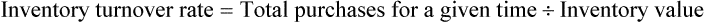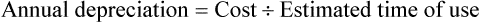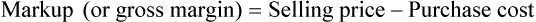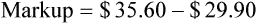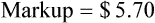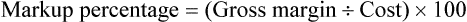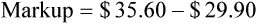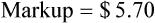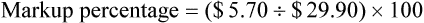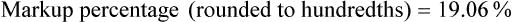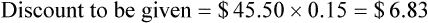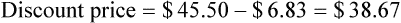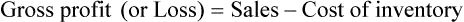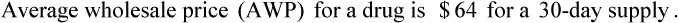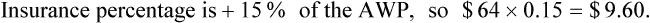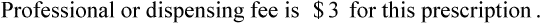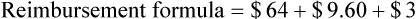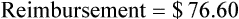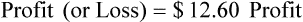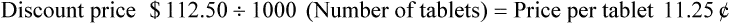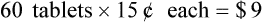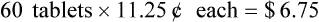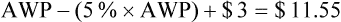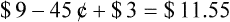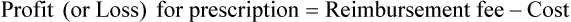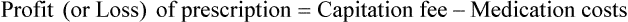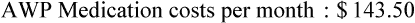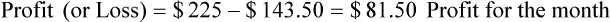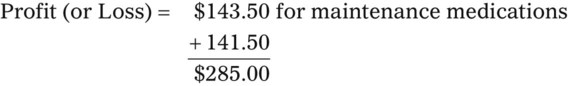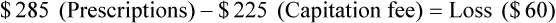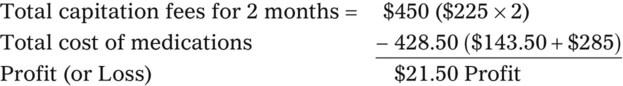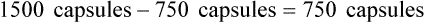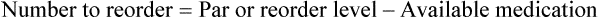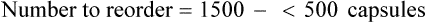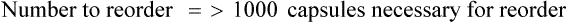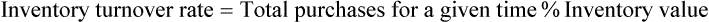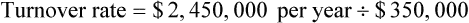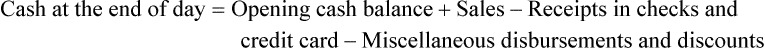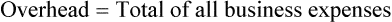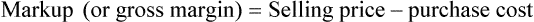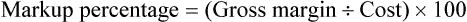Business Math for Pharmacy Technicians
• Calculate overhead expenses for a specified period of time including calculating annual depreciation
• Calculate prescription markup or gross margin
• Calculate discounts on merchandise
• Calculate gross profit for a specified period of time
• Calculate insurance reimbursement using average wholesale prices and capitation fees
• Manage inventory including par levels and inventory turnover rate
Net Income
Net income (sometimes referred to as the bottom line or net profit) is gross profit less overhead. Using Example 15-5, if the overhead for the same store were $18,000 for the month, the net income would be $7,000.
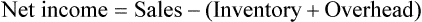
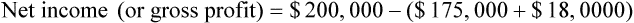
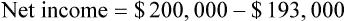
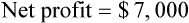
Review of Rules
Calculation of Annual Depreciation
• Annual depreciation is used to indicate the loss of asset value over a years time.
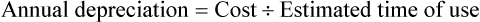
Profit or Loss
• The gross profit is the difference between the sales price and the cost of the inventory.
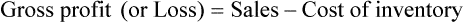
• Net income is difference between selling price and costs related to the business.
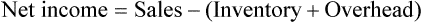
• Markup rate is the difference between selling price and purchase price.
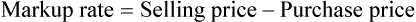
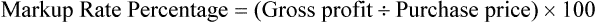
Discounts
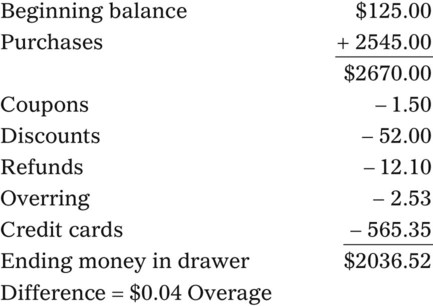
• Discounts are given for multiple reasons and reduce the selling price for the item. These include calculating the discount amount and then subtracting this amount from the selling price. Discounts may also be given when using manufacturers’ coupons. The amount of the coupon should be subtracted from the selling price and the coupon placed in the cash drawer.

Insurance Reimbursements
• The third-party price for a prescription may be computed using AWP or the average wholesale price nationally.

• The pharmacy needs to know if the reimbursement provides a profit or loss using the reimbursement fee less the cost of preparing the prescription.
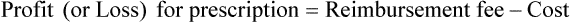
• Capitation fees are a set reimbursement fee usually paid to the pharmacy per month by the third-party insurance carrier.
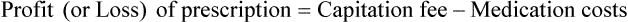
• A minimal/reorder level is predetermined by sales history or human input and is used to maintain the drug flow and minimize the need for extra shelf space while replacing medications as needed to maintain business efficiency. This predetermined point is called the par level.
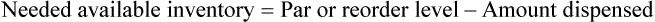
• Inventory turnover rate is the frequency at which medications sell over a specified time. This calculation is used to control the amount of cash that is tied up in inventory.