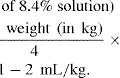CHAPTER 20 Apnoea
Background
An episode of apnoea may or may not be accompanied by bradycardia and cyanosis.
• infection — meningitis, septicaemia, pneumonia, necrotising enterocolitis, viral upper respiratory tract infection (especially respiratory syncytial virus, RSV)
Apnoea of prematurity
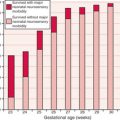
• Apnoea occurs because of brain-stem immaturity in babies less than about 34 weeks gestational age.
Management of apnoea
• Feed slowly, give small volumes, avoid gastric or abdominal distension; prone positioning may help.
1. If a baby’s apnoea is controlled on a standard dose and they are not tachycardic, then the baby is either receiving adequate drug or doesn’t need any.
2. If a baby is persistently tachycardic on theophylline, then they are toxic by definition, whatever the serum theophylline level might be.