•
Diffuse type (Brunner gland hyperplasia)
Multiple, small, submucosal nodules < 5 mm in proximal duodenum
“Cobblestone” or “strawberry” appearance
•
Solitary type (Brunner gland hamartoma)
Solitary, sessile, or pedunculate lesion > 5 mm in proximal duodenum
•
Submucosal heterogeneous and hypoechoic lesion on endoscopic US
•
Duodenitis
Diffuse, inflammatory changes are seen
•
Duodenal flexure pseudotumor
Redundant mucosa can simulate luminal mass
•
Hamartomatous polyposis (Peutz-Jeghers)
Associated lesions (mucocutaneous pigmentation, etc.)
•
Familial polyposis syndrome
Associated extraintestinal manifestations (epidermoid cyst, lipoma, fibroma, desmoid tumors, etc.)
•
Duodenal metastases and lymphoma
Metastases: “Target” or bull’s-eye lesion with rounded submucosal mass; ulceration is common
•
Epigastric pain is most common symptom
•
No treatment needed for diffuse type
•
Endoscopic or surgical resection for large hamartoma to verify histology
•
Brunner gland hamartoma, Brunner gland adenoma (misnomer)
•
Nonneoplastic hyperplasia of duodenal submucosal glands
Diffuse type (Brunner gland hyperplasia)
–
Multiple, small, submucosal nodules < 5 mm
Solitary type (Brunner gland hamartoma)
–
Solitary, sessile or pedunculated lesion > 5 mm
•
Best diagnostic clue
“Strawberry” or “cobblestone” appearance in proximal duodenum on barium study
•
Location
Diffuse type: Most commonly in 1st part of duodenum (bulb) proximal to ampulla
Hamartoma: Most commonly in 1st and 2nd parts of duodenum
•
Morphology
Diffuse type: Solitary or multiple, small, rounded, submucosal nodules
Hamartoma: Solitary, polypoid, may have pedicle
•
Best imaging tool
Upper GI barium study
Endoscopic ultrasound
•
Diffuse type
Multiple, small, rounded nodules in proximal duodenum
“Cobblestone” or “strawberry” appearance
Central collections of barium (erosions) or thickened folds may indicate duodenitis
•
Brunner gland hamartoma
≥ 1 smooth polypoid lesions
May be sessile or pedunculated
•
Submucosal heterogeneous and hypoechoic lesion on endoscopic US
•
Heterogeneous, slightly enhancing, polypoid lesion
•
Diffuse, inflammatory changes are seen
•
Erosions, thickened folds
•
Acute angulation of lumen at apex of duodenal bulb
•
Redundant mucosa can simulate luminal mass
•
Cluster of small polyps in ileum and jejunum (less common in duodenum, large bowel, and stomach)
•
Associated lesions (mucocutaneous pigmentation, etc.)
•
Innumerable adenomatous colonic polyps (less common in stomach, small bowel, and duodenum)
•
Associated extraintestinal manifestations (epidermoid cyst, lipoma, fibroma, desmoid tumors, etc.)
•
Metastases: “Target” or bull’s-eye lesion with rounded submucosal mass; ulceration is common
•
Lymphoma: Bulky, hypovascular, soft tissue mass infiltrating submucosa of stomach and duodenum on CECT
•
Etiology
Acid hypersecretion (no causal relationship has been proven)
Brunner glands secrete alkaline, bicarbonate-rich fluid to buffer gastric acid
•
Diffuse type: Prominent Brunner glands separated by fibrous septa
•
Hamartoma: Mixture of acini, ducts, smooth muscle, adipose tissue, and lymphoid tissue
Considerable histological overlap between 2 types
Better differentiated based on morphology and size
•
Most common signs/symptoms
Epigastric pain
•
Other signs/symptoms
Upper GI bleeding, upper GI obstruction, intussusception (all rare)
•
Age
Any age, commonly 40-60 years
•
Epidemiology
Constitute 5-10% of duodenal masses
•
No treatment needed for diffuse type
•
Endoscopic or surgical resection for large hamartoma to verify histology
1. Gastroenterology . 2014; 146(4):e7–e8.
2. Dig Dis Sci . 2013; 58(1):194–201.
3. Trop Gastroenterol . 2010; 31(2):121–123.
4. AJR Am J Roentgenol . 2006; 187(3):715–722.
Ultraschall Med . 2012; 33(7):E210–E217.
Surg Clin North Am . 2008; 88(4):779–817. [vii].
J Gastroenterol . 2008; 43(6):492–497.
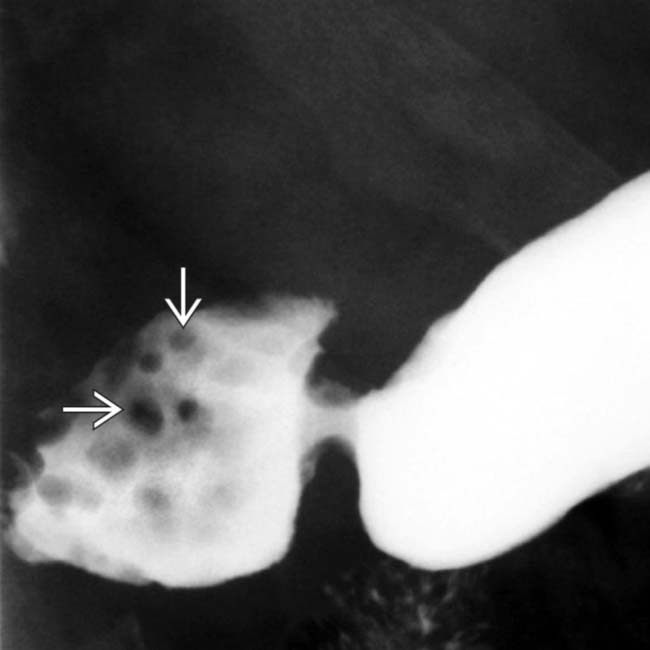
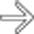 in the duodenal bulb, characteristic of Brunner gland hyperplasia.
in the duodenal bulb, characteristic of Brunner gland hyperplasia.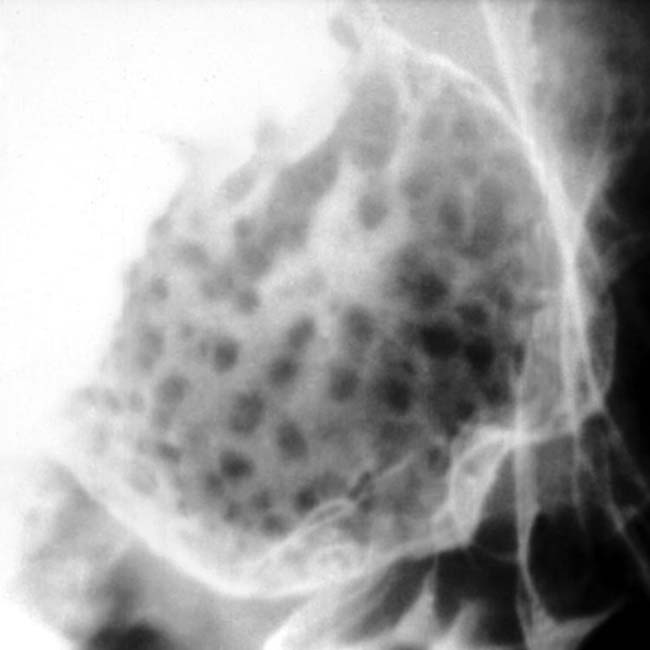
 in the proximal duodenum. An endoscopic biopsy revealed hyperplasia and elements of hamartoma arising from Brunner glands.
in the proximal duodenum. An endoscopic biopsy revealed hyperplasia and elements of hamartoma arising from Brunner glands.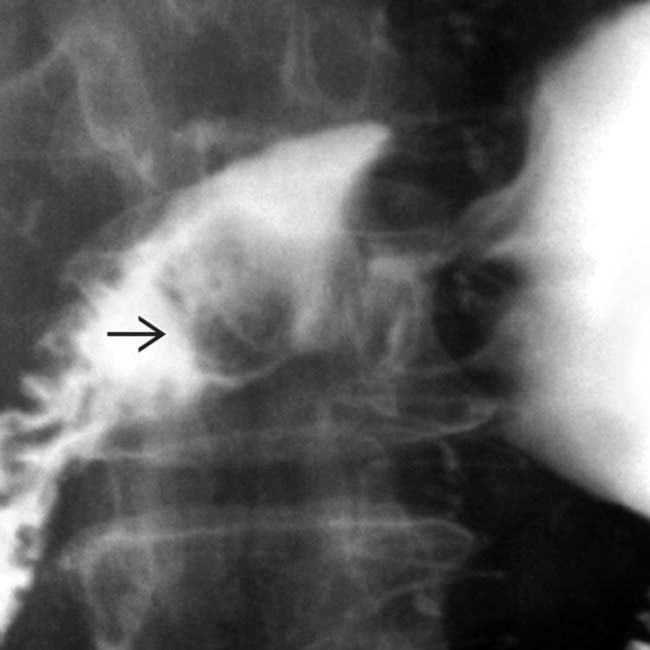
 within the duodenal bulb. An endoscopic biopsy and resection revealed a hamartoma of a Brunner gland. Larger, isolated lesions, as in this case, are indistinguishable from many other duodenal masses and require a biopsy.
within the duodenal bulb. An endoscopic biopsy and resection revealed a hamartoma of a Brunner gland. Larger, isolated lesions, as in this case, are indistinguishable from many other duodenal masses and require a biopsy.

































