Absent spleen in virtually all patients
• Polysplenia (PSP) syndrome: Left isomerism or bilateral left-sidedness
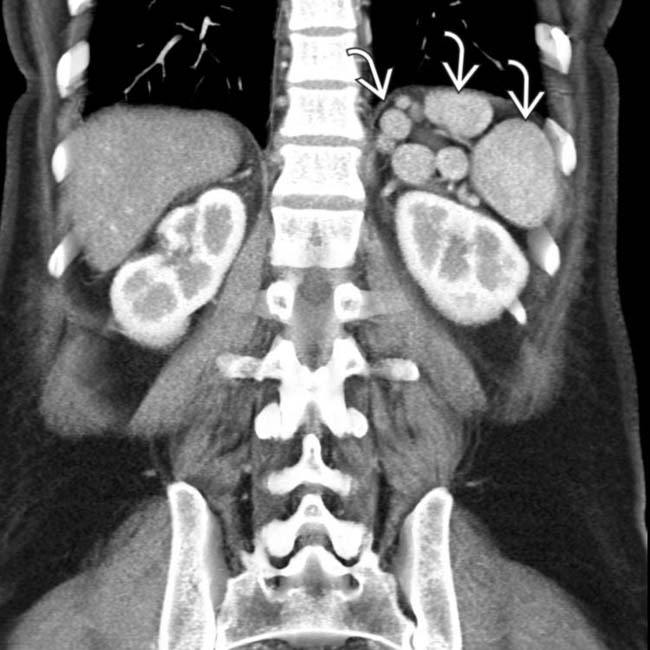
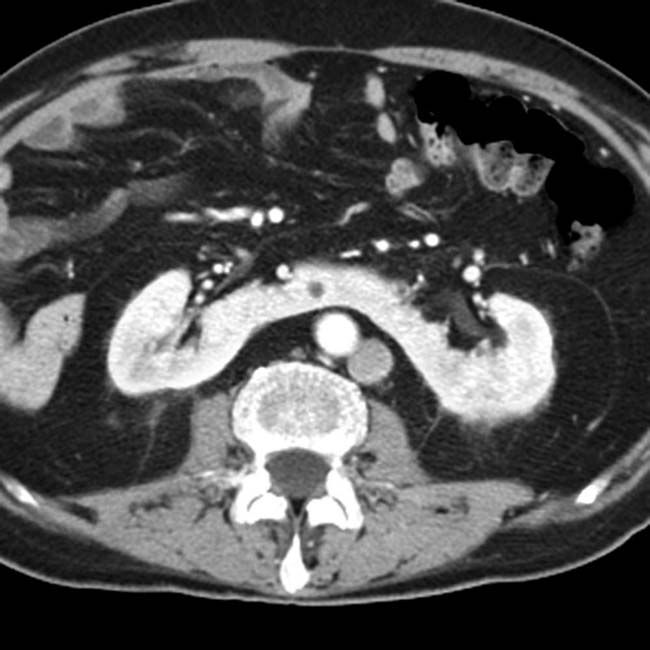
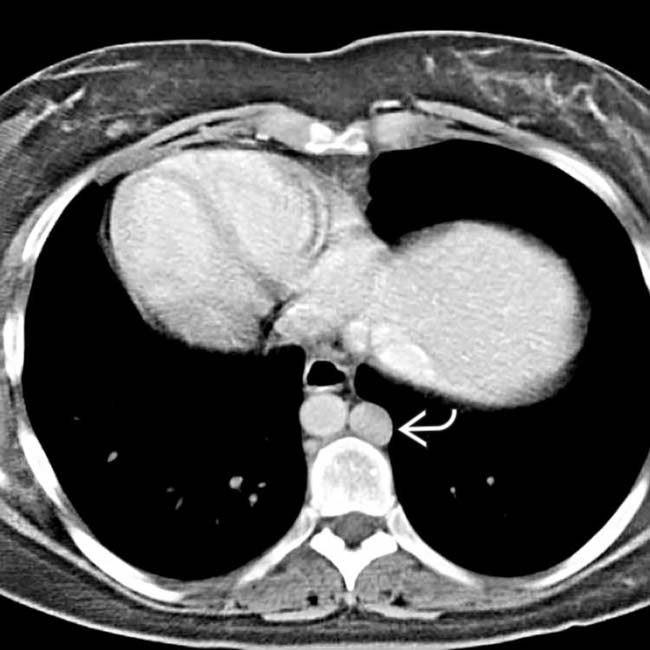
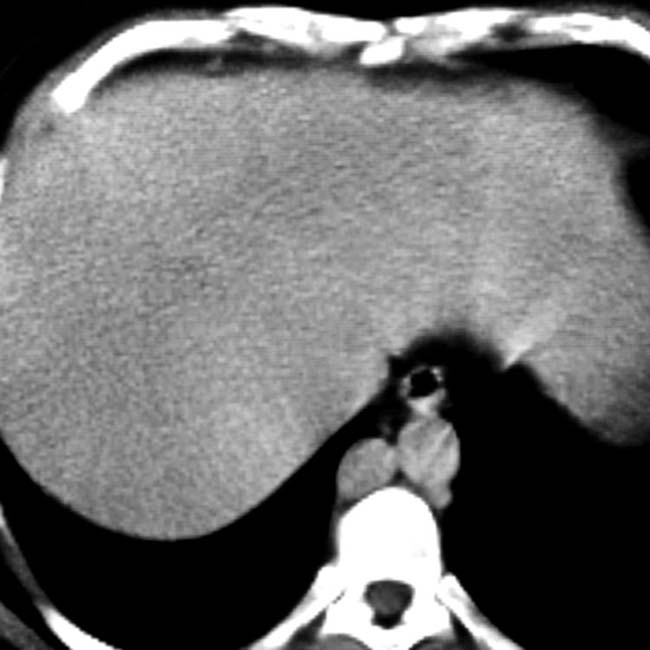
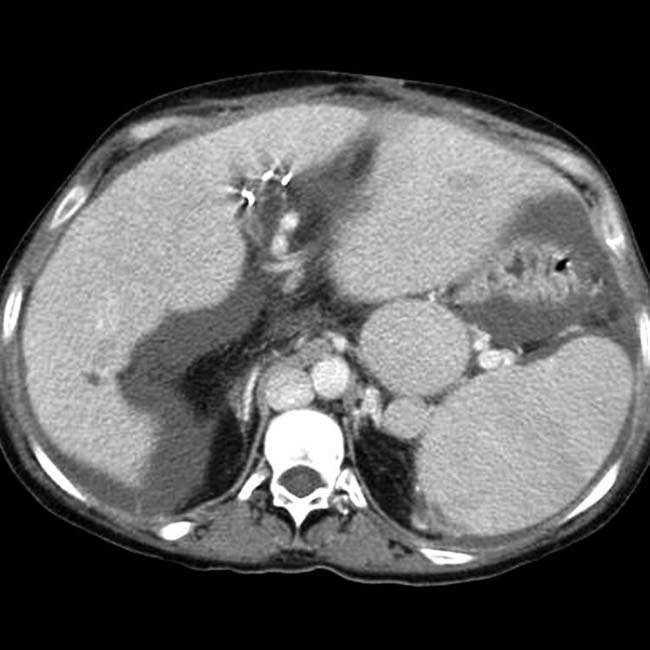
 in the left upper quadrant. The multiple spleens in PSP are typically in the left abdomen, but can rarely be on the right.
in the left upper quadrant. The multiple spleens in PSP are typically in the left abdomen, but can rarely be on the right.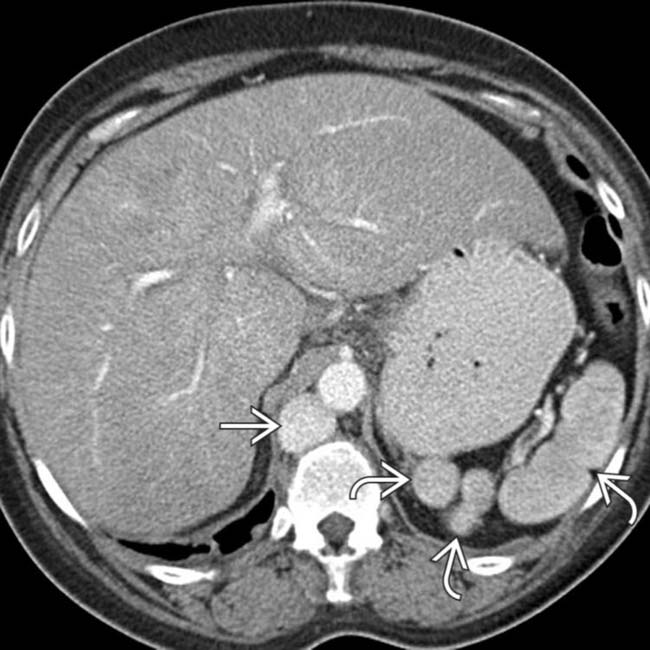
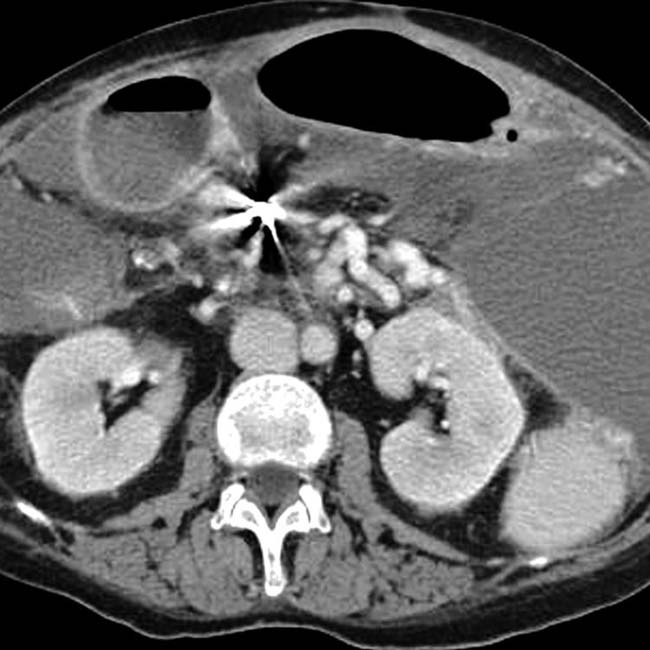
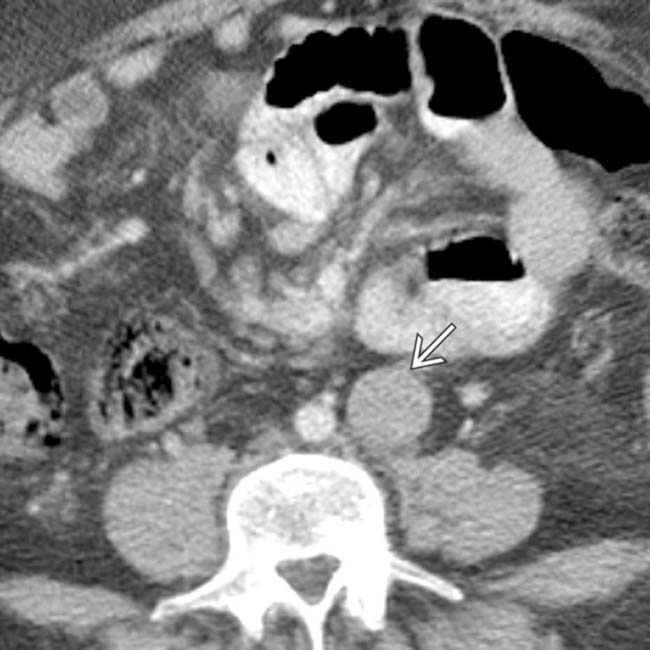
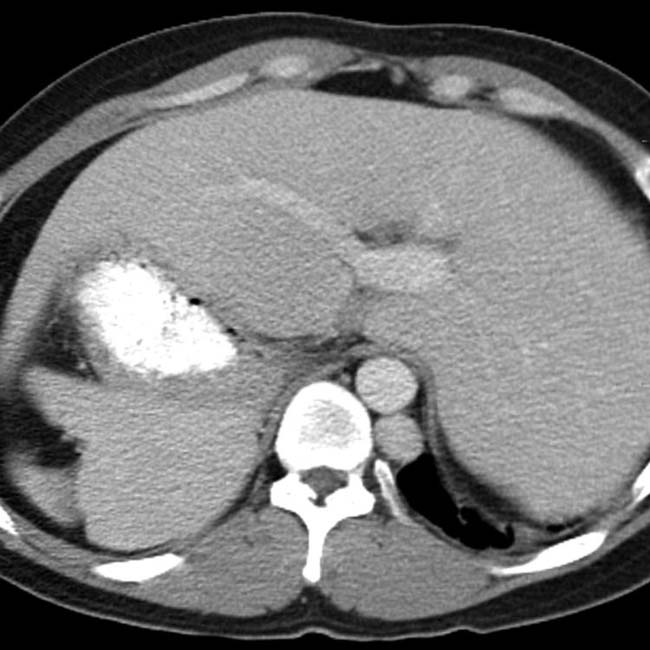
 and a dilated azygous vein
and a dilated azygous vein  to the right of the aorta. Azygous continuation of the inferior vena cava (IVC) is a very common abnormality in PSP syndrome.
to the right of the aorta. Azygous continuation of the inferior vena cava (IVC) is a very common abnormality in PSP syndrome.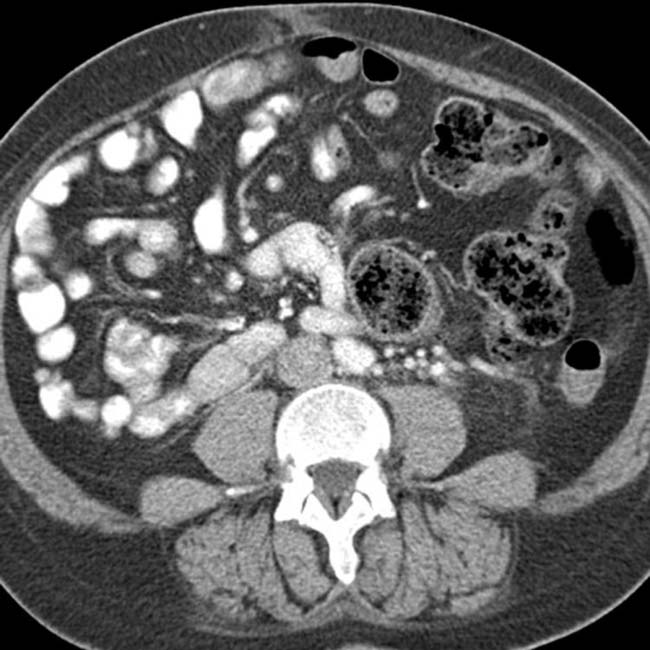
IMAGING
General Features
• Best diagnostic clue
• Key concepts
 ASP syndrome: Right isomerism or bilateral right-sidedness
ASP syndrome: Right isomerism or bilateral right-sidedness
 PSP syndrome: Left isomerism or bilateral left-sidedness
PSP syndrome: Left isomerism or bilateral left-sidedness
 ASP syndrome: Right isomerism or bilateral right-sidedness
ASP syndrome: Right isomerism or bilateral right-sidedness
– Situs ambiguus and bilateral right-sidedness; no fixed set of findings, abnormalities exist across a spectrum
– Cardiovascular
 Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (almost 100%), endocardial cushion defect (85%), single ventricle (51%), transposition of great vessels (58%), pulmonary stenosis or atresia (70%), dextrocardia (42%), mesocardia, ventricular septal defect, single atrioventricular valve, bilateral superior vena cava (SVC)
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (almost 100%), endocardial cushion defect (85%), single ventricle (51%), transposition of great vessels (58%), pulmonary stenosis or atresia (70%), dextrocardia (42%), mesocardia, ventricular septal defect, single atrioventricular valve, bilateral superior vena cava (SVC)
 Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (almost 100%), endocardial cushion defect (85%), single ventricle (51%), transposition of great vessels (58%), pulmonary stenosis or atresia (70%), dextrocardia (42%), mesocardia, ventricular septal defect, single atrioventricular valve, bilateral superior vena cava (SVC)
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (almost 100%), endocardial cushion defect (85%), single ventricle (51%), transposition of great vessels (58%), pulmonary stenosis or atresia (70%), dextrocardia (42%), mesocardia, ventricular septal defect, single atrioventricular valve, bilateral superior vena cava (SVC) PSP syndrome: Left isomerism or bilateral left-sidedness
PSP syndrome: Left isomerism or bilateral left-sidedness
– Situs ambiguus and bilateral left-sidedness: No fixed set of findings and abnormalities exist across a spectrum
– Cardiovascular
 Increased risk of complex cardiac anomalies, although less common with PSP than with ASP, accounting for better long-term survival
Increased risk of complex cardiac anomalies, although less common with PSP than with ASP, accounting for better long-term survival
 Transposition of great vessels (13%), double outlet right ventricle (13%), pulmonary valvular stenosis (23%), subaortic stenosis, or atresia
Transposition of great vessels (13%), double outlet right ventricle (13%), pulmonary valvular stenosis (23%), subaortic stenosis, or atresia
 Increased risk of complex cardiac anomalies, although less common with PSP than with ASP, accounting for better long-term survival
Increased risk of complex cardiac anomalies, although less common with PSP than with ASP, accounting for better long-term survival Transposition of great vessels (13%), double outlet right ventricle (13%), pulmonary valvular stenosis (23%), subaortic stenosis, or atresia
Transposition of great vessels (13%), double outlet right ventricle (13%), pulmonary valvular stenosis (23%), subaortic stenosis, or atresiaCLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
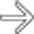
 located in the right upper quadrant and situs inversus. Note the reversed positions of the liver and stomach.
located in the right upper quadrant and situs inversus. Note the reversed positions of the liver and stomach.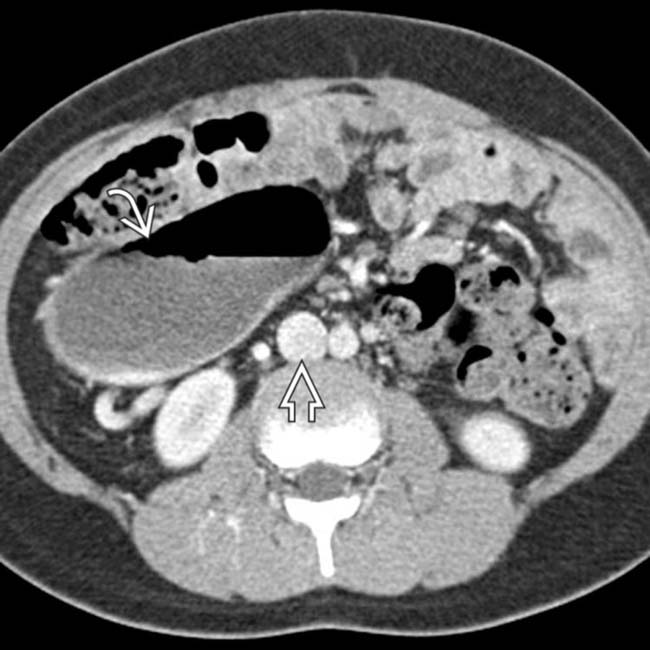
 . Note that the IVC
. Note that the IVC  is normally located on the right. The majority of the small bowel is on one side of the abdomen, in keeping with malrotation.
is normally located on the right. The majority of the small bowel is on one side of the abdomen, in keeping with malrotation.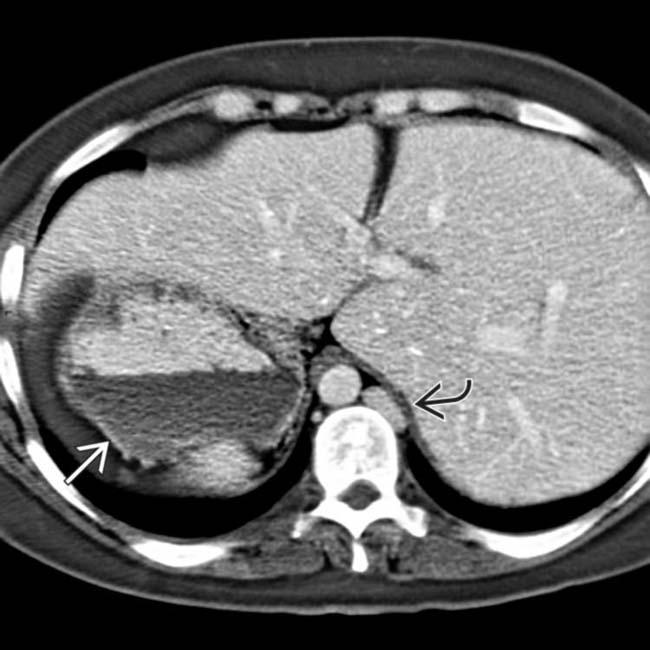
 and liver on the right-hand side. Note the left-sided IVC
and liver on the right-hand side. Note the left-sided IVC  .
.
 in the right upper quadrant along with abdominal situs inversus.
in the right upper quadrant along with abdominal situs inversus.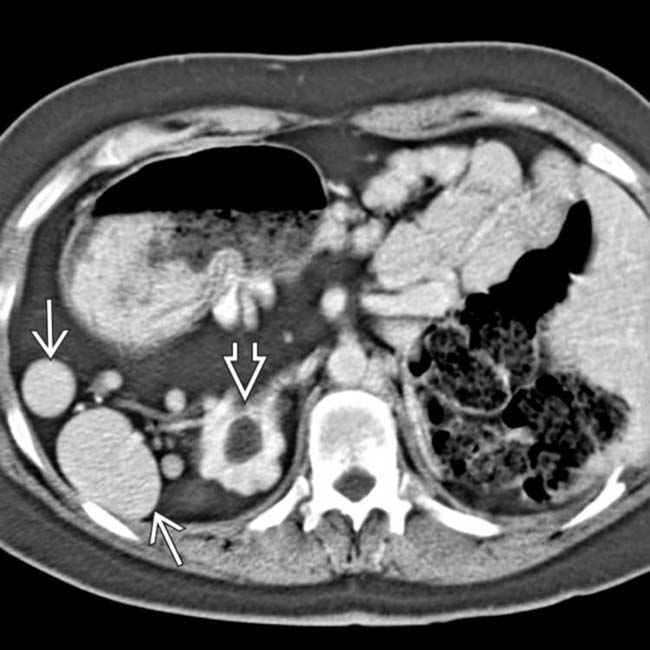
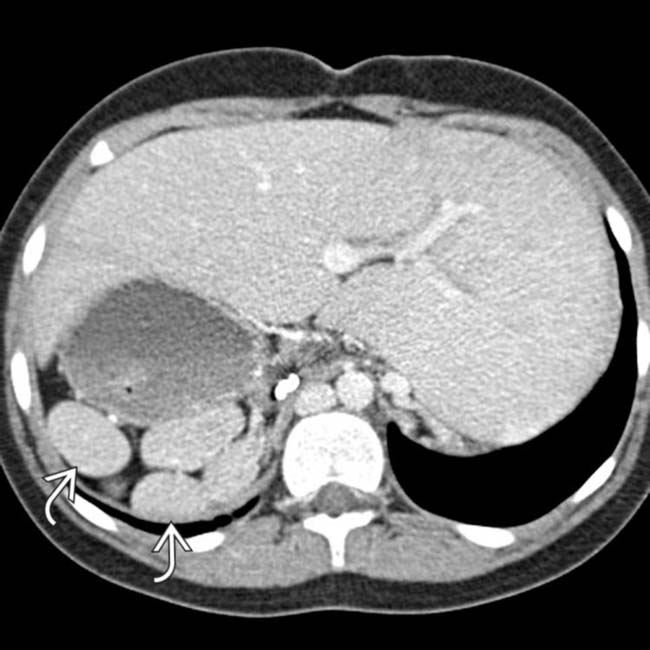
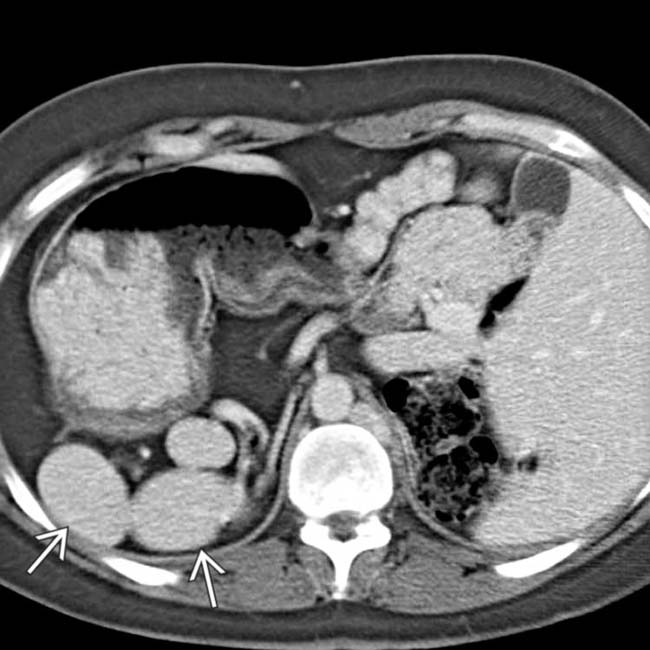
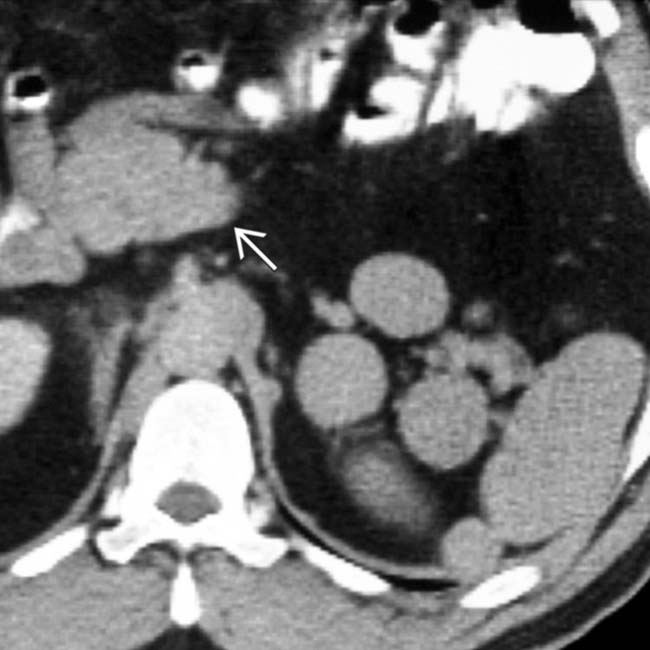
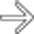 , situs inversus, and cystic disease of the kidneys
, situs inversus, and cystic disease of the kidneys  . This patient was 35 years old (patients with PSP are much more likely to reach adulthood than ASP).
. This patient was 35 years old (patients with PSP are much more likely to reach adulthood than ASP).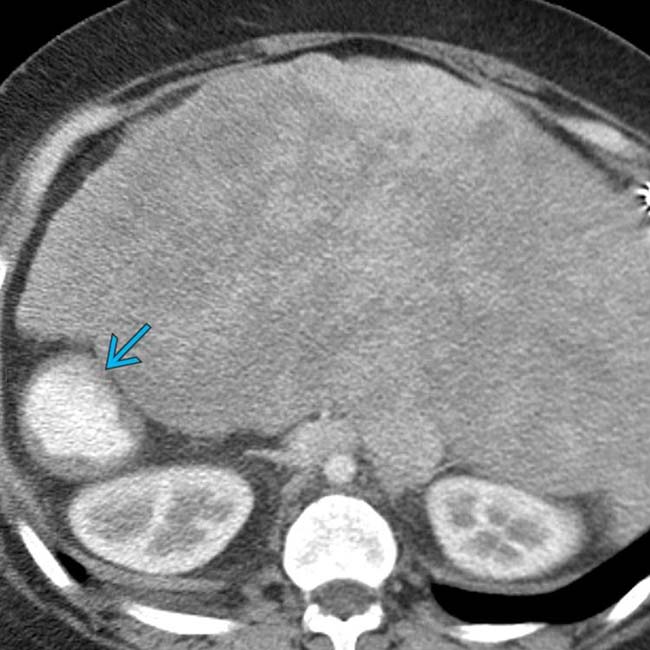
 . Extensive cardiac anomalies were also noted (not shown).
. Extensive cardiac anomalies were also noted (not shown).














 .
.






















































 .
.
 .
.
 .
.
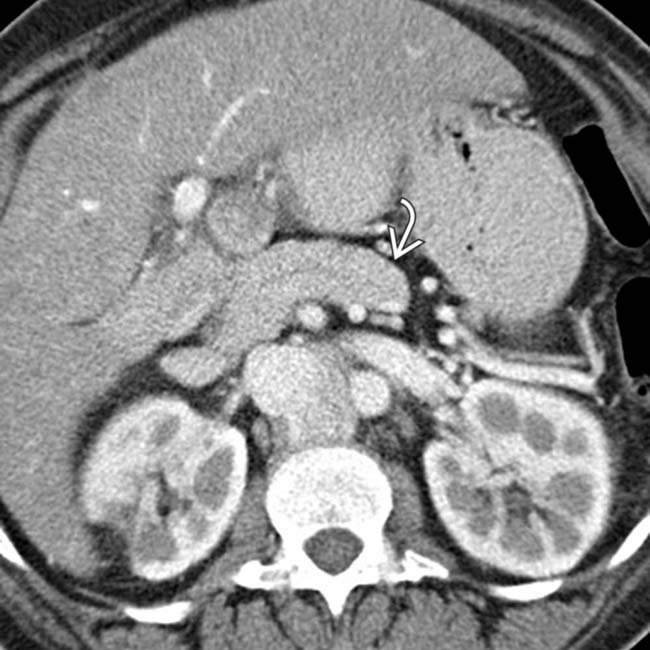
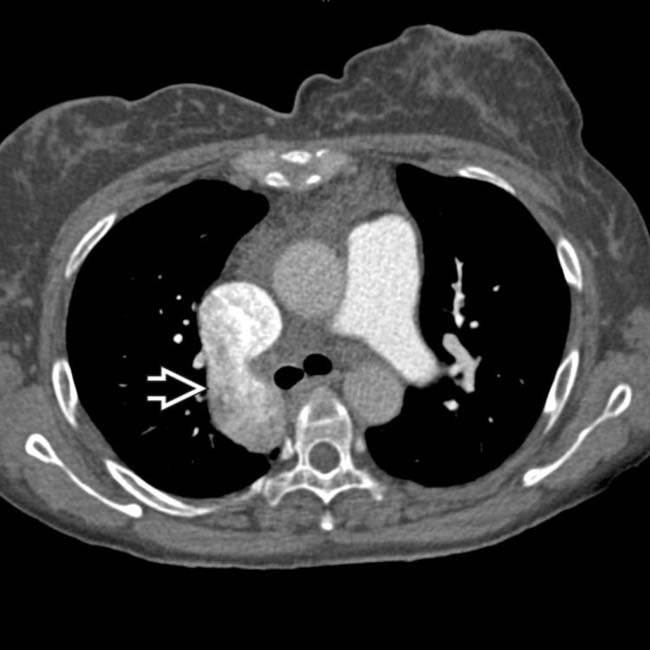
 , a commonly associated abnormality in PSP.
, a commonly associated abnormality in PSP.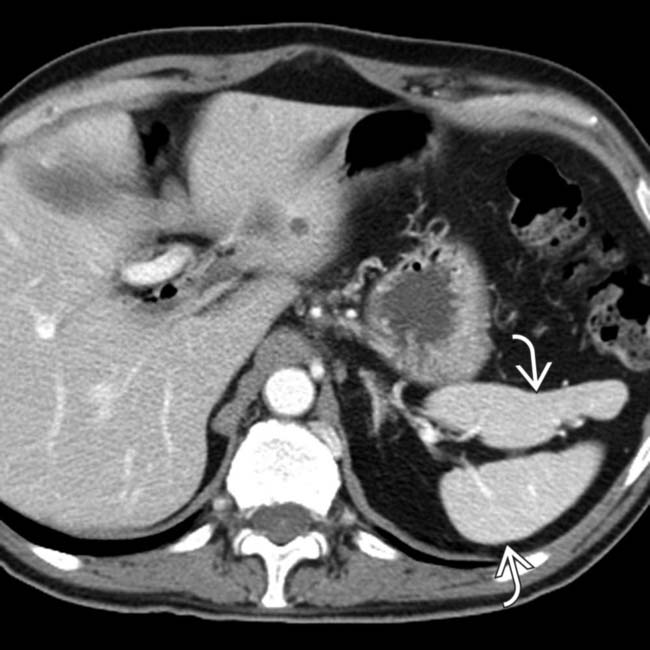
 in the left upper quadrant.
in the left upper quadrant.