Strictures long and smooth without irregularity and may cause proximal biliary dilatation
• MR: MRCP images nicely demonstrate irregularity and strictures of intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts (most commonly affecting distal CBD)
• CT: Circumferential focal or diffuse bile duct wall thickening with hyperenhancement of affected segments
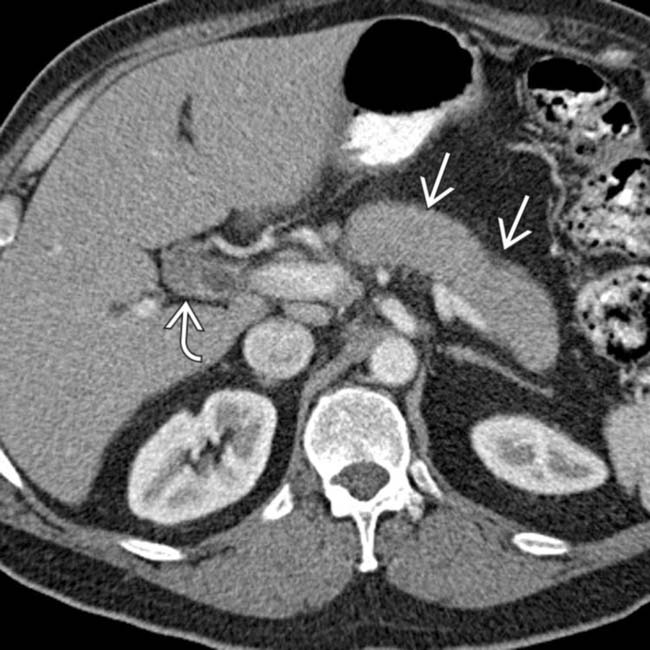
 and an enlarged, sausage-shaped pancreas
and an enlarged, sausage-shaped pancreas  . The appearance of the pancreas is consistent with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), and an elevated IgG4 indicates that the bile duct thickening is due to IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (ISC).
. The appearance of the pancreas is consistent with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), and an elevated IgG4 indicates that the bile duct thickening is due to IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (ISC).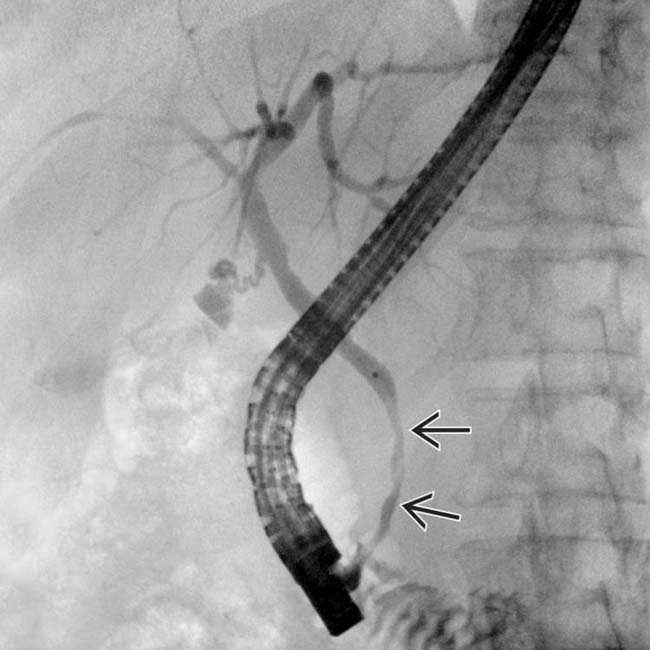
 of the distal CBD, the most common manifestation of ISC. ISC and AIP resolved after steroid and azathioprine therapy.
of the distal CBD, the most common manifestation of ISC. ISC and AIP resolved after steroid and azathioprine therapy.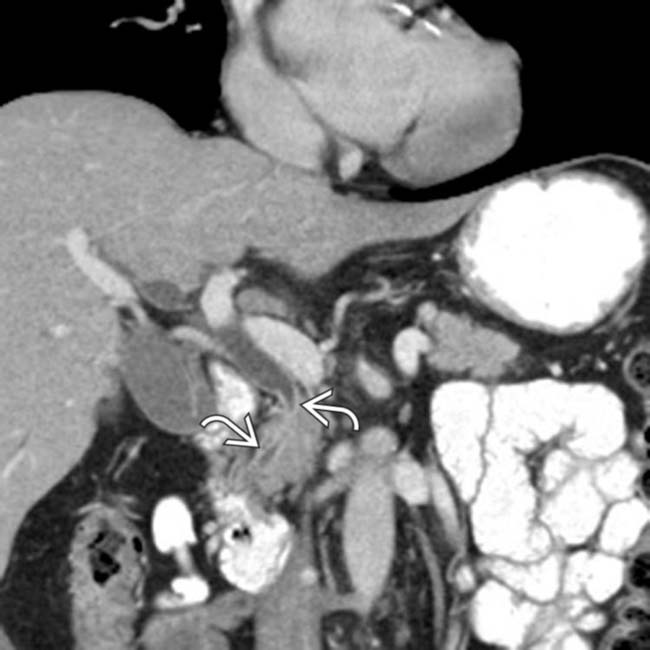
 with wall hyperenhancement, compatible with autoimmune cholangitis.
with wall hyperenhancement, compatible with autoimmune cholangitis.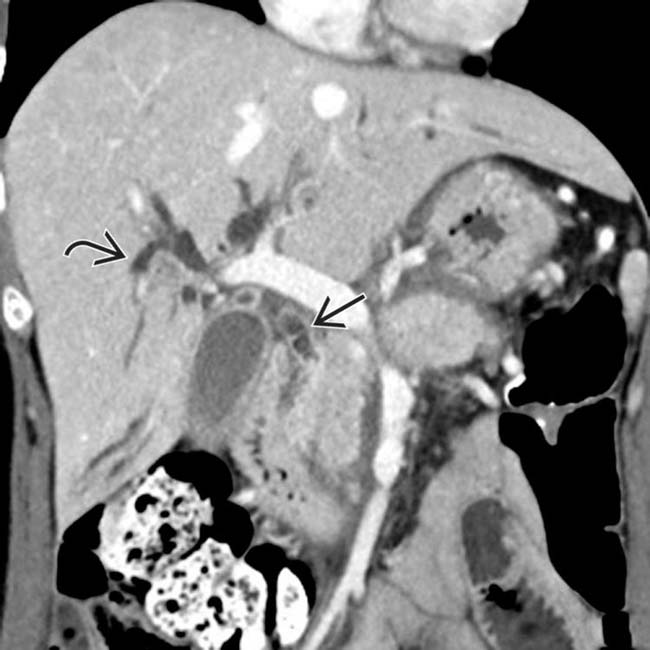
 with proximal biliary dilatation
with proximal biliary dilatation  , in keeping with IgG4-related cholangitis.
, in keeping with IgG4-related cholangitis.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• No clear association between ISC and malignancy, but involved sites in biliary tree may rarely appear mass-like and mimic malignancy (inflammatory pseudotumor)
• Diffuse gallbladder wall thickening (due to either lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and transmural fibrosis or superimposed cholecystitis)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
• Irregular strictures affecting both intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts with alternating sites of dilatation, stricture, and normal-appearing ducts
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Image Interpretation Pearls
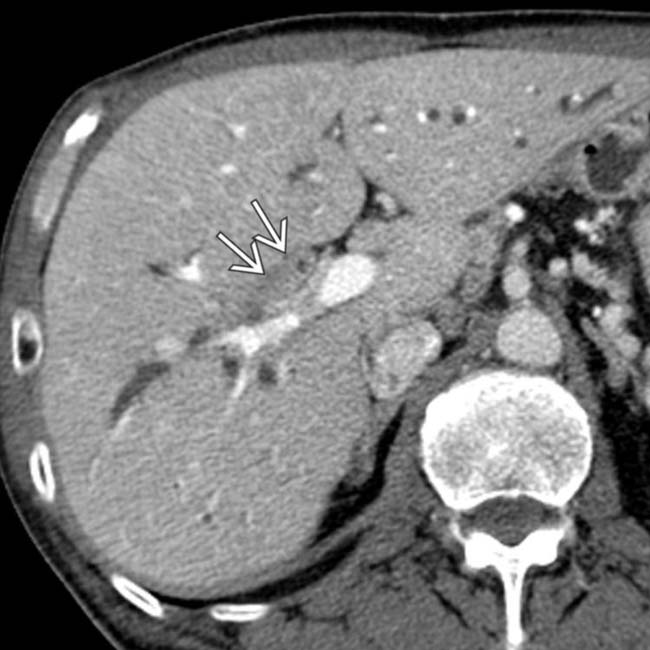
 and mild intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation.
and mild intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation.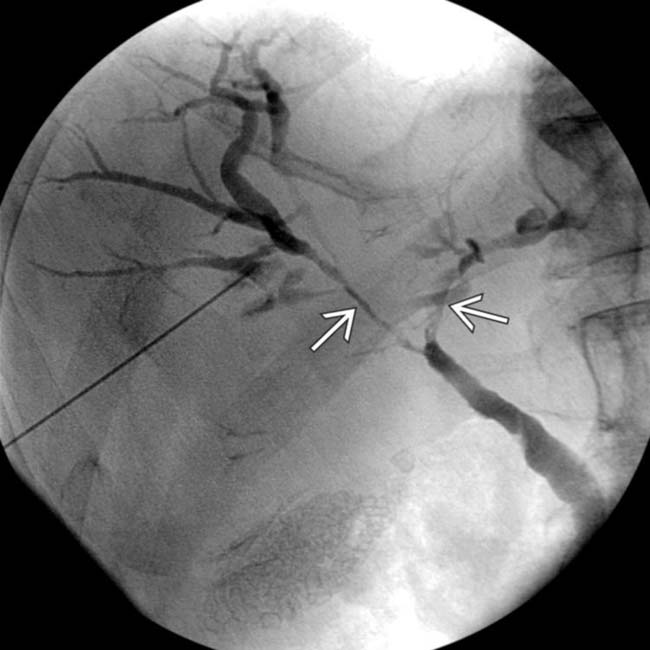
 of the proximal right and left hepatic ducts. The patient’s serum IgG4 was not elevated, but the strictures improved with empiric steroid therapy. An elevated IgG4 is a highly sensitive and specific marker for ISC, though IgG4 levels may vary widely during the disease course.
of the proximal right and left hepatic ducts. The patient’s serum IgG4 was not elevated, but the strictures improved with empiric steroid therapy. An elevated IgG4 is a highly sensitive and specific marker for ISC, though IgG4 levels may vary widely during the disease course.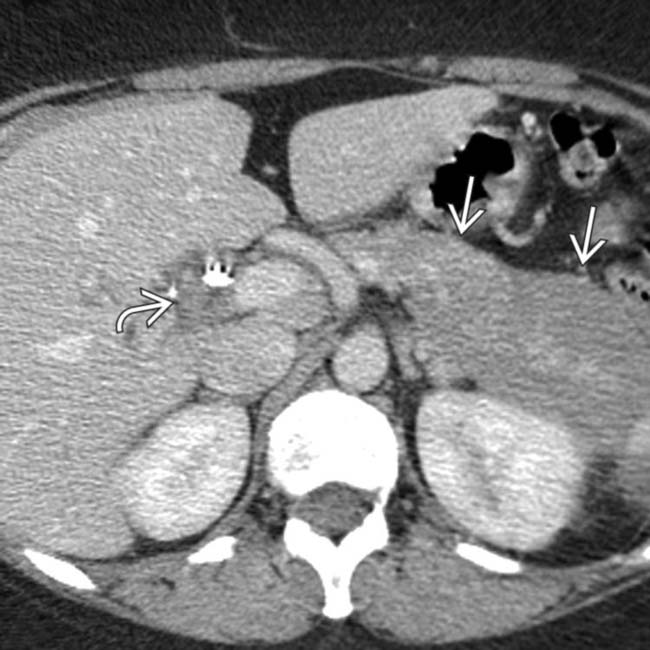
 and mild thickening of the common duct
and mild thickening of the common duct  post stent placement.
post stent placement.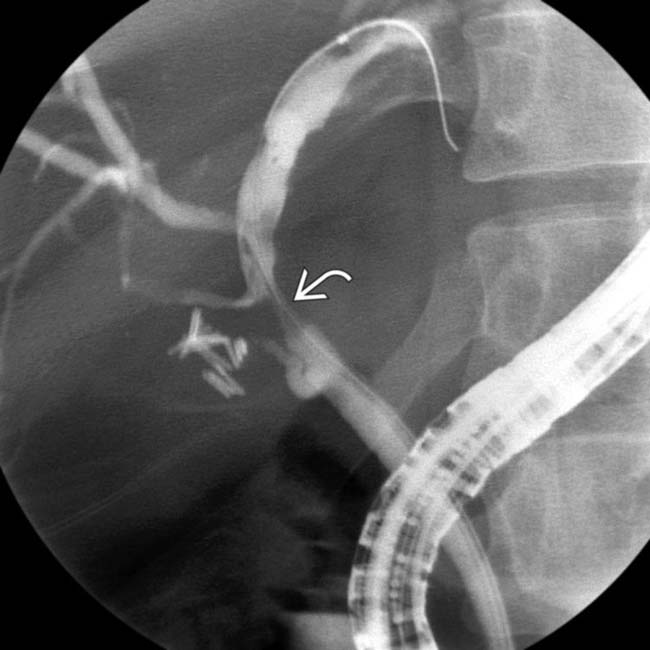
 . The patient had an elevated IgG4, and these imaging findings were found to represent AIP and ISC. The patient also had Riedel thyroiditis, a finding indicating a systemic fibrosclerosing process. The stricture and AIP improved after steroid therapy.
. The patient had an elevated IgG4, and these imaging findings were found to represent AIP and ISC. The patient also had Riedel thyroiditis, a finding indicating a systemic fibrosclerosing process. The stricture and AIP improved after steroid therapy.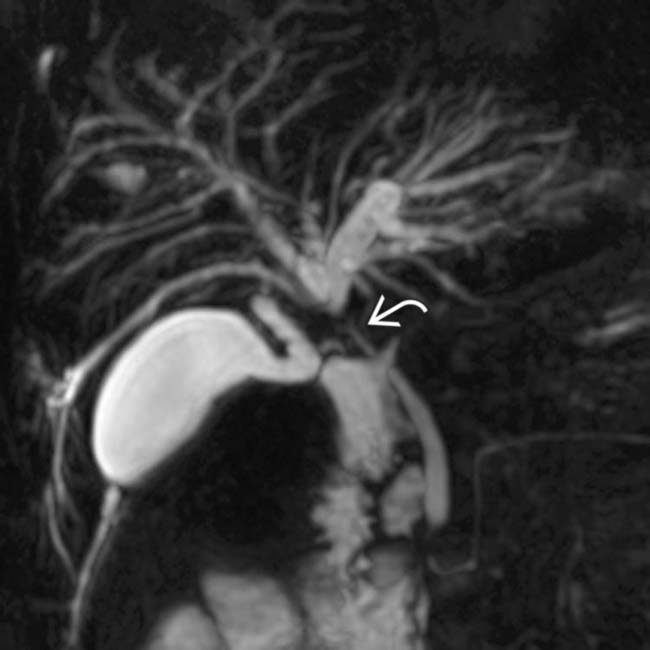
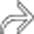 and mild intrahepatic biliary dilatation. The location of the stricture strongly suggested cholangiocarcinoma, but an elevated serum IgG4 and positive IgG4 staining at cytology indicated ISC.
and mild intrahepatic biliary dilatation. The location of the stricture strongly suggested cholangiocarcinoma, but an elevated serum IgG4 and positive IgG4 staining at cytology indicated ISC.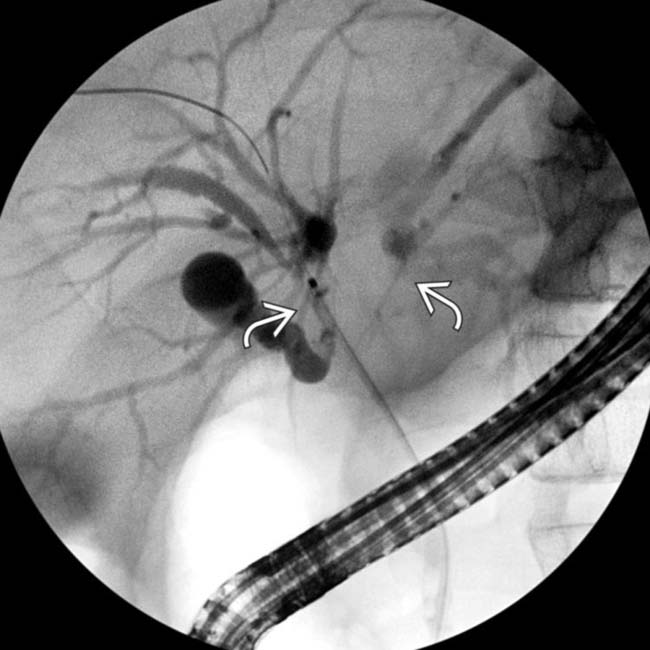
 extending into the proximal right and left hepatic ducts. A preoperative diagnosis of ISC may be difficult if imaging findings of AIP are absent.
extending into the proximal right and left hepatic ducts. A preoperative diagnosis of ISC may be difficult if imaging findings of AIP are absent.
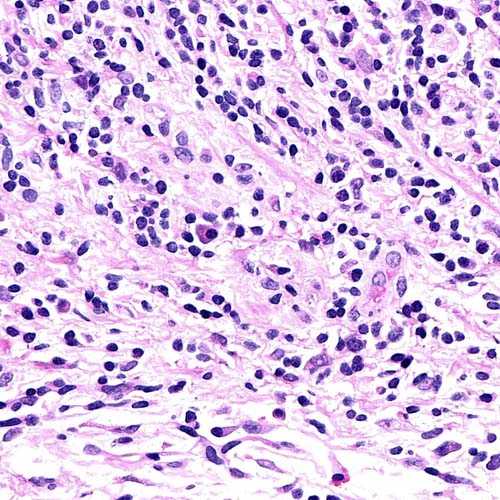
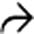 are demonstrated by immunohistochemical stain performed on a bile duct biopsy, confirming the diagnosis of IgG4-associated cholangitis. (Courtesy H. Wang, MD, PhD.)
are demonstrated by immunohistochemical stain performed on a bile duct biopsy, confirming the diagnosis of IgG4-associated cholangitis. (Courtesy H. Wang, MD, PhD.)