Chapter 30 Botanical Cosmeceutical Myths
There are numerous botanical cosmeceutical myths. This may be due in part to the aura that plants are natural, preservative-free, healthy, holistic, relaxing, restoring, healing, etc. Certainly, the plant kingdom is a rich source of active ingredients. Plants have adapted to thrive in an environment rich in UV radiation. It is for this reason that humans look to plants for solutions to oxidative insults. Plant extracts provide a rich source of antioxidants and anti-inflammatories. However, a major dermatologic question is whether the plant materials are more effectively consumed or topically applied. Most of the botanicals used in cosmeceuticals have been highly processed to allow their efficient addition to moisturizers and other topically applied products. Cosmeceuticals typically take the form of creams, lotions, serums, and solutions. Botanicals must be liquids or powders to easily blend into an aesthetic formulation of this type. This chapter examines some of the more common cosmeceutical myths, providing insight into their fallacies.
HYPOALLERGENIC BOTANICAL COSMECEUTICALS DO NOT PRODUCE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
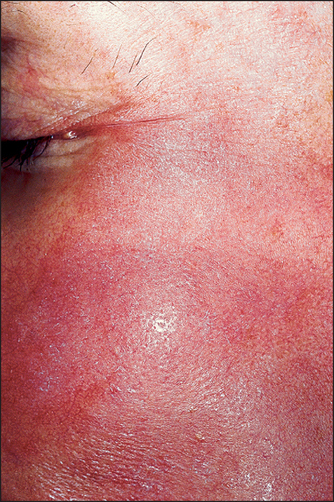
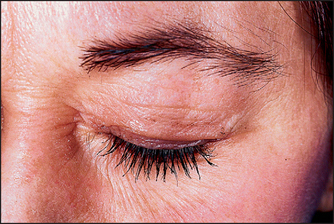
The term hypoallergenic is a marketing term meaning ‘reduced allergy’ not ‘nonallergenic’. This term was first popularized by Clinique cosmetics, a division of Estée Lauder, for advertising purposes to create a unique image for this new make-up line. There are no governmental guidelines that apply to the hypoallergenic concept. Dermatologists should consider hypoallergenic cosmetics as a source of allergic contact dermatitis for all patients Fig. 30.1. It is hoped that companies making the hypoallergenic claim have conducted repeat insult patch testing as part of their product safety assessment, but this cannot always be assumed.
PRESERVATIVE-FREE BOTANICAL COSMECEUTICALS PRODUCE FEWER SKIN REACTIONS
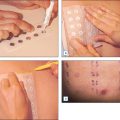
Many products are now claiming to be better for the skin because they are ‘preservative-free’. This is a somewhat meaningless term, since all products must contain preservatives Fig. 30.2. Preservatives fall into several categories. There are preservatives that are classified as antioxidants. These are substances designed to prevent the rancidity of the oils in the formulation and prevent the breakdown of coloring agents. Common antioxidant preservatives that perform this function are tocopheryl acetate, retinyl palmitate and ascorbic acid. These are of the same family as the topical vitamin E, A, and C additives that many companies are claiming prevent skin oxidation. Oxidation is a universal event leading to aging of any living or biologically derived material. However, tocopheryl acetate, retinyl palmitate, and ascorbic acid in the concentrations used for product preservation do not have much biologic activity for the prevention of skin oxidation.
BOTANICAL COSMECEUTICALS ARE NATURAL
There is a misconception that all botanical cosmeceuticals are natural because they are derived from plant sources. Most botanical actives were first discovered and isolated from plant sources, but are no longer obtained from plants. This is far too expensive in most cases. Many botanical extracts are modified and chemically synthesized to obtain a form that can be easily incorporated into a skin moisturizer. Ground-up leaves or cactus spines Fig. 30.3 typically do not create an aesthetic feel when sprinkled in a moisturizer and undergo extensive processing to create a liquid or fine powder suitable for cosmeceutical use. An excellent example is allantoin, botanically obtained from the root of the comfrey plant. However, most allantoin used as an anti-inflammatory agent in sensitive skin cosmeceuticals is obtained from uric acid. It is bioidentical to plant-derived allantoin, but synthesized in a chemical plant, not grown by ‘mother nature’. Thus, the claim that botanicals are natural is meaningless. All chemicals are in some sense natural, since they are derived from materials present on the earth.
BOTANICALLY DERIVED FRAGRANCES DO NOT CAUSE ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS
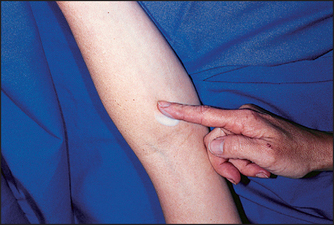
Many of the newer botanically derived fragrances entering the market claim to be ‘hypoallergenic’. Remember that the term hypoallergenic means reduced allergic potential and not zero allergic potential. Also remember that hypoallergenic refers to a reduced incidence of allergic contact dermatitis and not a reduced incidence of vasomotor rhinitis or other untoward nasal or respiratory effects from the perfume. Botanically derived fragrances can most certainly cause allergic contact dermatitis in the sensitized patient. I usually have my patients apply the new hypoallergenic perfume in one antecubital fossa for five nights in a row prior to more liberal application to avoid widespread allergic contact dermatitis Fig. 30.4.
BOTANICAL COSMECEUTICALS CAN REDUCE SEBUM PRODUCTION
Many skin care products on the market today contain botanical ingredients that claim to decrease facial sebum. Sometimes it is unclear from the label whether the appearance of sebum is reduced or whether the production of sebum is decreased. One mechanism for reducing the appearance of facial oil is to adsorb the sebum into 1–30 μm diameter polymer spheres composed of three monomers: isobornyl methacrylate (IBMA), lauryl methacrylate (LMA), and divinylbenzene (DVB). The DVB serves to crosslink the IBMA and LMA to form a three-dimensional copolymer network capable of absorbing liquid oil-soluble substances. This technology was originally developed to control industrial organic solvent spills.
ANTIPERSPIRANTS CONTAIN CHEMICALS THAT ARE NOT NATURALLY DERIVED AND ARE THEREFORE DAMAGING TO THE SWEAT GLANDS
BOTANICALS AND MINERAL COSMETICS ARE SAFE AND DO NOT CAUSE ACNE
Botanicals are plant-derived materials and mineral cosmetics contain pigments derived from rock sources. Botanicals and mineral cosmetics are no more or less likely to produce acne than any other raw materials. They must undergo the same comedogenicity testing and clinical testing as any other ingredient. Their safety must be demonstrated in a cosmetic chemistry laboratory and cannot be assumed Fig. 30.5.
ALL NATURAL INGREDIENTS ARE SAFER IN SKIN CARE PRODUCTS
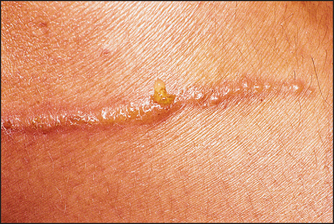
It is hard to know exactly what ‘all natural ingredients’ constitutes. All natural has come to mean actives derived from the plants and minerals of the earth. But isn’t everything we see in our world derived from the plants and minerals of the earth? Something that is chemically altered still has its basis in the plants and minerals of the earth. Thus, this term is basically marketing jargon with little medical credibility. All natural ingredients are not necessarily safer in skin care products. Even poison ivy which causes an intense allergic contact dermatitis is ‘natural’ Fig. 30.6.
NUMEROUS BOTANICALS IN COSMECEUTICALS ARE BETTER
There is an unspoken rule in cosmeceutical formulation that if one active ingredient is good, 20 active ingredients are great. This had led to the botanical cocktails present in many facial moisturizing products. A quick read through the label reveals at least 10 different plant extracts. Why are they all there? Many times the botanical cocktail is purchased from a supplier with the intent to create a pleasant fragrance from the botanical mixture. Other times the cosmetic formulator selects the concoction to meet some marketing or media needs at the time. Botanical cocktails are extremely problematic for the dermatologist who is trying to figure out which ingredient is the cause of a patient’s allergic contact dermatitis Fig. 30.7. For this reason, I typically recommend that my patients avoid facial moisturizers that contain numerous botanical extracts.
CLEANSERS WITH GROUND BOTANICAL MATERIALS ARE GOOD FOR DEEP CLEANING PORES
A number of botanical facial cleansers contain ground fruit pits, leaves, or other abrasive substances for the purpose of cleaning the pores Fig. 30.8. In fact it is impossible to clean the sebaceous gland and the duct. Only the follicular ostia of the pilosebaceous unit can be accessed from the skin surface. This means that these facial scrubs can basically only mechanically exfoliate the skin surface and the follicular ostia. Comedonal plugs sticking above the skin surface might be removed, as well as any desquamating corneocytes. It is possible to scrub too hard with fruit pits and induce sensitive skin or milia. For patients who wish to mechanically exfoliate, I recommend one of the scrubs with the dissolving sodium tetrahydrate decaborate granules that wear away with continued scrubbing. This prevents the obsessive–compulsive patient from inducing skin damage.
TOPICAL BOTANICAL COSMECEUTICALS MINIMIZE POSTMENOPAUSAL SKIN CHANGES
Postmenopausal skin changes are typically due to a low estrogen state leading to an increase in facial folds and upper lip rhytides. A number of topical botanical preparations have been introduced to minimize postmenopausal wrinkling. These cosmeceuticals contain genistein, an extract of fermented soy, which is structurally similar to human estrogen and can thus bind to some of the same receptors. It is for this reason that genistein has been termed a phytoestrogen and credited with the decrease in cardiovascular disease, breast cancer, and postmenopausal facial wrinkling seen in Asian women.