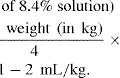CHAPTER 13 Chronic lung disease (CLD)
Background
After discharge, many will need home oxygen and the rate of re-hospitalisation is high. Lung function measurements (especially measurements of air flow) are often below average, recurrent respiratory infections are common, and there is an increased risk of neurodevelopmental delay.
Management
Dexamethasone
For chronic lung disease (CLD)
Dexamethasone may be used for management of CLD, especially as an aid to weaning from assisted ventilation. Its use is controversial given an increased incidence of cerebral palsy (or an abnormal neurological examination), seen when multiple randomised controlled trials are combined in meta-analysis. However, it should be noted that the majority of trials allowed the use of dexamethasone in the nontreatment groups and the same meta-analysis showed no increase in the rate of disability.