Chapter 563 Carcinoma of the Thyroid
Epidemiology
Alzahrani AS, Baitei EY, Zou M, et al. Clinical case seminar: metastatic follicular thyroid carcinoma arising from congenital goiter as a result of a novel splice donor site mutation in the thyroglobulin gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:740-746.
Amrikachi M, Ponder TB, Wheeler TM, et al. Thyroid fine-needle aspiration biopsy in children and adolescents: experience with 218 aspirates. Diagn Cytopathol. 2005;32:189-192.
Brignardello E, Corrias A, Isolato G, et al. Ultrasound screening for thyroid carcinoma in childhood cancer survivors: a case series. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4840-4843.
Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, et al. Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2006;16:109-142.
Corrias A, Cassio A, Weber G, et alStudy Group for Thyroid Diseases of Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology (SIEDP/ISPED). Thyroid nodules and cancer in children and adolescents affected by autoimmune thyroiditis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008;162:526-531.
Corrias A, Mussa A, Baronio F, et al. Diagnostic features of thyroid nodules in pediatrics. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010;164(8):714-719.
Davies SM. Subsequent malignant neoplasms in survivors of childhood cancer: Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS) studies. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48:727-730.
Frio TR, Bahubeshi A, Kanellopoulou C, et al. DICER1 mutations in familial multinodular goiter with and without ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors. JAMA. 2011;305(l):68-77.
Handkiewicz-Junak D, Wloch J, Roskosz J, et al. Total thyroidectomy and adjuvant radioiodine treatment independently decrease locoregional recurrence risk in childhood and adolescent differentiated thyroid cancer. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:879-888.
Lando A, Holm K, Nysom K, et al. Serum thyroglobulin as a marker of thyroid neoplasms after childhood cancer. Acta Paediatr. 2003;92:1284-1290.
Lazar L, Lebenthal Y, Steinmetz A, et al. Differentiated thyroid cancer in pediatric patients: comparison of presentation and course between prepubertal children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2009;154:708-714.
Machens A, Lorenz K, Thanh PN, et al. Papillary thyroid cancer in children and adolescents does not differ in growth patterns and metastatic behavior. J Pediatr. 2010;157:648-652.
Mehanna HM, Jain A, Morton RP, et al. Investigating the thyroid nodule. BMJ. 2009;338:705-709.
Mendelsohn AH, Elashoff DA, Abemayor E, et al. Surgery for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136(11):1055-1061.
Palmer BA, Zarroug AE, Poley RN, et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma in children: risk factors and complications of disease recurrence. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1284-1288.
Peretz A, Leibermann E, Kapelushnik J, et al. Thyroglossal duct carcinoma in children: case presentation and review of the literature. Thyroid. 2004;14:777-785.
Rachmiel M, Charron M, Gupta A, et al. Evidence-based review of treatment and follow up of pediatric patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006;19:1377-1393.
Ross DS. Radioiodine therapy for hyperthyroidism. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(6):542-550.
Savio R, Gosnell J, Palazzo FF, et al. The role of a more extensive surgical approach in the initial multimodality management of papillary thyroid cancer in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1696-1700.
Seaberg RM, Eski S, Freeman JL. Influence of previous radiation exposure on pathologic features and clinical outcome in patients with thyroid cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;135:355-359.
Sosa JA, Tuggle CT, Wang TS, et al. Clinical and economic outcomes of thyroid and parathyroid surgery in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3058-3065.
Utiger RD. The multiplicity of thyroid nodules and carcinomas. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2376-2378.
563.1 Solitary Thyroid Nodule
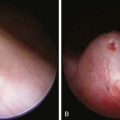
Benign disorders that can occur as solitary thyroid nodules include benign adenomas (follicular, embryonal, Hürthle cell), colloid (adenomatous) nodule, a simple cyst, lymphocytic thyroiditis, a thyroid abscess, and developmental anomalies such as thyroglossal duct cyst or hemiagenesis (Table 563-1). A suddenly appearing or rapidly enlarging thyroid mass can indicate hemorrhage into a cyst or benign adenoma. Ultrasonography is particularly useful in detecting cystic lesions. In most cases, the child is euthyroid, and thyroid function studies are normal. When lymphocytic thyroiditis is the cause of the nodule, thyroid antibodies are usually present. Ultrasonography shows diffuse hypoechogenicity. Radionuclide imaging reveals a moth-eaten appearance. Rarely, lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with carcinoma of the thyroid.
Corrias A, Cassio A, Weber G, et al. Thyroid nodules and cancer in children and adolescents affected by autoimmune thyroiditis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008;162:526-531.
Hansen PS, Brix TH, Bennedbaek FN, et al. The relative importance of genetic and environmental factors in the aetiology of thyroid nodularity: a study of healthy Danish twins. Clin Endocrinol. 2005;62:380-386.
Hegedüs L. The thyroid nodule. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1764-1771.
Josefson J, Zimmerman D. Thyroid nodules and cancers in children. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008;6:14-23.
Niedziela M. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules in children. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13:427-453.
Svensson J, Nilsson PE, Olsson C, et al. Interpretation of normative thyroid volumes in children and adolescents: is there a need for a multivariate model? Thyroid. 2004;14:536-543.
Wiersinga WM. Management of thyroid nodules in children and adolescents. Hormones. 2007;6:194-199.
563.2 Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Machens A, Dralle H. Genotype-phenotype based surgical concept of hereditary medullary thyroid carcinoma. World J Surg. 2007;31:957-968.
Puñales MK, da Rocha AP, Meotti C, et al. Clinical and oncological features of children and young adults with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A. Thyroid. 2008;18:1261-1268.
Szinnai G, Meier C, Komminoth P, et al. Review of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A in children: therapeutic results of early thyroidectomy and prognostic value of codon analysis. Pediatrics. 2003;111:E132-E139.
Szinnai G, Sarnacki S, Polak M. Hereditary medullary thyroid carcinoma: how molecular genetics made multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 a pediatric disease. Endocr Dev. 2007;10:173-187.