39 Congenital Anomalies of the Lung
Congenital Anomalies of the Airway
Etiology and Pathogenesis
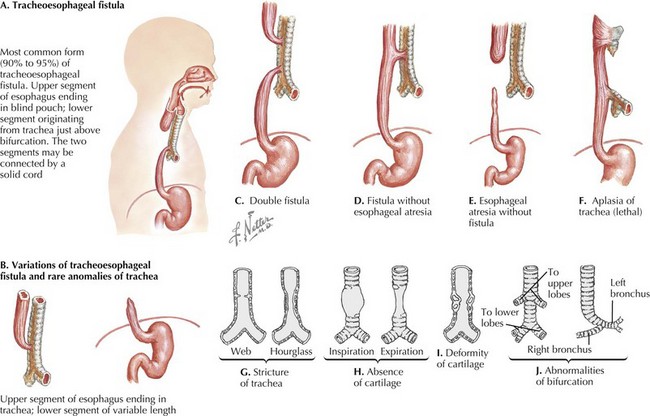
Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) occurs when there is incomplete mesodermal septation of the primitive foregut. The trachea is anatomically abnormal, causing primary malacia. In 85% of cases, there is a proximal blind-ending pouch with a distal fistula (Figure 39-1). The pouch expands and compresses the trachea, thus also causing secondary malacia. Less common types include the H-type fistula and upper esophageal fistula with distal atresia. The fistulae are often small and found between the larynx and the thoracic inlet.
Congenital Anomalies of Lung Parenchyma
Etiology and Pathogenesis
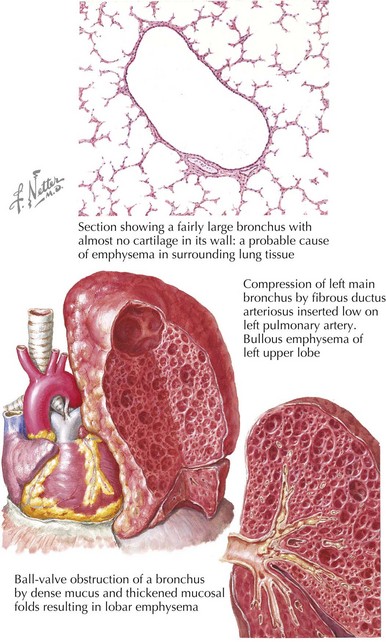
Congenital lobar emphysema (CLE) describes cases of an overdistended, hyperlucent lobe (Figure 39-2). The most commonly affected region is the left upper lobe (42% of cases). CLE may be caused by partial bronchial obstruction producing a ball-valve effect or a deficiency of bronchial cartilage. Less commonly, alveolar hyperplasia produces a polyalveolar lobe.
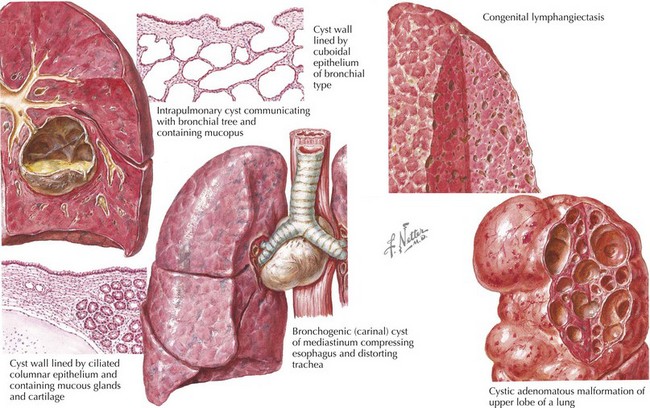
Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) or congenital pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM) represents a broad spectrum of hamartomatous defects resulting from developmental arrest during morphogenesis of the bronchial tree. Genetic defects, including mutations in the platelet-derived growth factor B gene, have been proposed to trigger abnormal cell signaling and proliferation resulting in these defects. Histologically, there are five types, although some are not cystic, and only type 3 is adenomatoid. Type 1 is the most common, occurring in 50% of cases. It is usually localized to a single lobe with no regional predilection (Figure 39-3). The cysts are lined with bronchial cells and hyperplastic mucous cysts. In rare situations, this hyperplasia extends into surrounding parenchyma and is reclassified as bronchoalveolar carcinoma. Type 2 is the next most common histologic pattern consisting of bronchiolar cell hyperplasia within the cysts.
Bronchogenic cysts are a type of foregut duplication cyst produced when a segment of bronchial-type tissue separates from the developing bronchial tree. The cysts are lined with ciliated bronchial epithelium and contain cartilage in their walls, which differentiates them from simple foregut cysts. The majority of these cysts are located in the mediastinum close to the main carina and usually do not communicate with the tracheobronchial tree (see Figure 39-3).
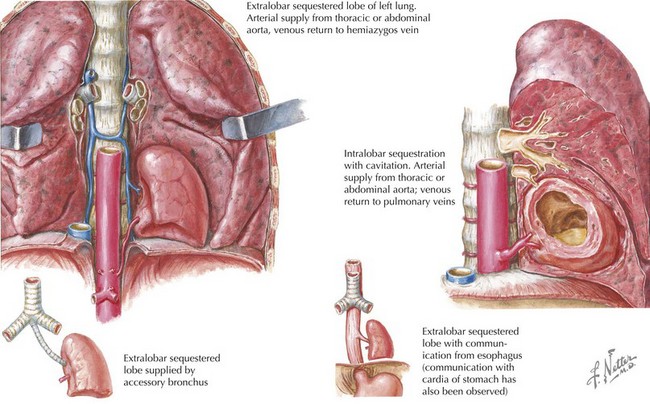
Pulmonary sequestrations are generally thought to be masses of nonfunctioning pulmonary tissue derived from accessory foregut budding. They have no connection with the tracheobronchial tree and receive their arterial supply from the systemic circulation; in 20% of cases, the systemic artery is subdiaphragmatic in origin. Whereas extralobar sequestrations usually have both arterial and venous systemic blood supply, the venous drainage of intralobar sequestrations is by pulmonary veins (Figure 39-4). Extralobar sequestrations are covered by their own pleura; in contrast, intralobar sequestrations are surrounded by the same visceral pleura as the rest of the lung. In 40% of cases of extralobar sequestration, there are associated anomalies, including hindgut duplications or congenital heart defects. Histologically, in both types, there are cystic, nonaerated bronchial and alveolar tissue.
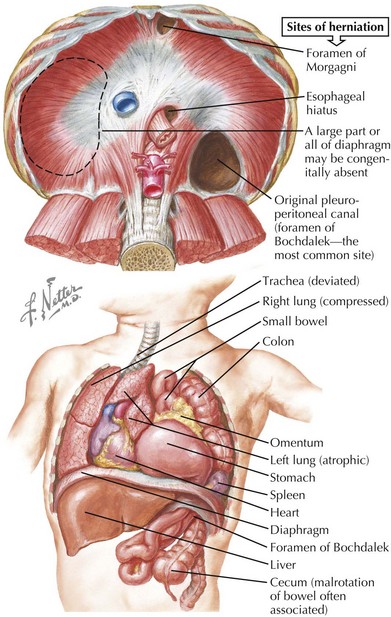
Pulmonary hypoplasia is defined as lung weight more than 2 standard deviations below the normal range for age. Causes include congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH), oligohydramnios, thoracic cage anomalies, and giant omphalocele. In cases of CDH, pulmonary hypoplasia most likely occurs before abdominal contents migrate into the thorax, but the additional insult of a space-occupying lesion further contributes to hypoplasia (Figure 39-5).
Pulmonary Vascular Malformations
Abdalla SA, Geisthoff UW, Bonneau D, et al. Visceral manifestations in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. J Med Genet. 2003;40:494-502.
Adzick NS. Management of fetal lung lesions. Clin Perinatol. 2003;30(3):481-492.
Azizkhan RG, Crombleholme TM. Congenital cystic lung disease: contemporary antenatal and postnatal management. Pediatr Surg Int. 2008;24(6):643-657.
Boogaard R, Huijsmans SH, Pijnenburg MW, et al. Tracheomalacia and bronchomalacia in children: incidence and patient characteristics. Chest. 2005;128(5):3391-3397.
Daniel SJ. The upper airway: congenital malformations. Paeditar Respir Rev. 2006;7(suppl 1):S260-S263.
Doyle NM, Lally KP. The CDH Study Group and advances in the clinical care of the patient with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin Perinatol. 2004;28(3):174-184.
Houben CH, Curry JI. Current status of prenatal diagnosis, operative management and outcome of esophageal atresia/tracheo-esophageal fistula. Prenat Diagn. 2008;28(7):667-675.
Kussman BD, Geva T, McGowan FX. Cardiovascular causes of airway compression. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004;14(1):60-74.
Langston C. New concepts in the pathology of congenital lung malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2003;12(1):17-37.
Masters IB. Congenital airway lesions and lung disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009;56(1):227-242.
Wilson RD, Hedrick HL, Liechty KW, et al. Cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung: review of genetics, prenatal diagnosis and in utero treatment. Am J Med Genet. 2006;140A:151-155.