Cook, MB, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the sex ratio for Barrett’s esophagus, erosive reflux disease, and nonerosive reflux disease. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 162(11):1050–1061.
Luedtke, P, et al. Radiologic diagnosis of benign esophageal strictures: a pattern approach. Radiographics. 2003; 23(4):897–909.
Yamamoto, AJ, et al. Short-segment Barrett’s esophagus: findings on double-contrast esophagography in 20 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176(5):1173–1178.
Rosch, T. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s esophagus. Endoscopy. 2000; 32(11):826–835.
Chen, MY, et al. Barrett esophagus and adenocarcinoma. Radiol Clin North Am. 1994; 32(6):1167–1181.
Glick, SN. Barium studies in patients with Barrett’s esophagus: importance of focal areas of esophageal deformity. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 163(1):65–67.
Levine, MS. Reflux esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus. Semin Roentgenol. 1994; 29(4):332–340.
Gilchrist, AM, et al. Barrett’s esophagus: diagnosis by double-contrast esophagography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988; 150(1):97–102.
Levine, MS, et al. Re: Reticular pattern as a radiologic sign of the Barrett esophagus. Radiology. 1985; 156(3):843–844.
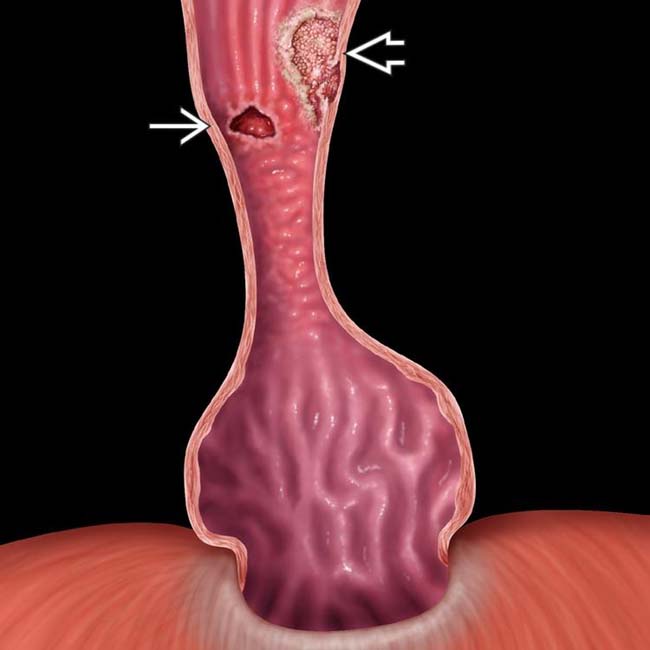
 and an adenocarcinoma
and an adenocarcinoma  represented by a raised sessile lesion with an irregular surface.
represented by a raised sessile lesion with an irregular surface.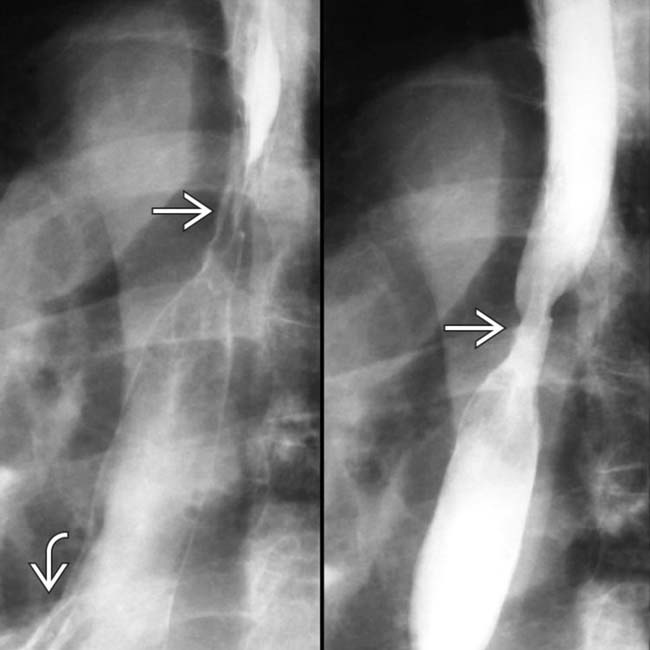
 and ulcer in a patient with a small hernia
and ulcer in a patient with a small hernia 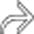 and reflux.
and reflux.
 with the velvet texture of Barrett mucosa and stricture. Normal esophageal mucosa has a shiny, smooth, pink surface.
with the velvet texture of Barrett mucosa and stricture. Normal esophageal mucosa has a shiny, smooth, pink surface.
 that represents an adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett mucosa.
that represents an adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett mucosa.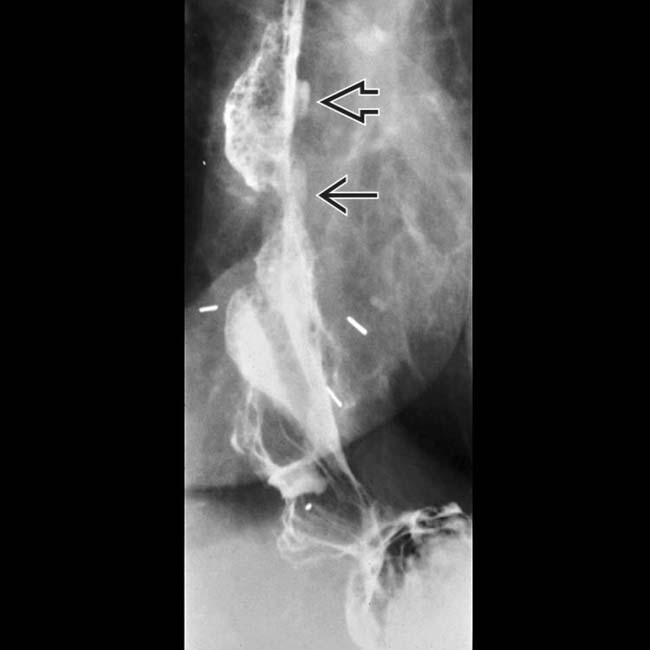
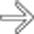
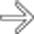
 and higher. Note the discrete ulcer
and higher. Note the discrete ulcer  .
.







































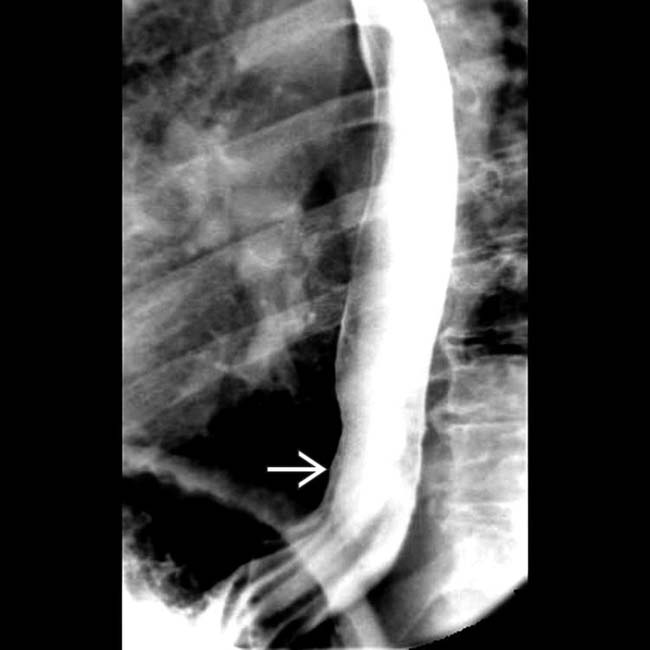
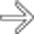 in the distal esophagus in this patient with adenocarcinoma on Barrett mucosa.
in the distal esophagus in this patient with adenocarcinoma on Barrett mucosa.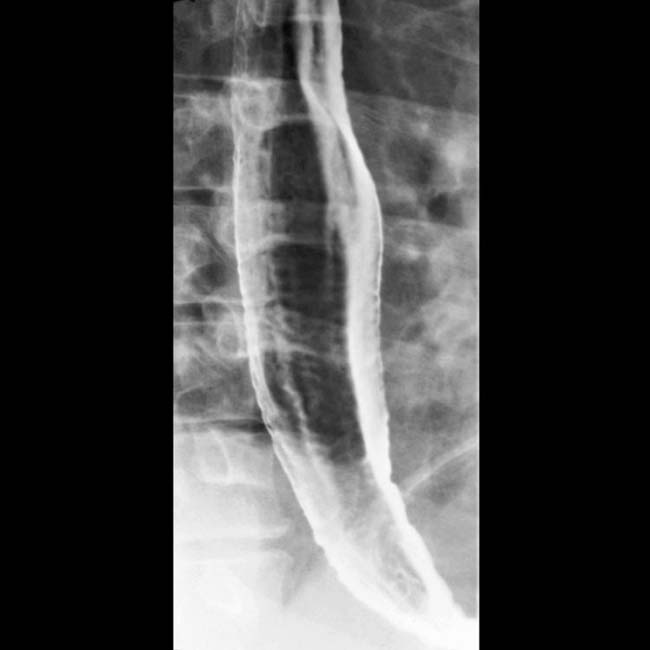
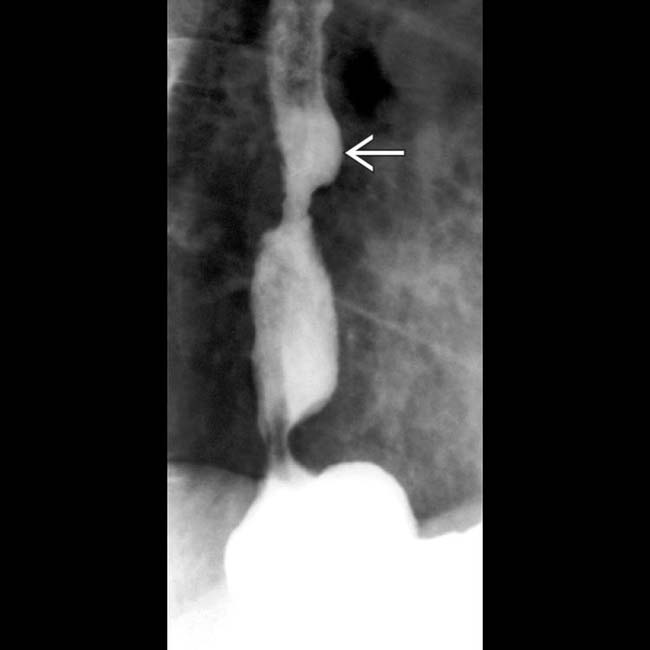
 and hiatal hernia.
and hiatal hernia.

