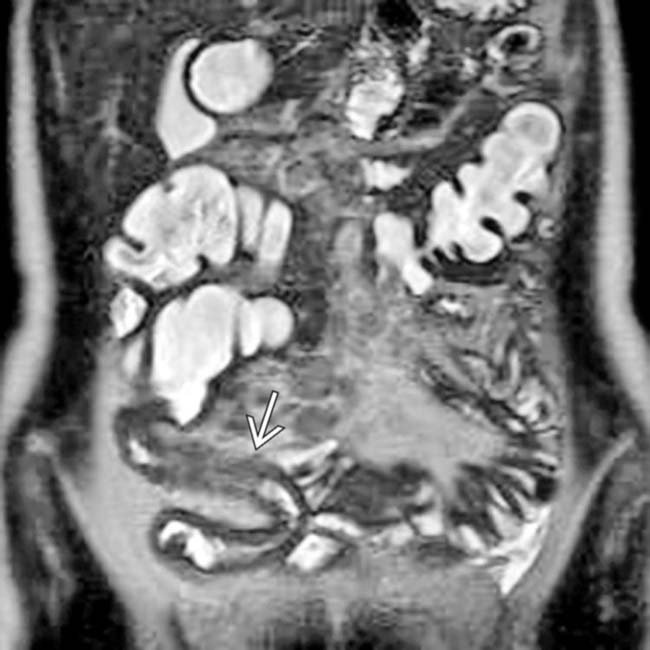
 representing the neoterminal ileum, where recurrent disease often occurs.
representing the neoterminal ileum, where recurrent disease often occurs.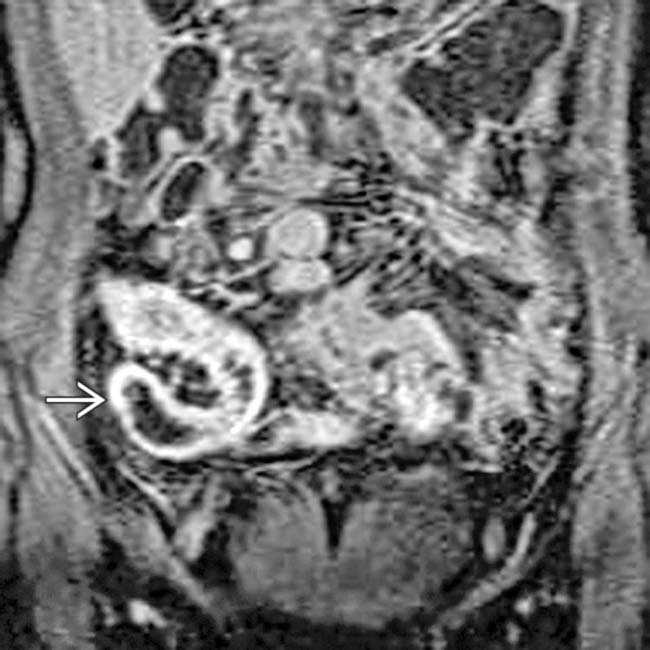
 . The adjacent small bowel and colon do not enhance with the same intensity.
. The adjacent small bowel and colon do not enhance with the same intensity.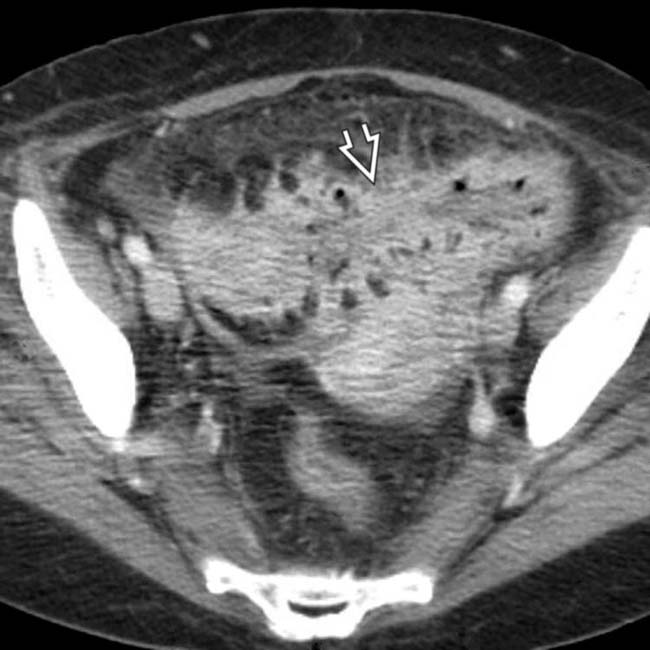
 and mesentery.
and mesentery.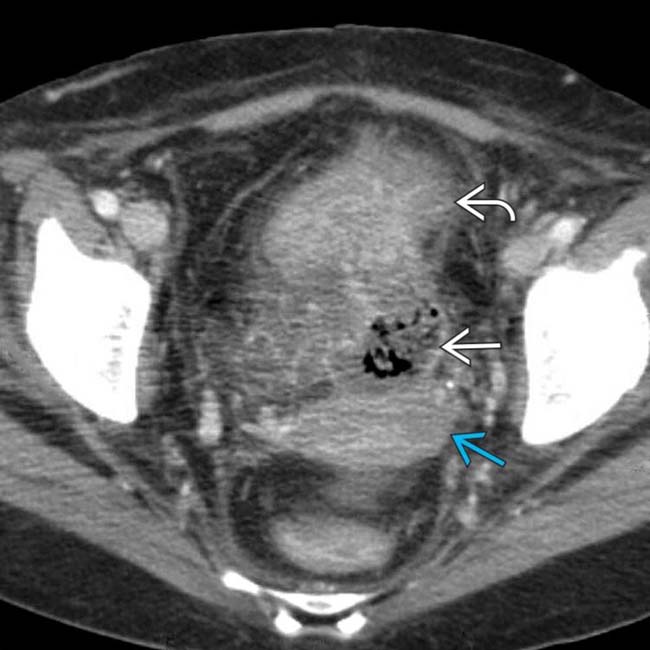
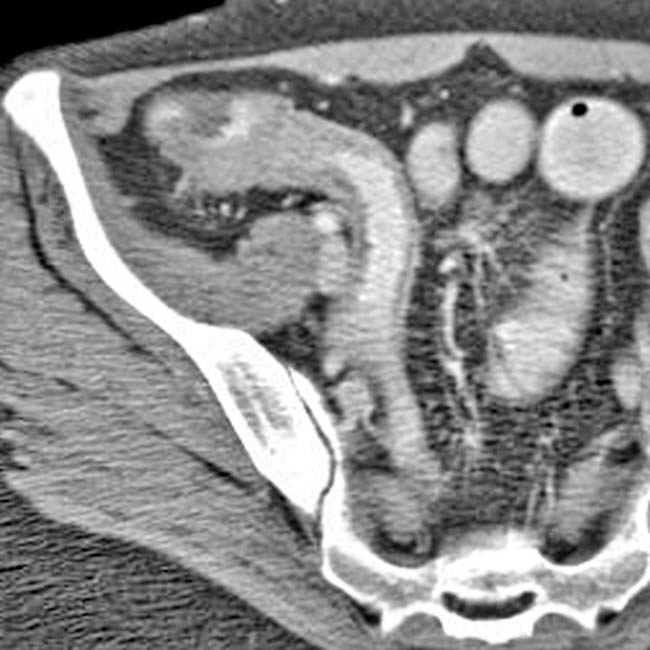
 interposed between the colon, uterus
interposed between the colon, uterus  , and top of the bladder
, and top of the bladder  .
.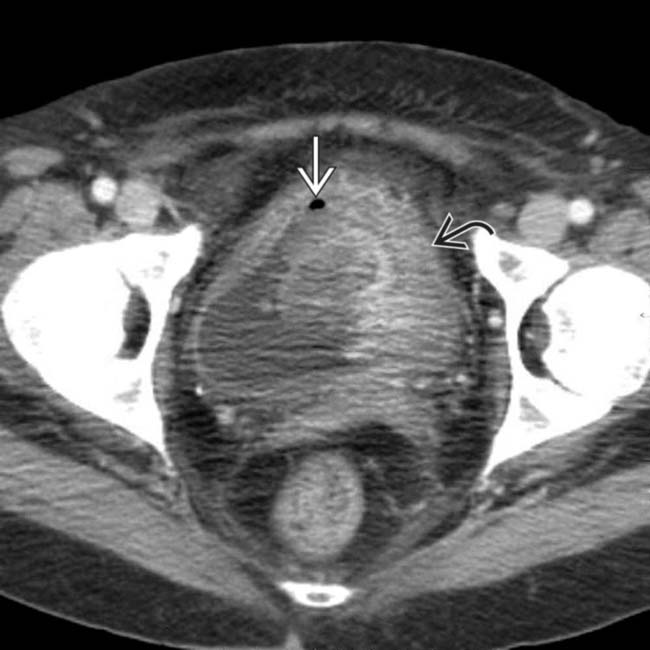
 along with gas
along with gas  and debris within the bladder.
and debris within the bladder.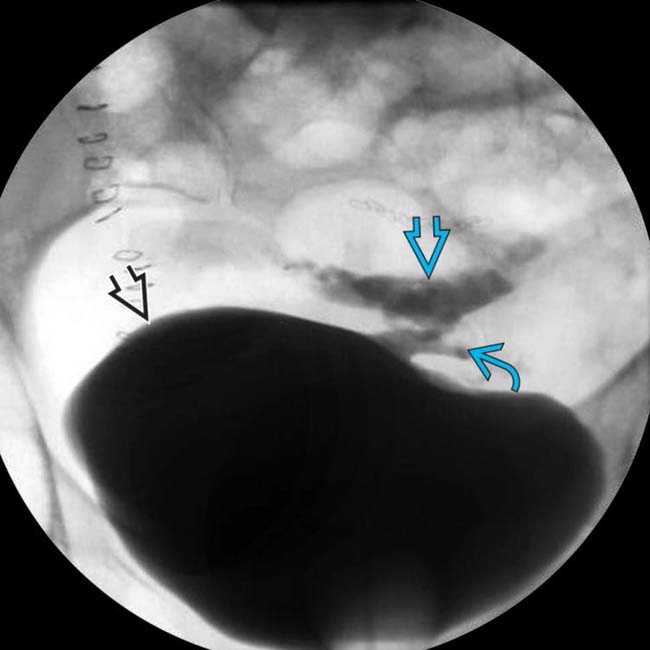
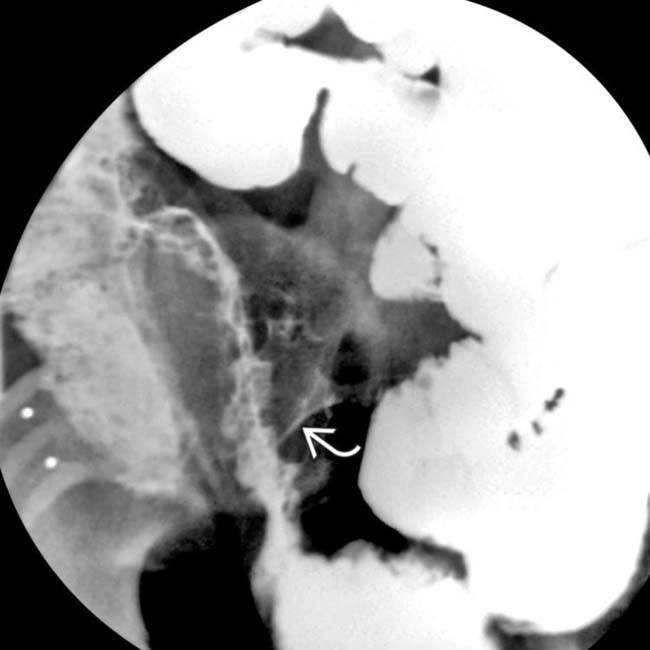
 opacifies the sigmoid colon
opacifies the sigmoid colon  through a fistulous tract
through a fistulous tract  . Fistulas are a key feature of the transmural inflammation caused by Crohn disease.
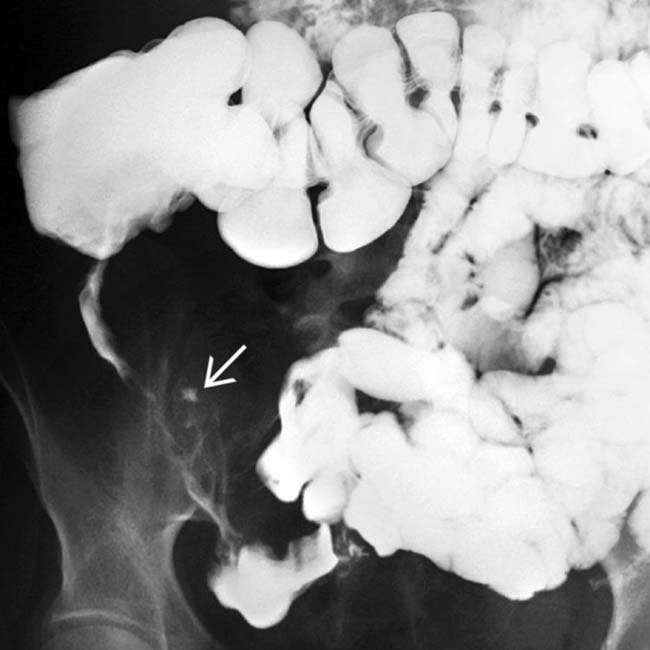
. Fistulas are a key feature of the transmural inflammation caused by Crohn disease.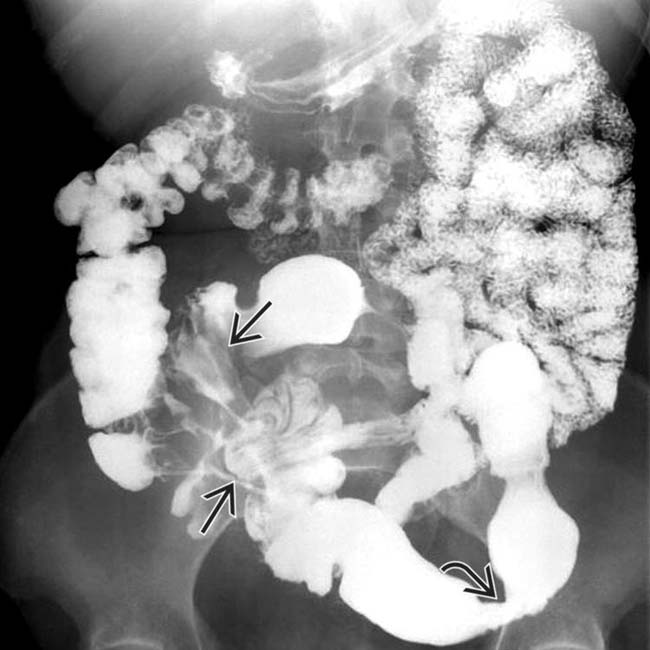
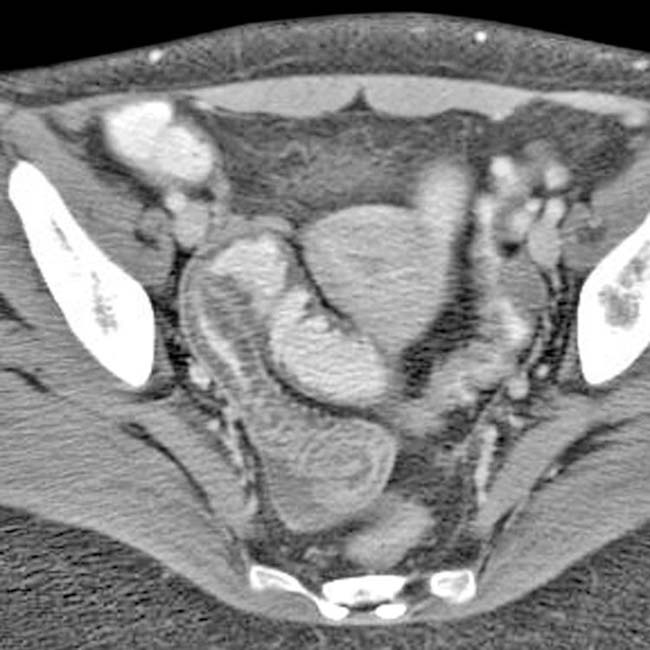
 , and ulceration with skip areas
, and ulceration with skip areas  .
.
 and indirect evidence of mesenteric fibrofatty proliferation separating the TI from other bowel segments.
and indirect evidence of mesenteric fibrofatty proliferation separating the TI from other bowel segments.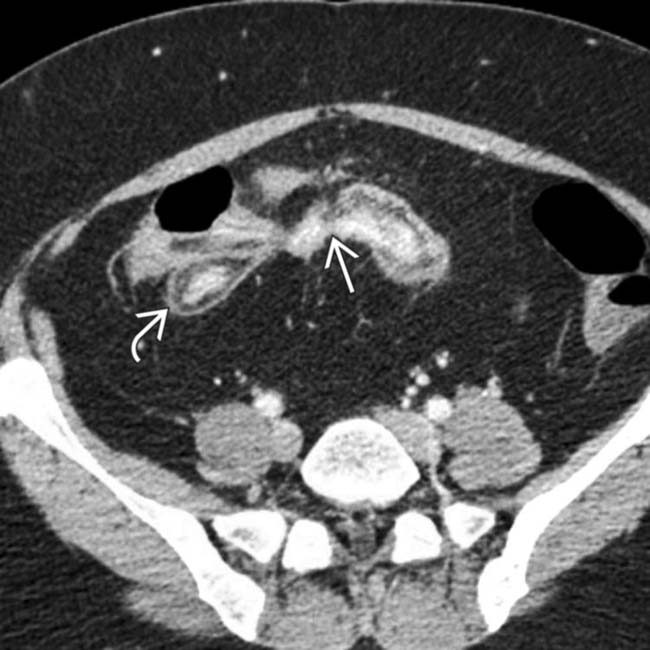
 , indicative of chronic inflammation. The nonepithelialized fistulas
, indicative of chronic inflammation. The nonepithelialized fistulas  extend from 1 bowel segment to the others.
extend from 1 bowel segment to the others.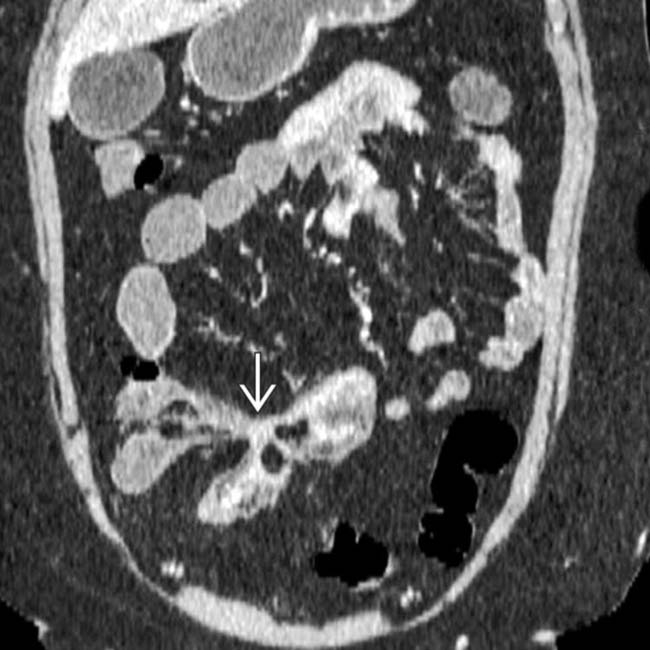
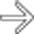 between the bowel segments.
between the bowel segments.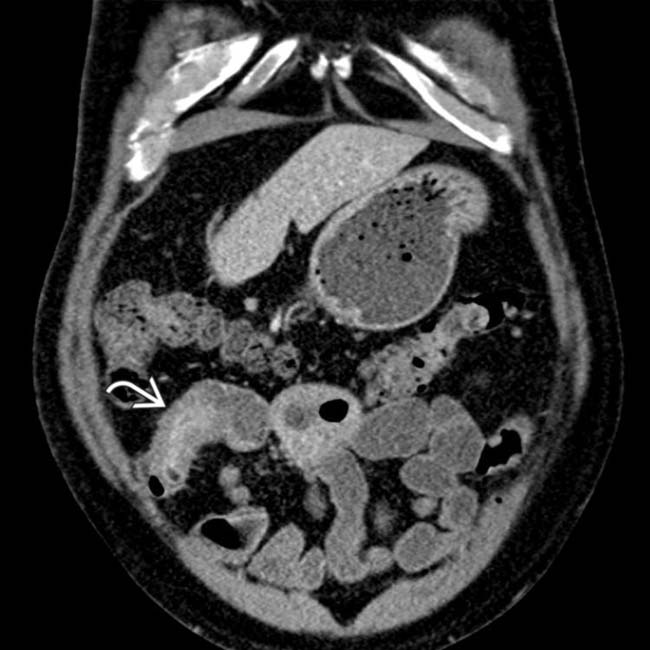
 with enhancing mucosa and submucosal edema.
with enhancing mucosa and submucosal edema.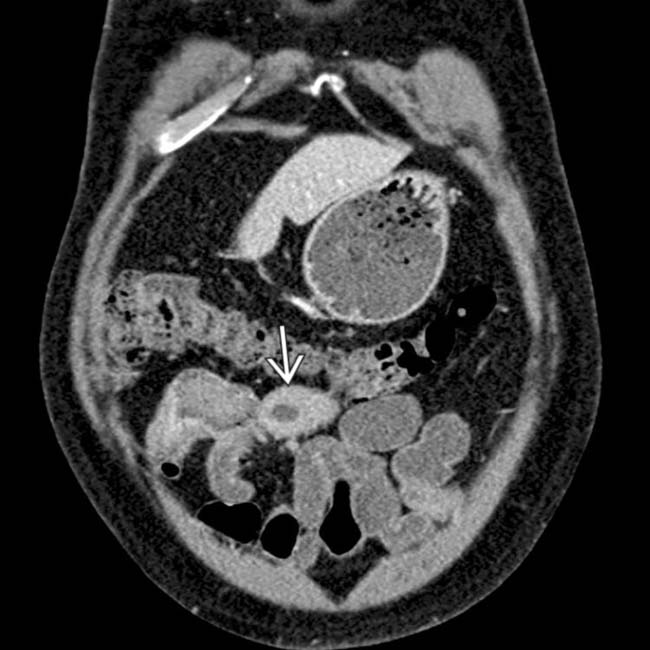
 felt to be concerning for neoplasm. Surgical resection confirmed lymphoma of the SB, a rare but recognized complication of CD or its medical therapy (steroids and immunomodulator drugs).
felt to be concerning for neoplasm. Surgical resection confirmed lymphoma of the SB, a rare but recognized complication of CD or its medical therapy (steroids and immunomodulator drugs).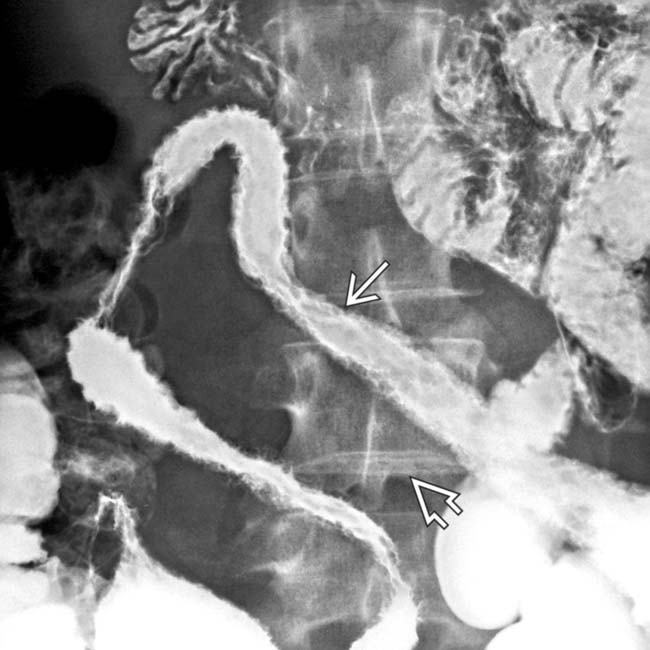
 and wide separation of the loops from creeping fat
and wide separation of the loops from creeping fat  .
.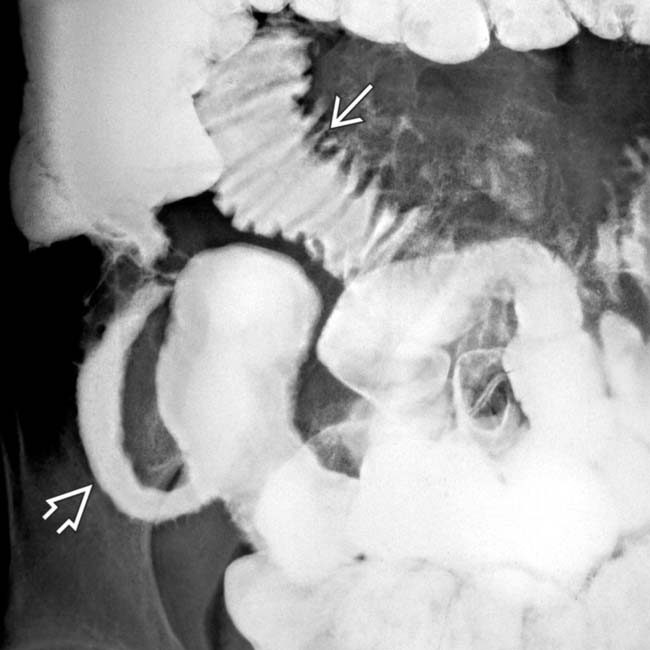
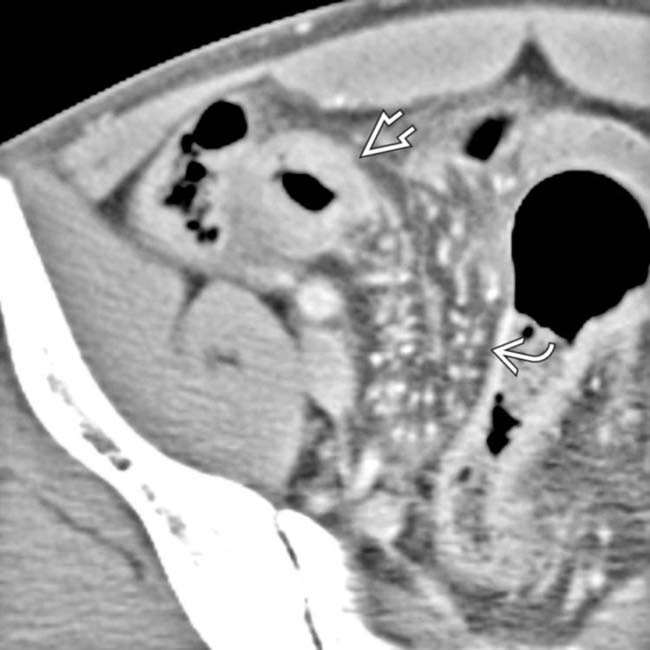
 and the featureless mucosa of terminal ileum in chronic disease
and the featureless mucosa of terminal ileum in chronic disease  .
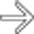
.
 and luminal narrowing. Note the hyperemia of the mesenteric blood vessels supplying the inflamed bowel
and luminal narrowing. Note the hyperemia of the mesenteric blood vessels supplying the inflamed bowel  .
.
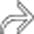 is also seen.
is also seen.
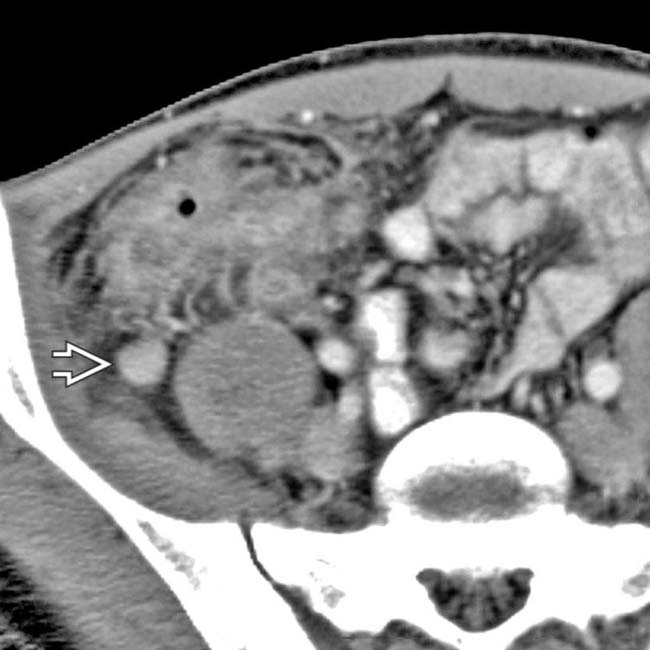
 of the distal ileum and marked inflammatory infiltration of the adjacent mesentery. Note the extraluminal bubbles of gas and the presence of small abscess
of the distal ileum and marked inflammatory infiltration of the adjacent mesentery. Note the extraluminal bubbles of gas and the presence of small abscess 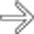 .
.
 throughout the colon.
throughout the colon.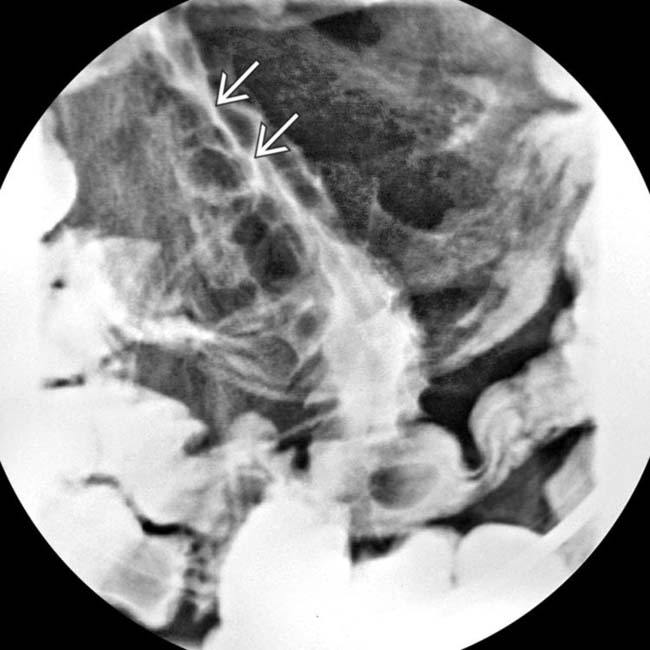
 .
.























































































 .
.
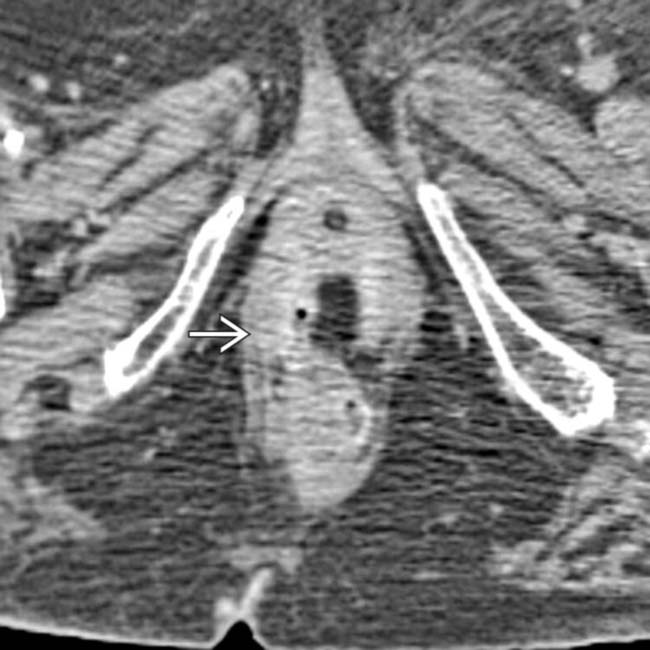
 due to Crohn disease.
due to Crohn disease.


