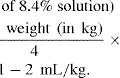CHAPTER 12 Common drugs and infusions
Common drug doses
Standard infusions
Note: Nsaline is Normal saline, 0.9%.
Dopamine
Dose of dopamine
• For both purposes, mix in Nsaline, 5% or 10% dextrose in a ‘low-stiction’ syringe, e.g. Braun or IVAC: 30 mg/kg of dopamine in 50 mL of fluid. This gives a solution of dopamine 600 μg/kg/mL. If run at 1 mL/hr, this is 10 μg/kg/min.
This may be doubled in strength if fluid management is a problem.
Dobutamine
An agent used to improve myocardial contractility (heart rate and strength of contraction — a beta agonist). Also has some pulmonary vasodilating effects, at least theoretically. Not as good as dopamine for elevating blood pressure, unless the cause of low BP is poor myocardial performance.
Midazolam
Used for sedation or for seizures. Use with caution in unintubated, non-ventilated infants.
Morphine
Dose of morphine
• Single dose: for elective intubation, a bolus of 50–100 μg/kg (0.05–0.1 mg/kg) should be given prior to intubation. Give as a one-off injection, or as a bolus of 2.5–5 mL of the standard solution below (if the baby’s clinical status can tolerate that much fluid). (It is safer to give as standard solution to avoid accidental overdose.)