± dilation of upstream intrahepatic ducts, as associated periductal fibrosis may impede ductal dilatation
• Distribution of strictures in biliary tree reflects hepatic arterial supply to bile ducts
 Proximal extrahepatic duct and biliary confluence strictures are most common due to blood supply from hepatic artery
Proximal extrahepatic duct and biliary confluence strictures are most common due to blood supply from hepatic artery
 Proximal extrahepatic duct and biliary confluence strictures are most common due to blood supply from hepatic artery
Proximal extrahepatic duct and biliary confluence strictures are most common due to blood supply from hepatic artery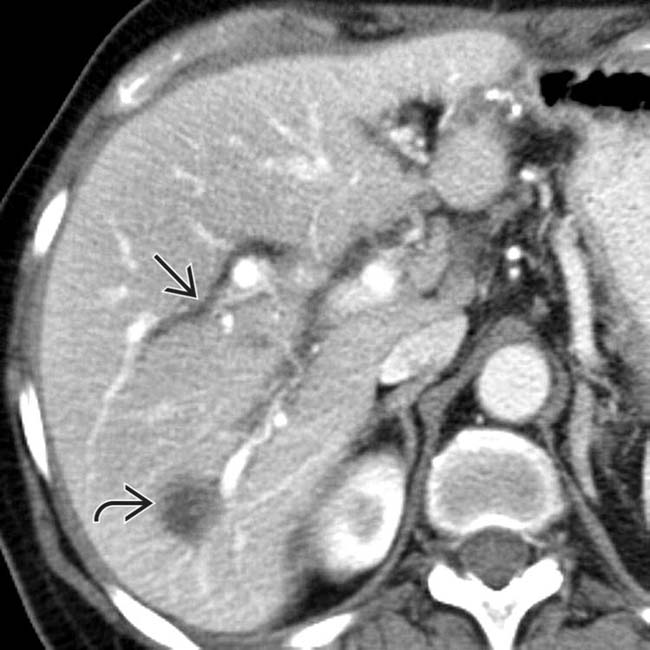
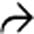 that is low in attenuation, likely as a result of necrosis. Note the dilated ducts
that is low in attenuation, likely as a result of necrosis. Note the dilated ducts 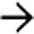 that resulted from a stricture of the biliary bifurcation and common hepatic duct, also due to chemotherapy.
that resulted from a stricture of the biliary bifurcation and common hepatic duct, also due to chemotherapy.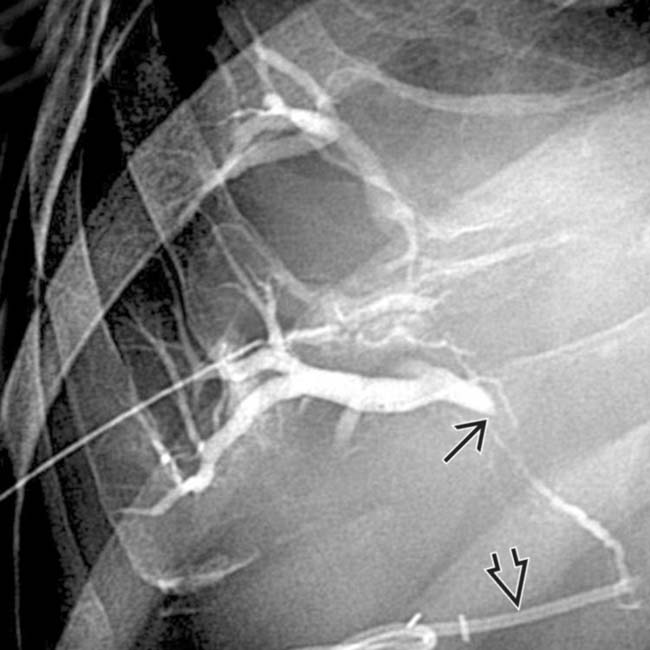
 at the confluence of the right and left ducts. This patient had received floxuridine through an arterial catheter
at the confluence of the right and left ducts. This patient had received floxuridine through an arterial catheter  .
.
 , pneumobilia, posterior segment atrophy, gastroesophageal varices
, pneumobilia, posterior segment atrophy, gastroesophageal varices  , and ascites
, and ascites  , compatible with chemotherapy-induced cholangitis and biliary cirrhosis.
, compatible with chemotherapy-induced cholangitis and biliary cirrhosis.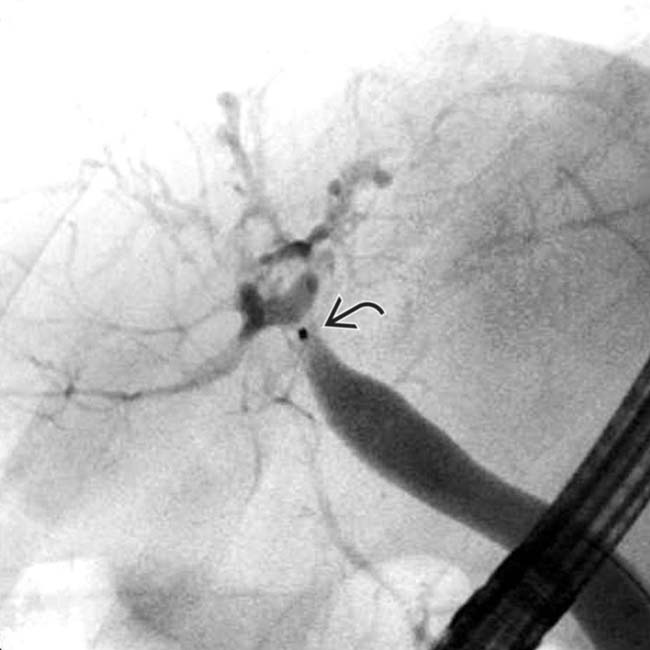
 and irregular, strictured intrahepatic ducts. A liver transplant was performed with cholangitis, bilomas, and biliary cirrhosis identified within the explant.
and irregular, strictured intrahepatic ducts. A liver transplant was performed with cholangitis, bilomas, and biliary cirrhosis identified within the explant.IMAGING
General Features
• Location
 Distribution of strictures in biliary tree reflects hepatic arterial supply to bile ducts
Distribution of strictures in biliary tree reflects hepatic arterial supply to bile ducts
 Distribution of strictures in biliary tree reflects hepatic arterial supply to bile ducts
Distribution of strictures in biliary tree reflects hepatic arterial supply to bile ducts
– Proximal extrahepatic duct and central intrahepatic ducts/biliary confluence are most commonly involved (∼ 50%) due to blood supply from hepatic artery branches
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
• Multifocal “beaded” stenoses of intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts with pruning, irregular wall thickening, and intervening sites of normal or dilated ducts
• Gallbladder and cystic duct are usually more severely involved in chemotherapy cholangitis than in PSC
PATHOLOGY
General Features
• Etiology
 Results from either direct toxic effects of drug on biliary ducts or fibrosis/occlusion of peribiliary vascular plexus with resultant biliary ischemic cholangiopathy
Results from either direct toxic effects of drug on biliary ducts or fibrosis/occlusion of peribiliary vascular plexus with resultant biliary ischemic cholangiopathy
 Results from either direct toxic effects of drug on biliary ducts or fibrosis/occlusion of peribiliary vascular plexus with resultant biliary ischemic cholangiopathy
Results from either direct toxic effects of drug on biliary ducts or fibrosis/occlusion of peribiliary vascular plexus with resultant biliary ischemic cholangiopathy
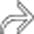 in spite of a transhepatic internal-external biliary drainage catheter
in spite of a transhepatic internal-external biliary drainage catheter  .
.
 could be mistaken for metastases.
could be mistaken for metastases.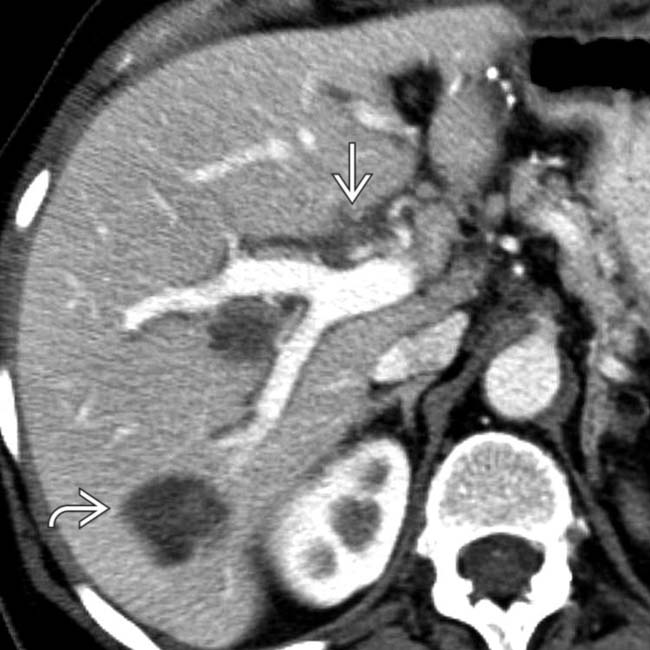
 in a patient with metastatic colon carcinoma
in a patient with metastatic colon carcinoma  who had undergone intraarterial chemotherapy.
who had undergone intraarterial chemotherapy.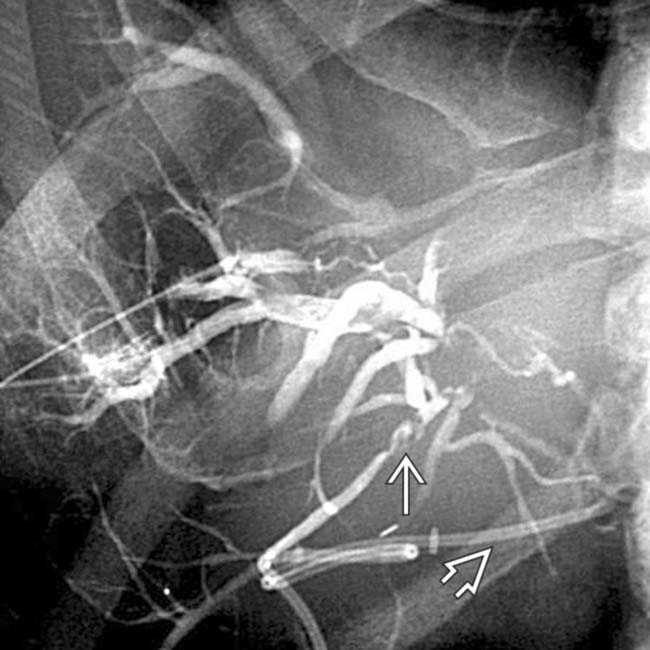
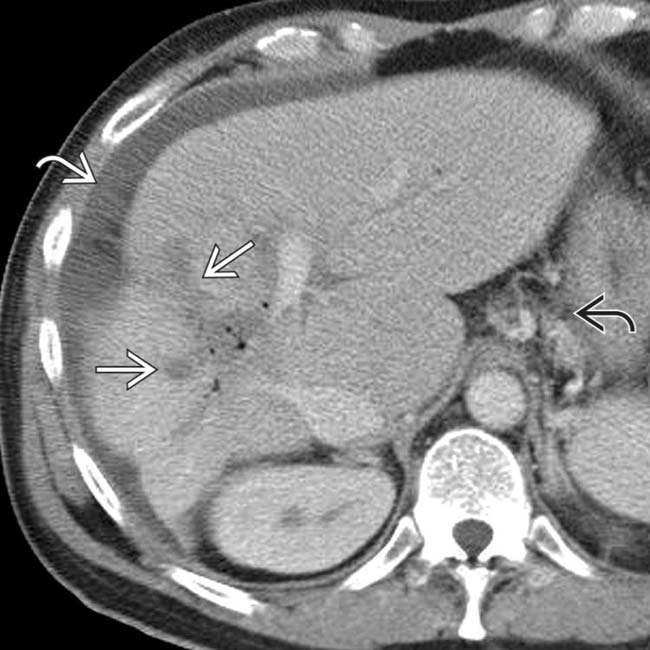
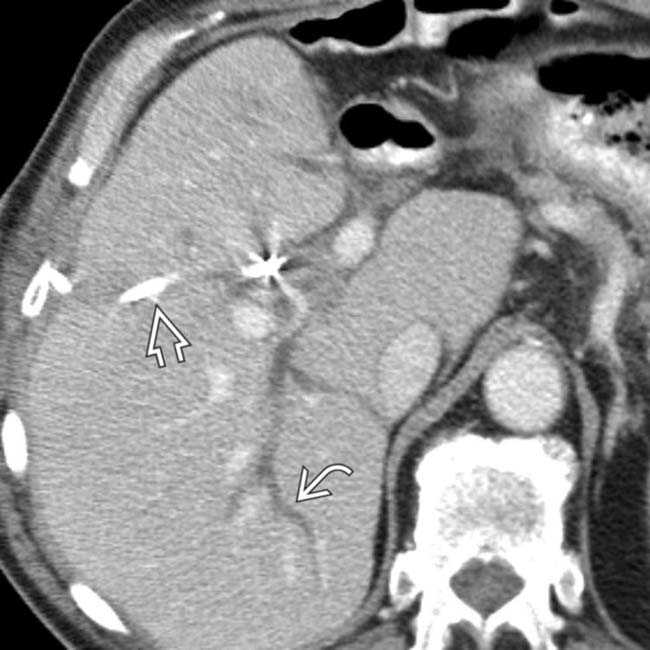
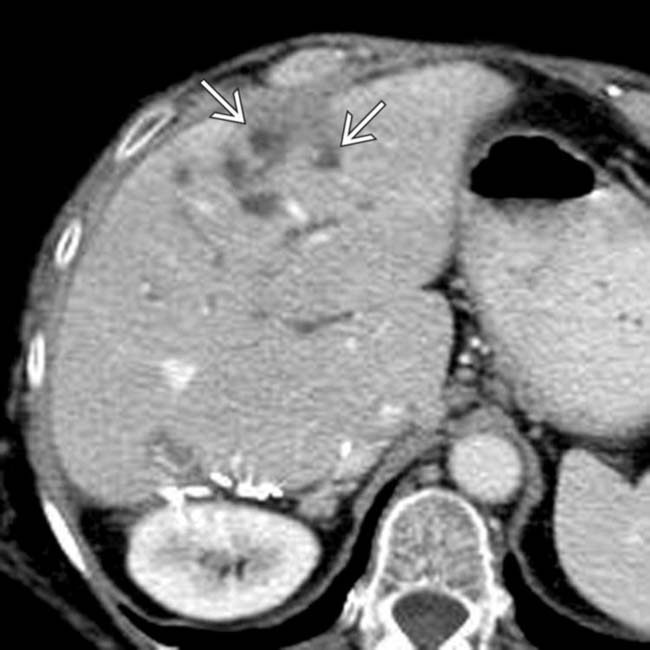
 shows a dilated right IHBD with multiple central biliary strictures
shows a dilated right IHBD with multiple central biliary strictures 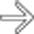 .
.


















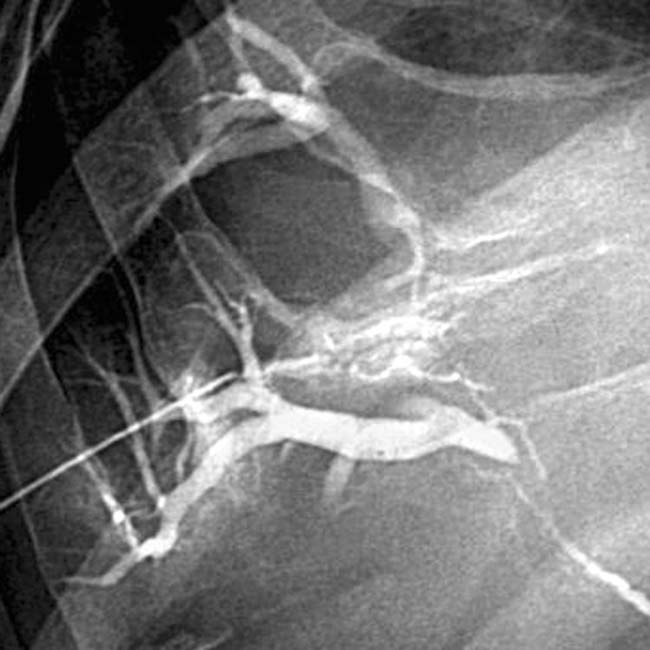
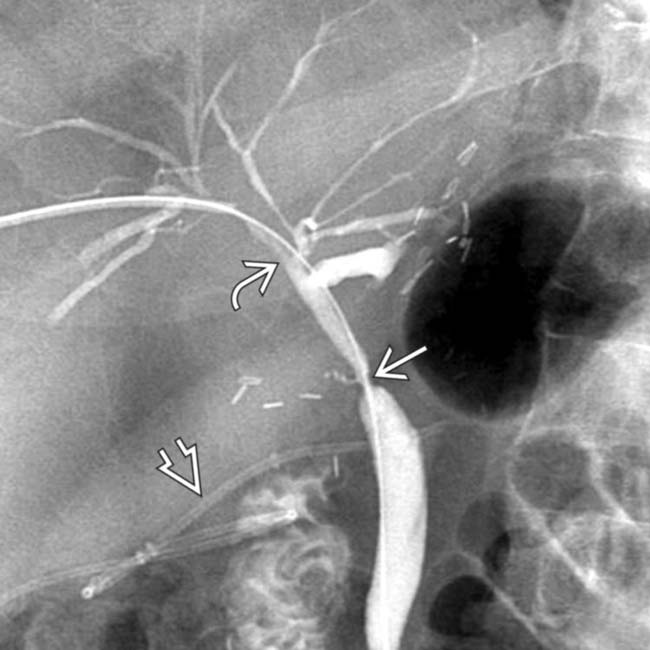
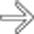
 of the common hepatic duct with a milder degree of stricture of the intrahepatic ducts
of the common hepatic duct with a milder degree of stricture of the intrahepatic ducts  as well. Note the indwelling hepatic arterial catheter
as well. Note the indwelling hepatic arterial catheter  .
.


