May simulate a large neoplasm within caudate lobe
• Large regenerative nodules (form of nodular regenerative hyperplasia) are characteristic of chronic BCS
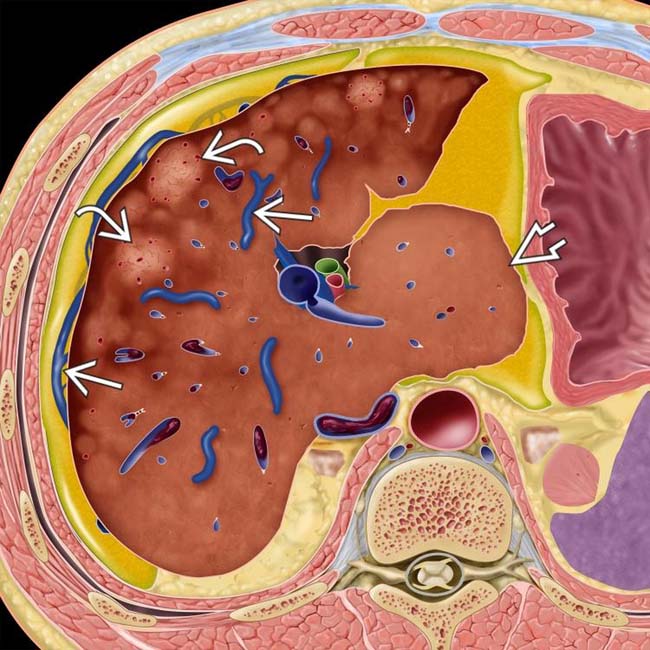
 , heterogeneous hepatic parenchyma due to centrilobular necrosis, and hypervascular regenerative nodules
, heterogeneous hepatic parenchyma due to centrilobular necrosis, and hypervascular regenerative nodules  . Note the sparing of the caudate lobe with hypertrophy
. Note the sparing of the caudate lobe with hypertrophy  , as well as the thrombosed IVC.
, as well as the thrombosed IVC.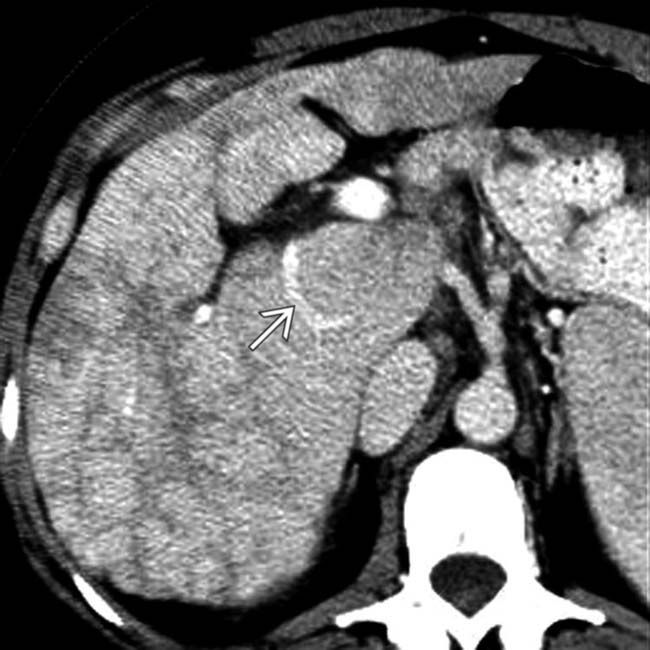
 , and peripheral atrophy and heterogeneity. The hepatic veins were occluded.
, and peripheral atrophy and heterogeneity. The hepatic veins were occluded.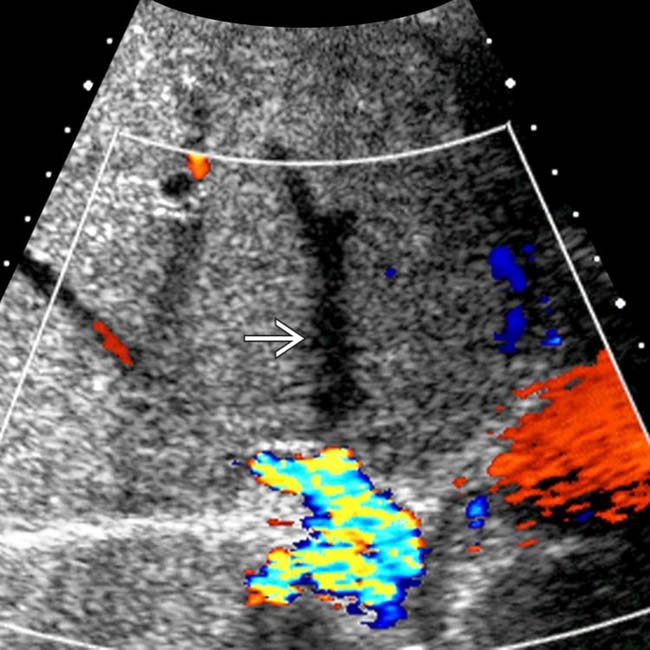
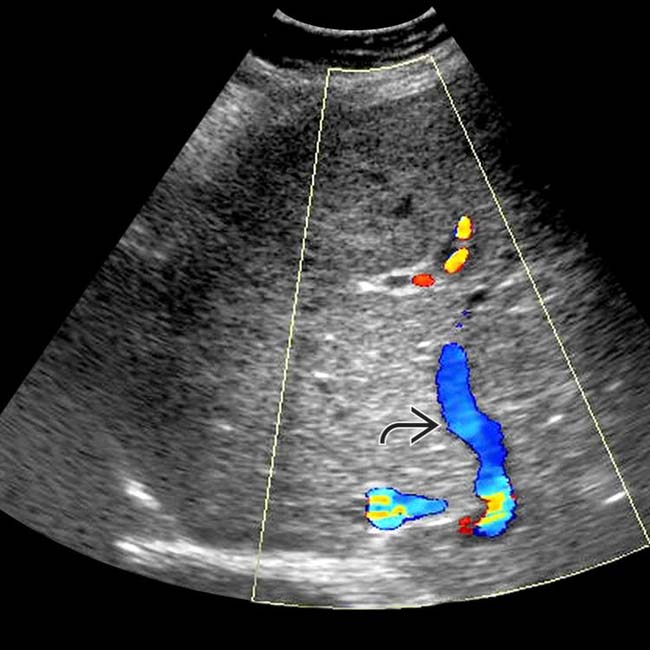
 .
.
 bypassing the occluded hepatic veins.
bypassing the occluded hepatic veins.IMAGING
General Features
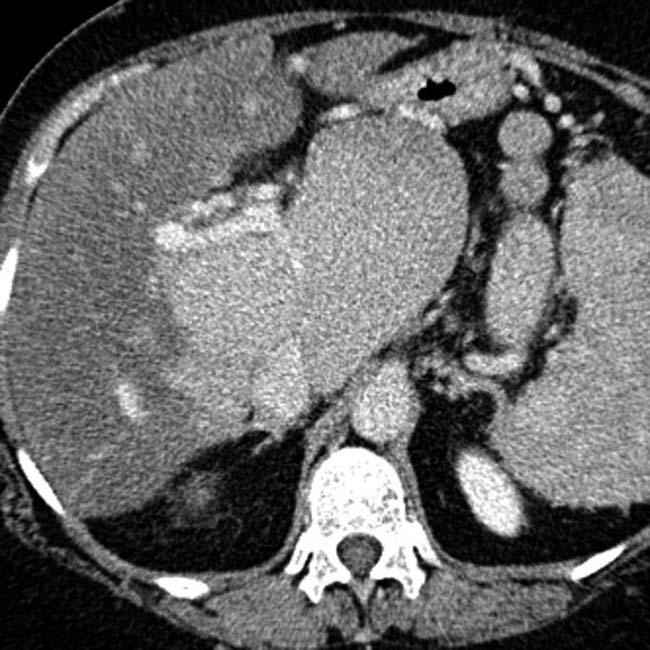
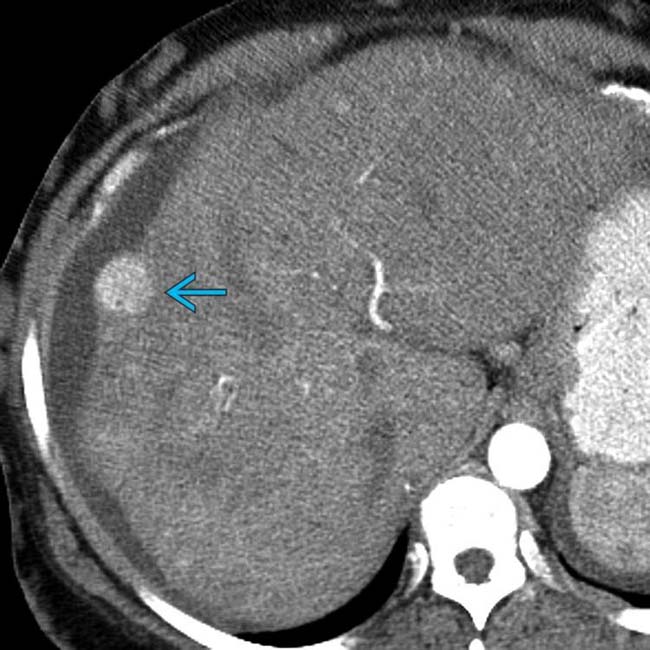
 .
.
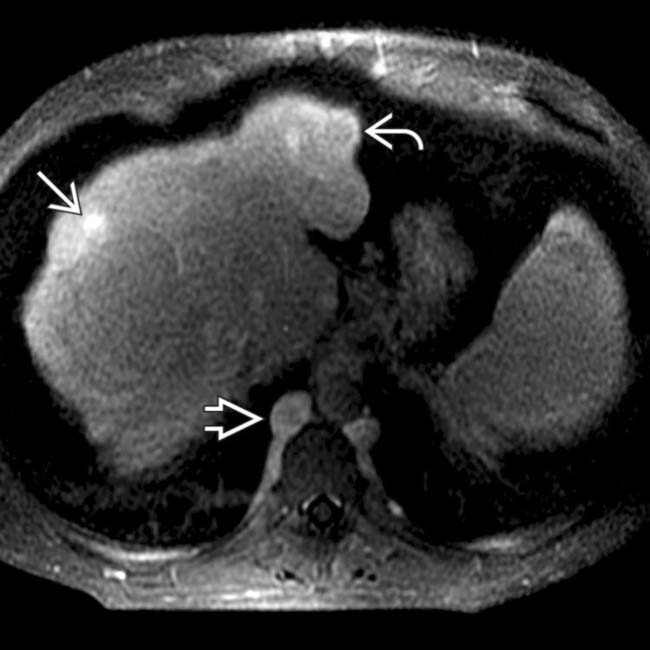
 , with a central scar, resembling a focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH). These large (multiacinar) regenerative nodules, also called focal nodular regenerative hyperplasia, occur commonly in BCS and resemble FNH on both imaging and histology.
, with a central scar, resembling a focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH). These large (multiacinar) regenerative nodules, also called focal nodular regenerative hyperplasia, occur commonly in BCS and resemble FNH on both imaging and histology.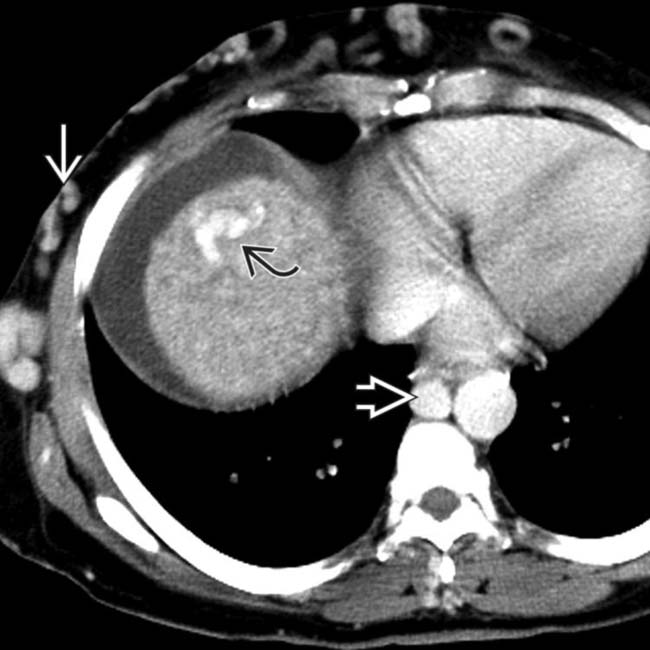
 , a large azygous vein
, a large azygous vein  , and subcutaneous collaterals
, and subcutaneous collaterals  bypassing the occluded IVC.
bypassing the occluded IVC.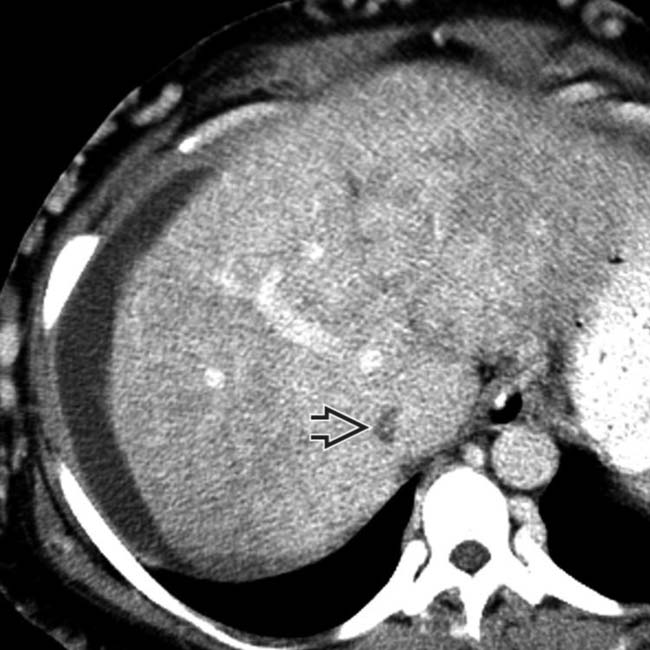
 . The liver is dysmorphic and enhances heterogeneously, especially in the periphery. Ascites is present.
. The liver is dysmorphic and enhances heterogeneously, especially in the periphery. Ascites is present.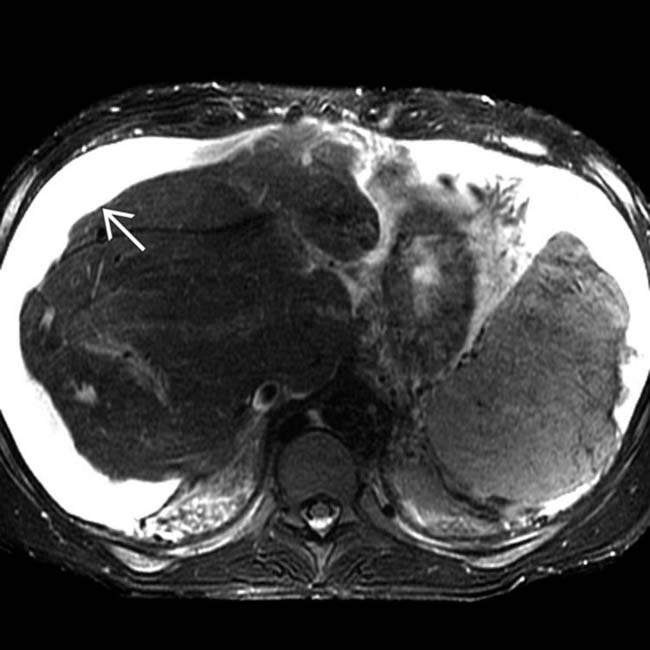
 and a dysmorphic liver, with central hypertrophy and peripheral atrophy.
and a dysmorphic liver, with central hypertrophy and peripheral atrophy.
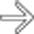
 that are hyperintense on this sequence. These are large regenerative nodules, the focal multiacinar form of nodular regenerative hyperplasia, that occur in BCS and other conditions that cause chronic hepatic ischemia.
that are hyperintense on this sequence. These are large regenerative nodules, the focal multiacinar form of nodular regenerative hyperplasia, that occur in BCS and other conditions that cause chronic hepatic ischemia.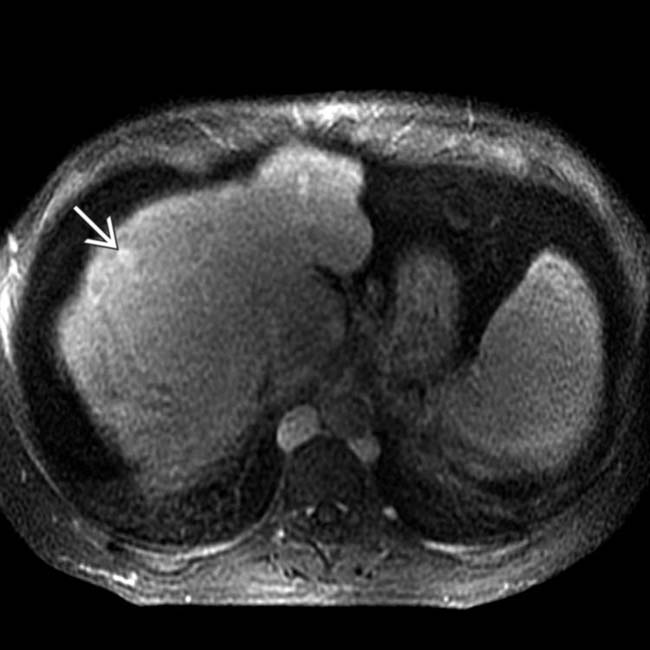
 .
.
 while another shows peripheral ring or halo enhancement
while another shows peripheral ring or halo enhancement  . The IVC is occluded, and large azygous collaterals are seen
. The IVC is occluded, and large azygous collaterals are seen  .
.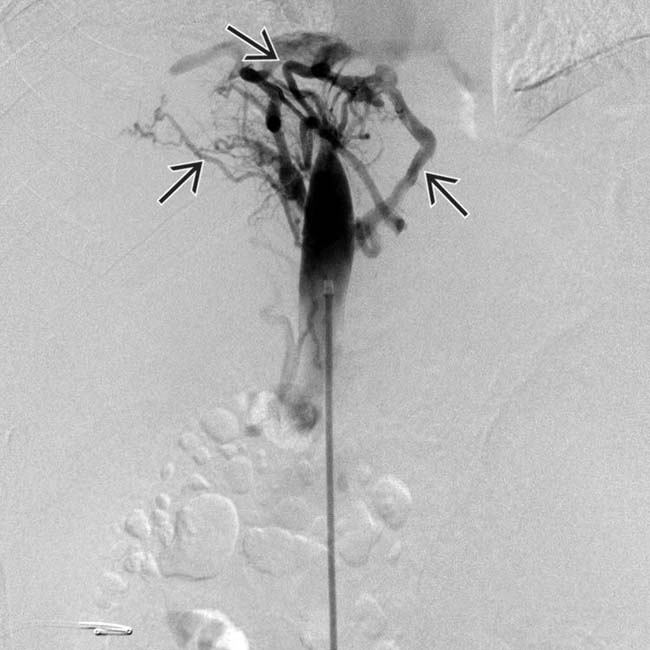
 , resembling a spider web.
, resembling a spider web.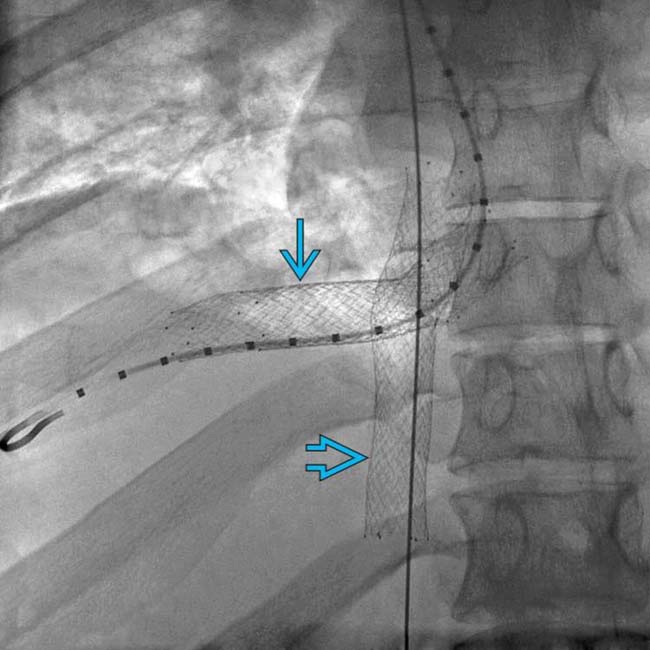
 and right hepatic vein
and right hepatic vein  following balloon dilation of these vessels. This patient was diagnosed as having BCS due to a hypercoagulable condition, the most common etiology in western countries.
following balloon dilation of these vessels. This patient was diagnosed as having BCS due to a hypercoagulable condition, the most common etiology in western countries.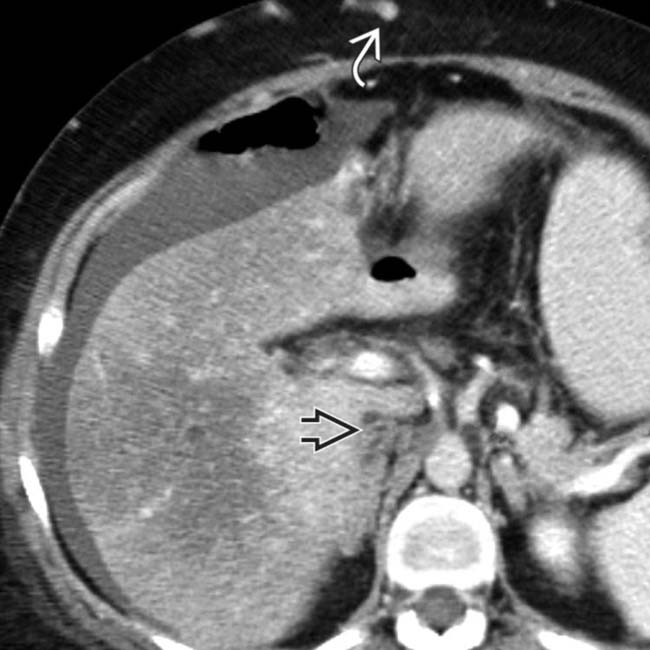
 bypassing the obstructed IVC
bypassing the obstructed IVC  . Ascites is present, and the liver enhances heterogeneously. The central right and caudate lobe enhance normally, and the peripheral right and left lobes enhance poorly. These are typical findings of subacute BCS.
. Ascites is present, and the liver enhances heterogeneously. The central right and caudate lobe enhance normally, and the peripheral right and left lobes enhance poorly. These are typical findings of subacute BCS.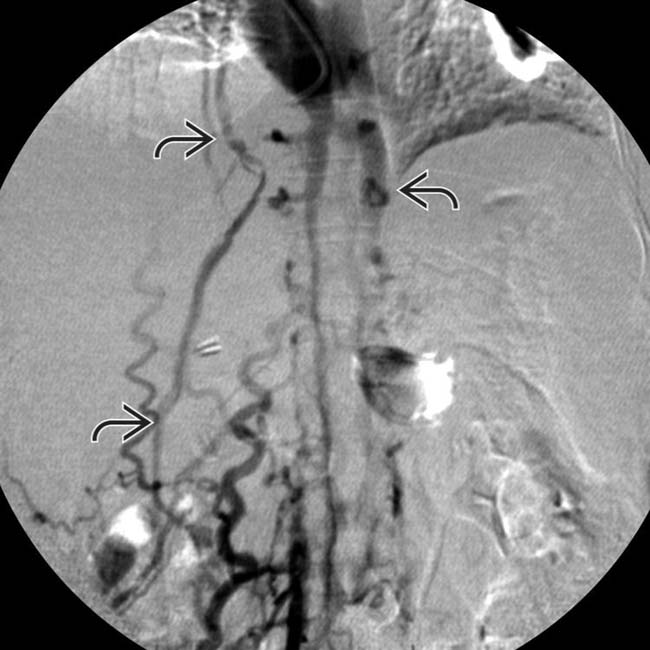
 bypassing the obstructed IVC.
bypassing the obstructed IVC.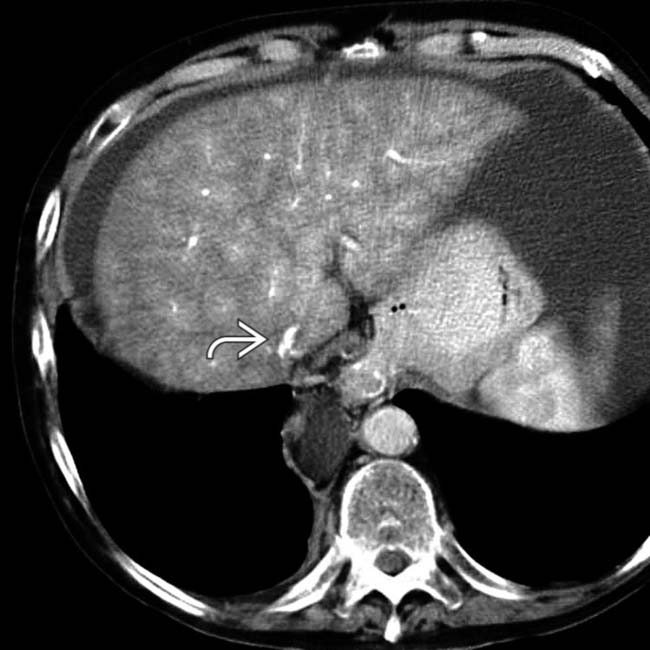
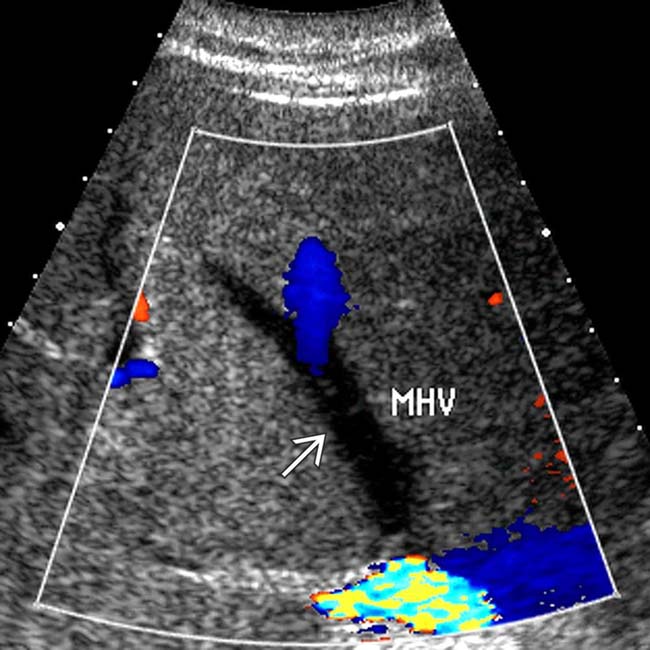
 . No patent hepatic veins were identified.
. No patent hepatic veins were identified.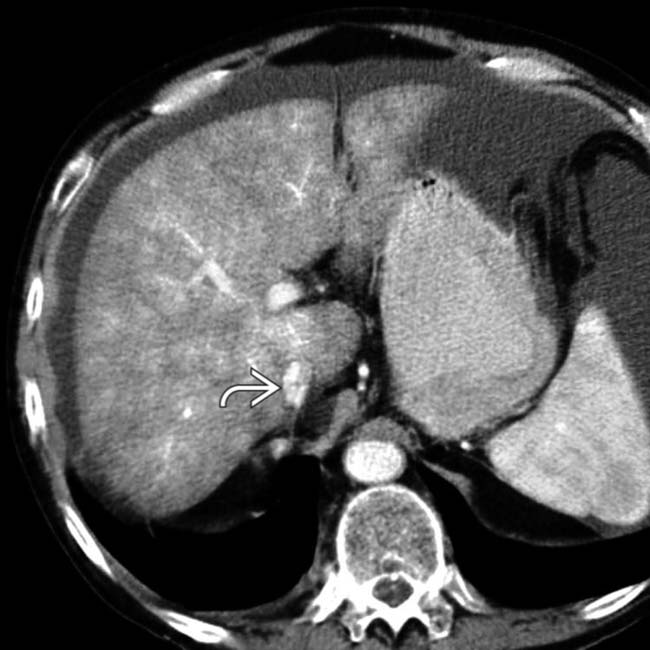
 . The liver is heterogeneous but does not yet show substantial atrophy or segmental hypertrophy. These findings are typical of acute BCS.
. The liver is heterogeneous but does not yet show substantial atrophy or segmental hypertrophy. These findings are typical of acute BCS.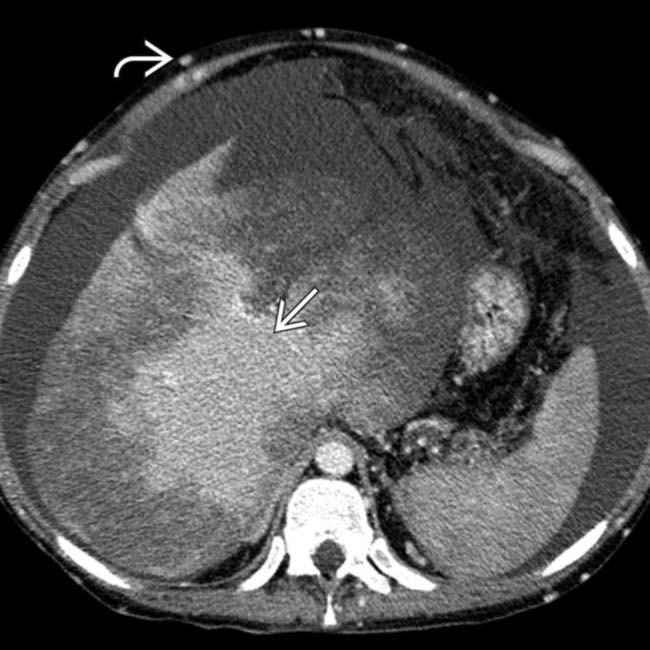
 . The central liver enhances normally
. The central liver enhances normally  and is hypertrophied, while the peripheral liver is hypodense and scarred.
and is hypertrophied, while the peripheral liver is hypodense and scarred.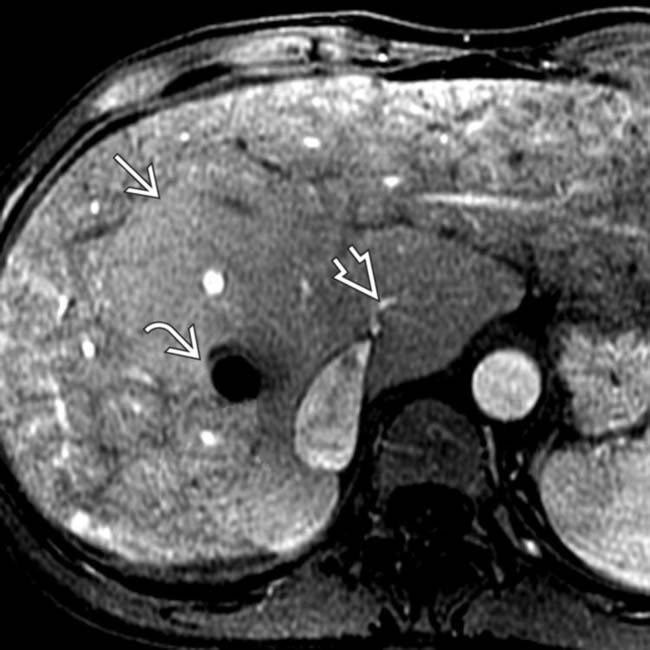
 with peripheral hepatic congestion and atrophy. Note the TIPS artifact
with peripheral hepatic congestion and atrophy. Note the TIPS artifact 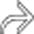 . A short, patent vein
. A short, patent vein  drains the caudate lobe into the IVC.
drains the caudate lobe into the IVC.
 .
.
 .
.
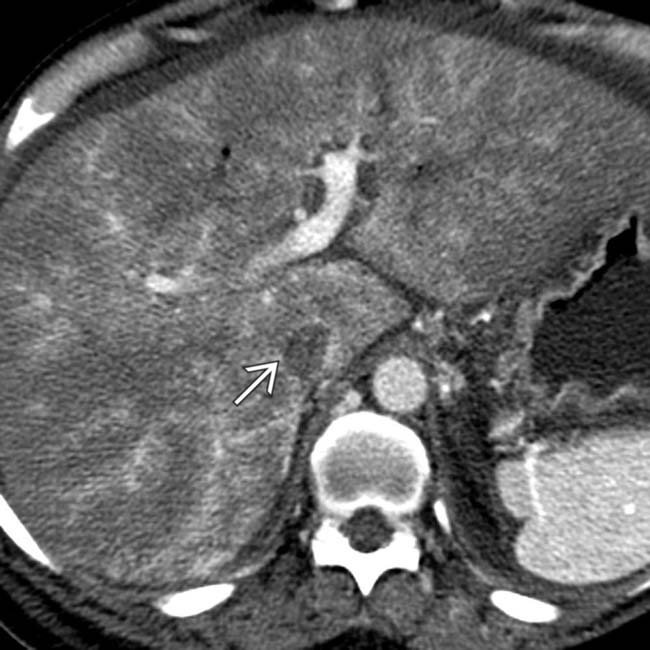
 .
.
 and mottled enhancement of the liver.
and mottled enhancement of the liver.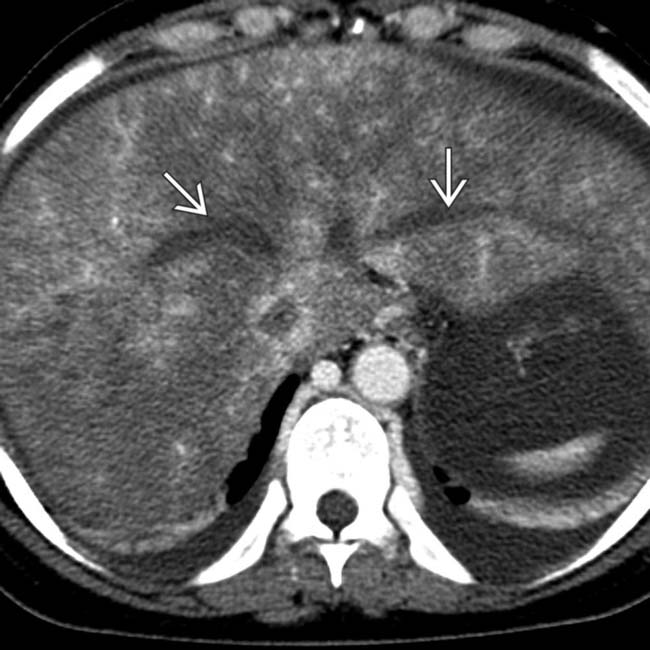
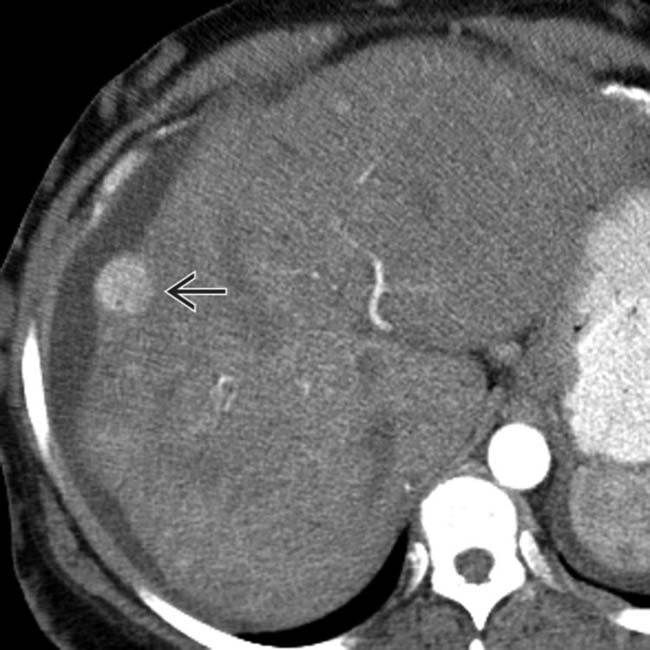
 .
.
 within the heterogeneously enhancing dysmorphic liver.
within the heterogeneously enhancing dysmorphic liver.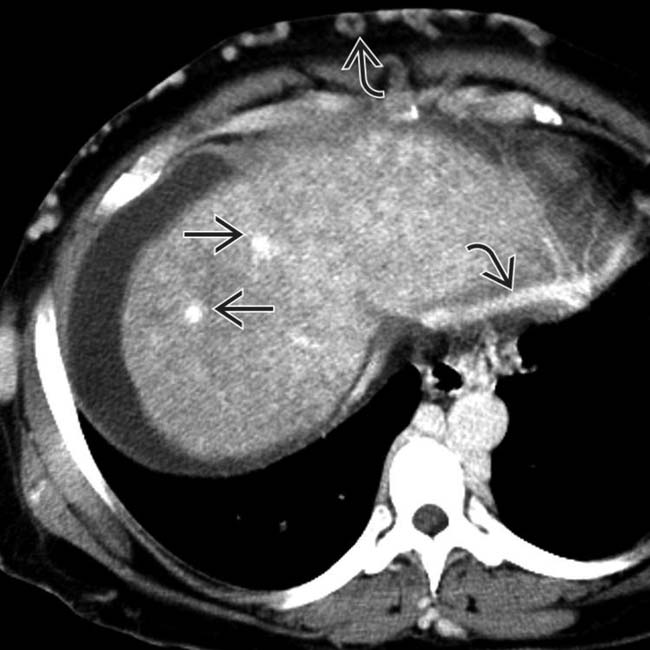
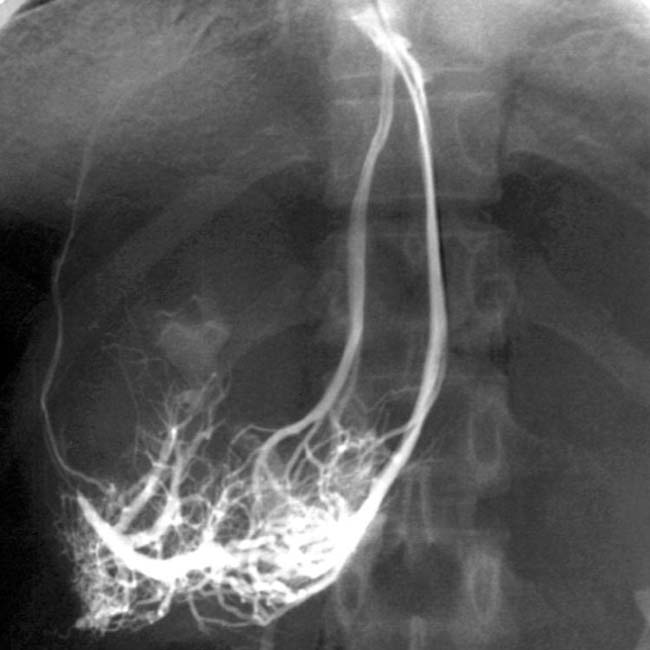
 with extensive subcutaneous and intrahepatic collaterals
with extensive subcutaneous and intrahepatic collaterals  .
.













































































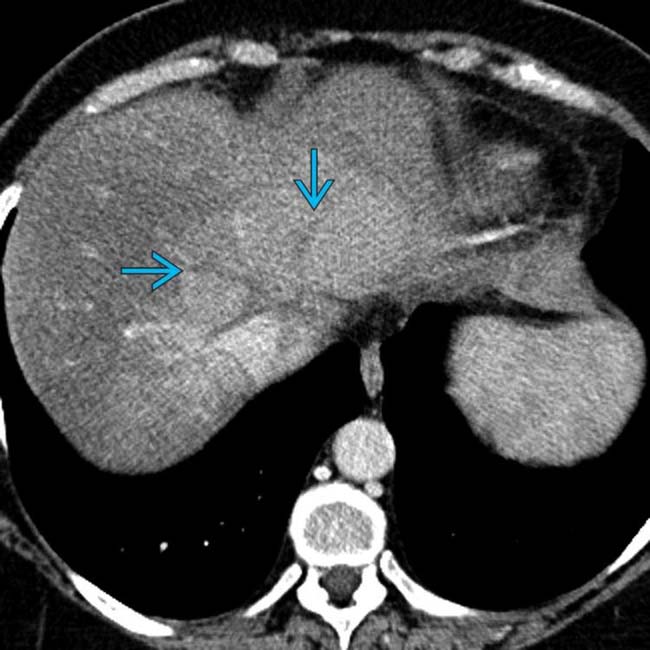
 and a heterogeneous liver.
and a heterogeneous liver.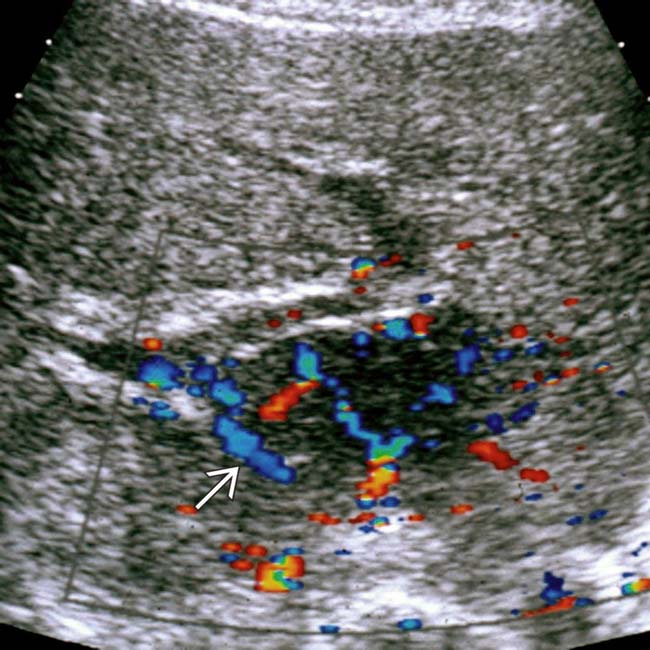
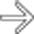 .
.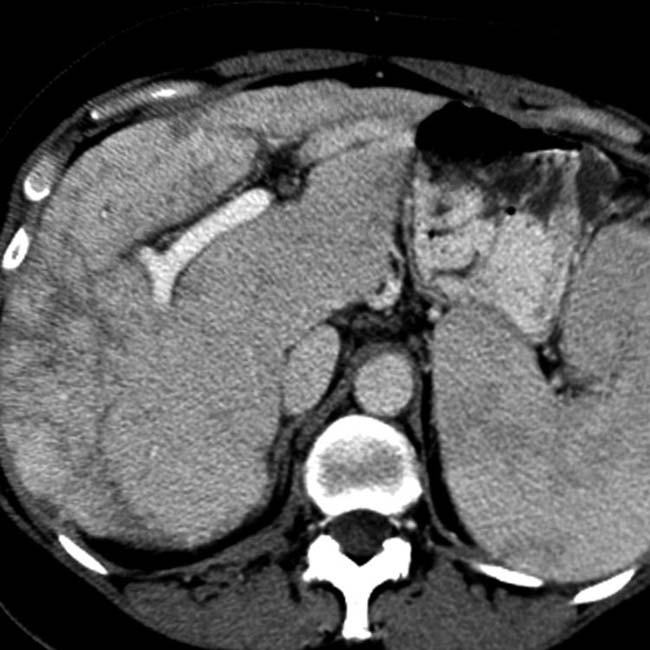
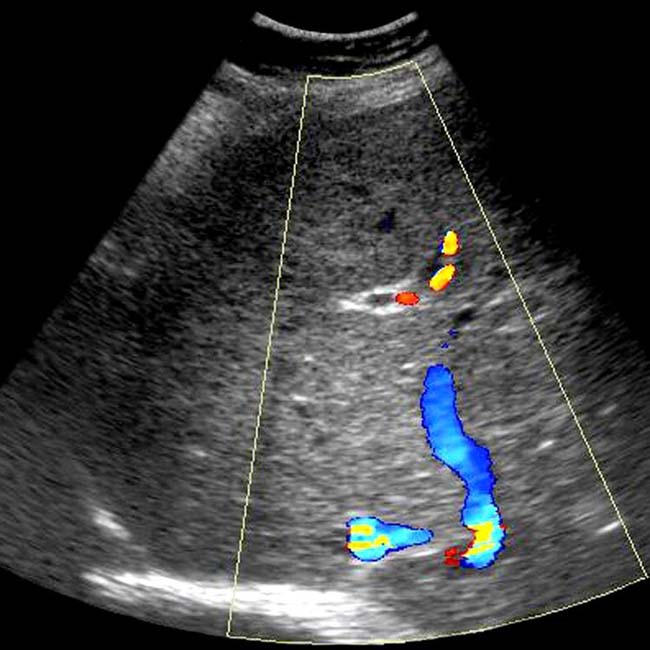
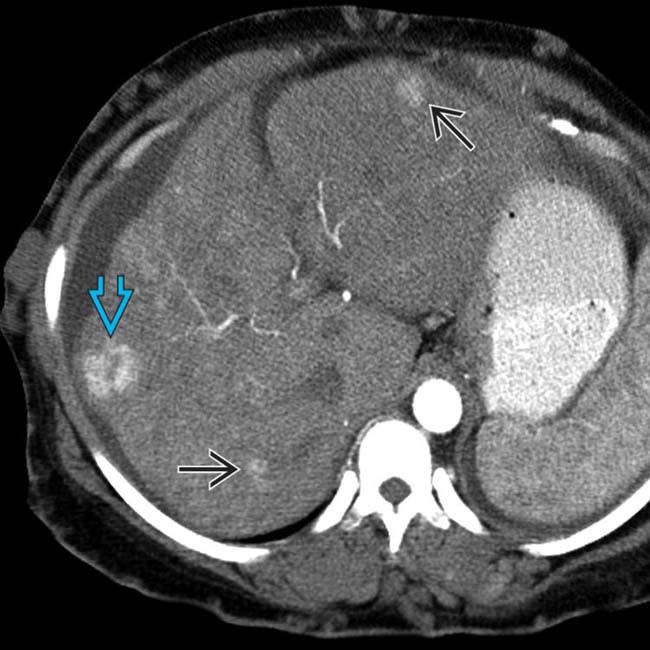
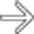
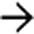 , the largest of which resembles focal nodular hyperplasia, and a central scar
, the largest of which resembles focal nodular hyperplasia, and a central scar  .
.
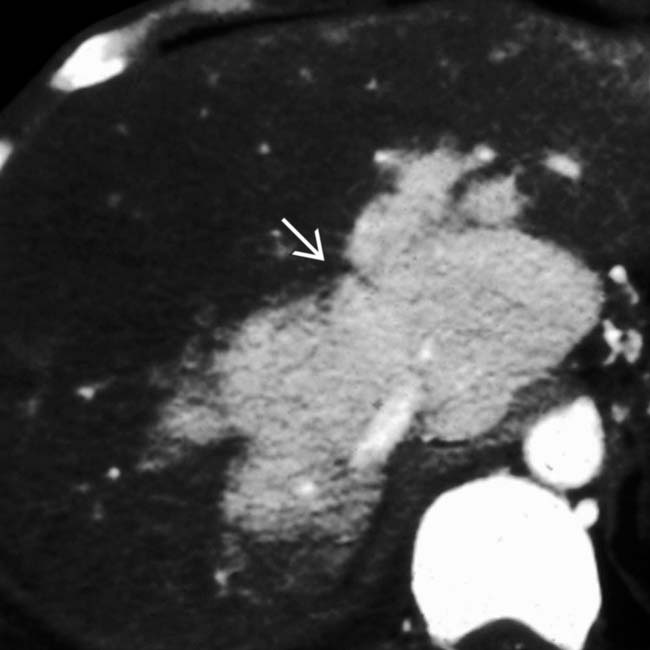
 nearly isodense to the liver.
nearly isodense to the liver.


