Chlamydiae and Zoonotic Intracellular Bacteria
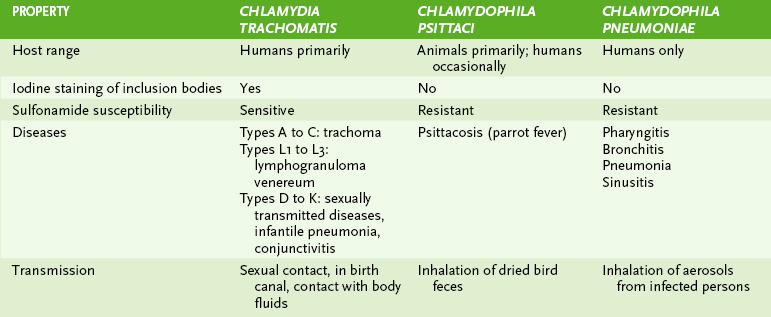
• Three chlamydial species are pathogenic for humans: C. trachomatis, C. psittaci, and C. pneumoniae (Table 17-1).
A Shared chlamydial properties
1. Chlamydiae are very small, obligate intracellular bacteria.
2. They possess a cytoplasmic membrane and outer membrane but lack peptidoglycan layer (unlike gram-negative bacteria) and thus are insensitive to β-lactam antibiotics.
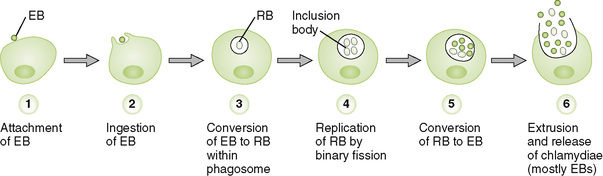
• Ingested EB is converted to RB within a cytoplasmic phagosome.
• RB replication by binary fission produces a large inclusion body containing numerous RBs, most of which are reorganized into EBs.
• Extrusion of the inclusion body releases infectious EBs into extracellular environment and ruptures the cell.
• Cytologic examination for iodine-staining inclusion bodies
• Growth and isolation in cell culture
• Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
• Detection of chlamydial antigens or nucleic acid sequences in clinical specimens
• Types A through K infect nonciliated epithelial cells of mucous membranes, which have EB-binding receptors on their surface.
a. These target cells are found in the urethra, vagina, fallopian tubes, anorectal tract, respiratory tract, and conjunctiva.
• Types L1, L2, and L3 infect macrophages.
• Destruction of target cells due to bacterial replication and severe host inflammatory reactions cause disease manifestations.
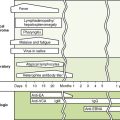
3. Chlamydial infections caused by types D through K (Box 17-1)
• Transmitted by sexual contact or during passage through infected birth canal
• Caused by types L1 through L3 and transmitted by sexual contact
1. C. psittaci causes psittacosis (parrot fever).
2. Parrot fever may be asymptomatic or manifest mild flu-like symptoms.
• May progress to serious interstitial pneumonitis with cyanosis, jaundice, and central nervous system involvement (headache, convulsions, coma)
3. Transmission occurs via inhalation of contaminated dried bird feces.
II Zoonotic Intracellular Bacteria (Box 17-2)
A Rickettsia and Related Species
1. Rickettsiae are small, gram-negative, nonmotile pleomorphic bacteria that are obligate intracellular parasites.
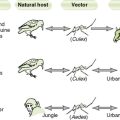
2. They cause zoonotic diseases and typically are transmitted by insect vectors from various animal reservoirs.
• Rickettsiae enter and replicate slowly within host cells, especially endothelial cells.
• Organisms are continuously shed from infected cells and are also released by cell lysis.
• Disease manifestations result from destruction of host cells and from systemic responses to cell damage.
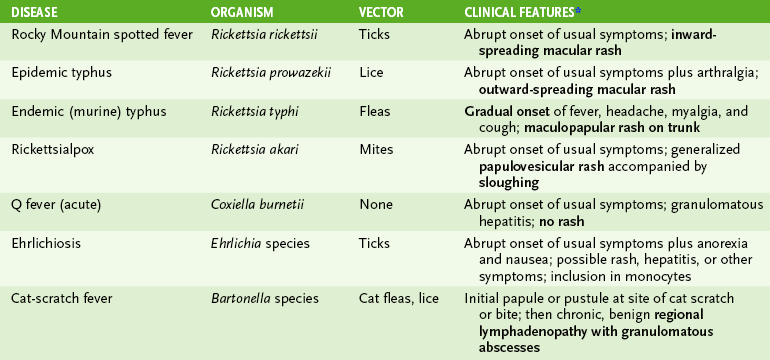
4. Rickettsial and related diseases (Table 17-2)
• The incubation period is 7 to 20 days except for chronic Q fever, which has a prolonged incubation period (months to years).
• Abrupt onset marks these diseases, except for endemic (murine) typhus and chronic Q fever.
• Fever, chills, headache, and myalgia are usual initial symptoms; characteristic rash develops in most rickettsial diseases.
5. Geographic distribution in the United States
• Rocky Mountain spotted fever, caused by Rickettsia rickettsii, usually occurs in the south-eastern Atlantic states and south-central states (not usually in the Rocky Mountains).
1. Four closely related Brucella species cause zoonotic disease in humans.
2. Brucella are small, gram-negative, nonencapsulated, facultative intracellular coccobacilli.
• Phagocytosed brucella are resistant to intracellular killing and survive within neutrophils and macrophages, thereby evading immune control.
• Infected phagocytes carry brucella to the spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and other sites.
• Granulomas form around infection foci as a result of host TH1 response.
4. Brucellosis (undulant fever)
• Subacute, acute, and chronic forms occur.
• Symptoms include malaise, chills, sweats, fatigue, weight loss, reactive arthritis, and undulating fever pattern.
1. F. tularensis is a very small, gram-negative, facultative intracellular coccobacillus that grows slowly on cysteine-containing media.
• Incubation period of 3 to 5 days is followed by abrupt onset of fever, chills, malaise, and fatigue.
• Ulceroglandular form: most common presentation in the United States
• Natural reservoirs for F. tularensis include rabbits, many other small wild animals, and ticks.
• Spread to humans occurs by bites from infected ticks, direct contact with infected animals, ingestion of contaminated meat or water, and inhalation of infectious aerosols (e.g., while skinning an infected animal).
1. L. monocytogenes, part of the normal gastrointestinal flora of many animals, is transmitted to humans by ingestion of contaminated food, especially unpasteurized dairy products.
2. Grows in the cold (e.g., ice cream)
• Small, gram-positive, facultative intracellular coccobacillus that does not form spores
• β-Hemolytic, catalase positive, tumbling motility at room temperatures
• Intracellular growth in macrophages and epithelial cells protects bacteria from humoral immune response.
• Listeriolysin O (a β-hemolysin similar to streptolysin) lyses phagosome, releasing bacteria into cytoplasm, where they replicate.
• Direct cell-to-cell transfer (actin rockets) permits spread of infection to new cells without exposing bacteria to extracellular antibodies or other bactericidal agents.
• Meningitis and sepsis in immunocompromised individuals
• Mild flu-like illness (fever, chills) with sepsis in pregnant women