 between the transverse duodenum and aorta at the site of the graft-aortic suture line
between the transverse duodenum and aorta at the site of the graft-aortic suture line  .
.
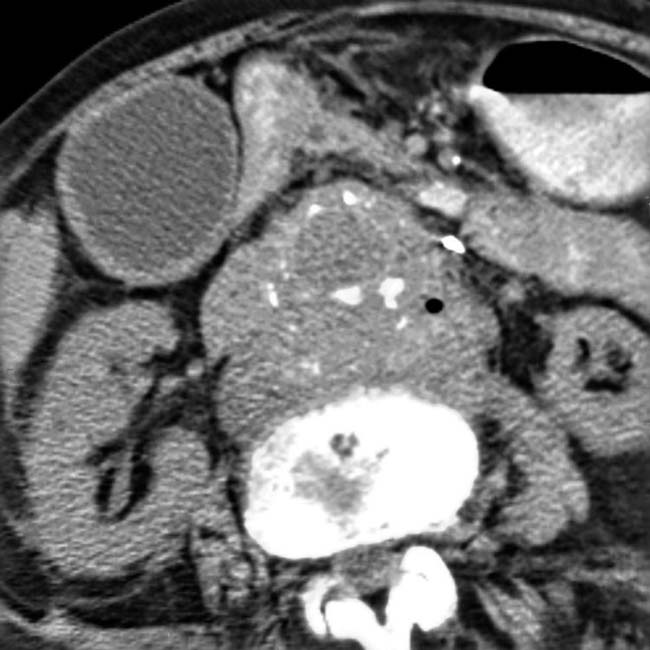
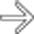
 wrapped around a synthetic graft. A gas collection is noted between the graft and aortic wall
wrapped around a synthetic graft. A gas collection is noted between the graft and aortic wall  , indicating infection or fistula. Note the soft tissue density surrounding the aorta and 3rd portion of duodenum
, indicating infection or fistula. Note the soft tissue density surrounding the aorta and 3rd portion of duodenum  .
.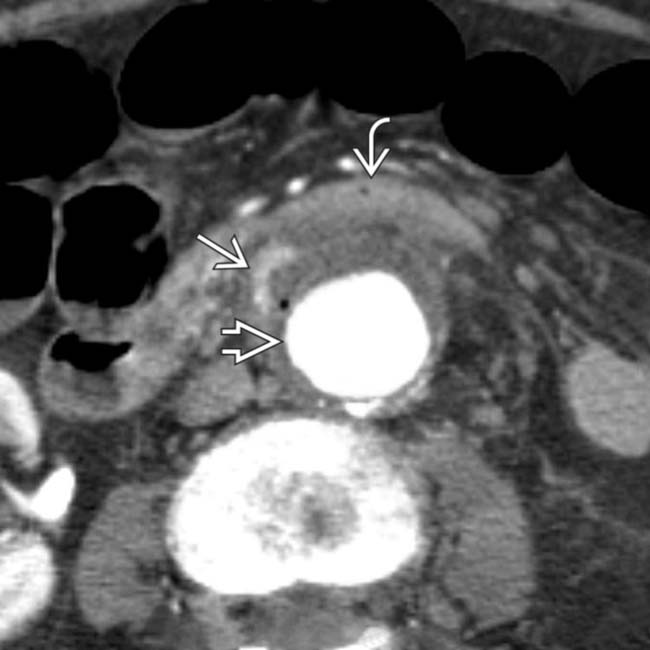
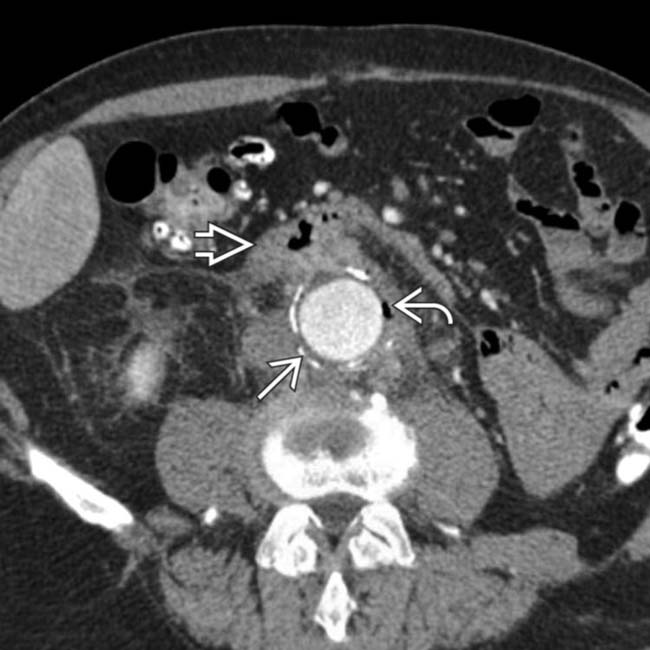
 . At the level of the 3rd portion of the duodenum, the duodenal wall
. At the level of the 3rd portion of the duodenum, the duodenal wall  appears to be adherent to the aorta. Note an enhanced focus
appears to be adherent to the aorta. Note an enhanced focus  that may represent active bleeding or inflammation.
that may represent active bleeding or inflammation.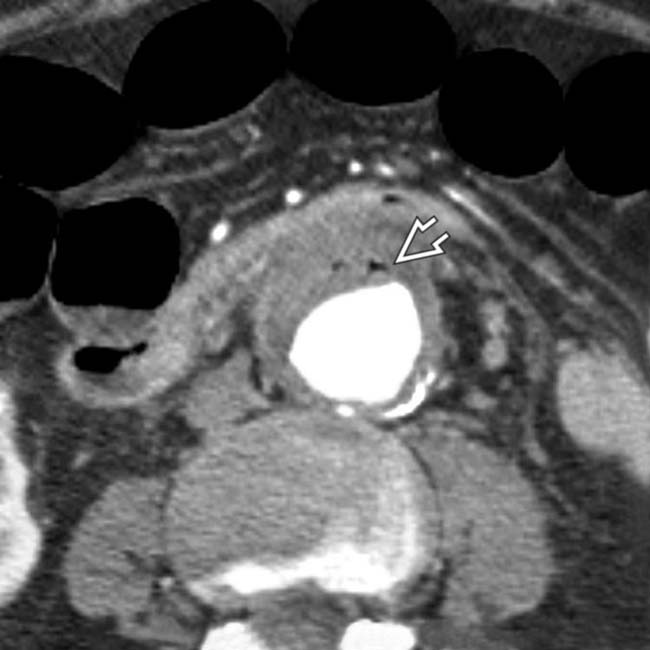
 ; aortoenteric fistula with underlying infection was surgically confirmed.
; aortoenteric fistula with underlying infection was surgically confirmed.
 and abnormal perigraft soft tissue indicating infection
and abnormal perigraft soft tissue indicating infection  . (Courtesy F. Hughes, MD.)
. (Courtesy F. Hughes, MD.)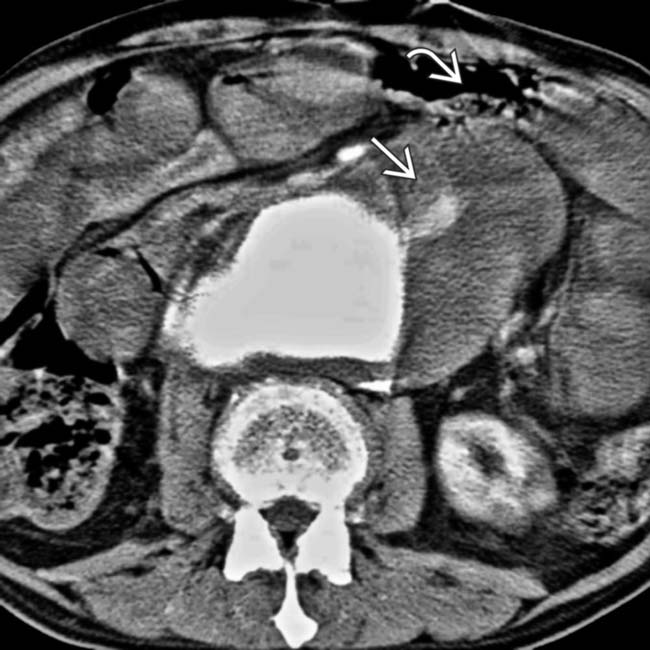
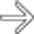
 . The transverse duodenum
. The transverse duodenum  is draped over the hematoma.
is draped over the hematoma.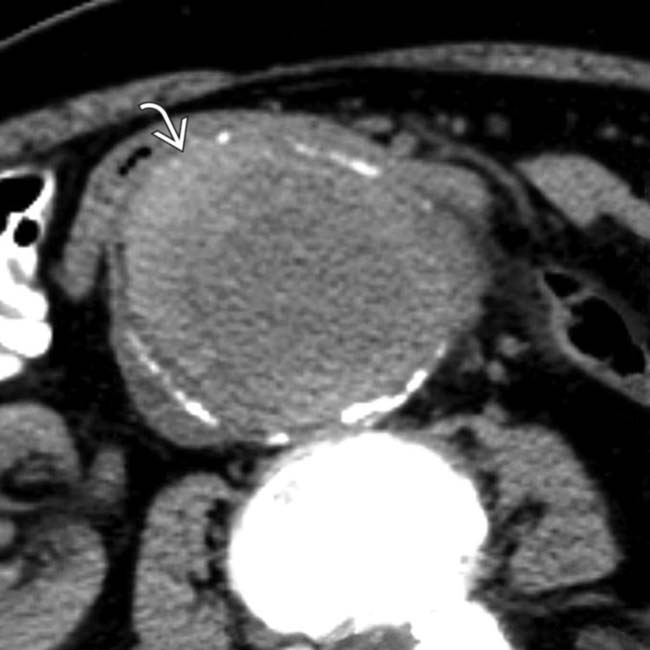
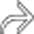 of higher density between the aortic intimal calcification and patent lumen.
of higher density between the aortic intimal calcification and patent lumen.
 within the thrombus, suggesting infection &/or communication to the bowel lumen. The 3rd portion of the duodenum stretches over and appears to adhere to the AAA
within the thrombus, suggesting infection &/or communication to the bowel lumen. The 3rd portion of the duodenum stretches over and appears to adhere to the AAA 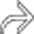 .
.





















 .
.
 .
.