10 Anterior Segment
Iris, ciliary body, and anterior chamber (AC) angle
Anatomy
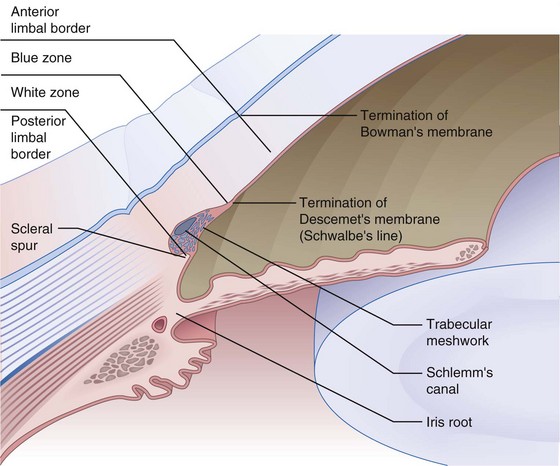
Limbus
Transition zone between cornea and sclera; 1–2 mm wide
Definitions
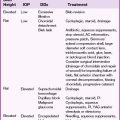
Disorders
Trauma
Hyphema
Treatment
Complications
Sickle cell and hyphema
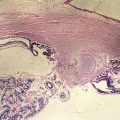
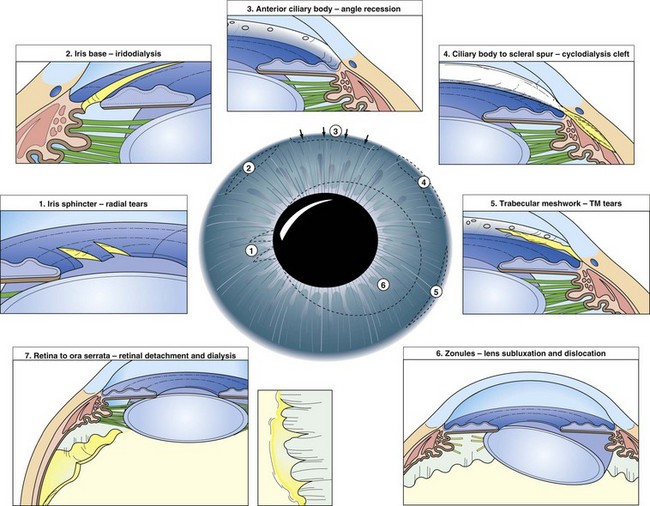
Iris and Angle Trauma (Figure 10-2)
Iridodialysis
tear in iris root; consider cosmetic contact lens or surgical repair if large or symptomatic
Open Globe/Intraocular Foreign Body
Full-thickness defect in cornea or sclera
Types of foreign bodies
Other Disorders
Iris Heterochromia
May be congenital or acquired, unilateral (heterochromia iridis) or bilateral (heterochromia iridum)
Pigment Dispersion Syndrome
Pigment liberation from posterior iris surface (due to contact with zonules)
Iridocorneal Endothelial (ICE) Syndrome
Nonhereditary, progressive abnormality of corneal endothelium
Unilateral, mostly women, occurs during middle age
Syndromes
common features of iris distortion, corneal edema, secondary angle-closure glaucoma
Iris Nodules
Iris Tumors
Perform transillumination to differentiate cyst from solid tumor
Melanocytosis
Congenital ocular: usually unilateral with diffuse iris nevus causing iris heterochromia
Malignant Melanoma
Elevated, vascular, darkly pigmented or amelanotic lesion; usually located inferiorly
Lens
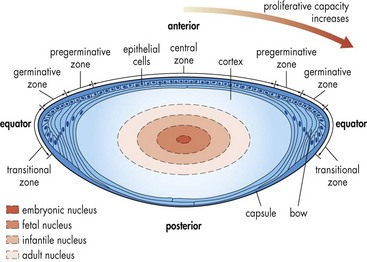
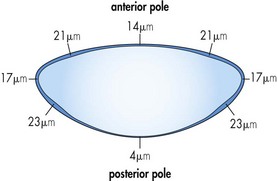
Anatomy/Physiology (Figures 10-3 and 10-4)
Lens capsule
Properties of the crystalline lens
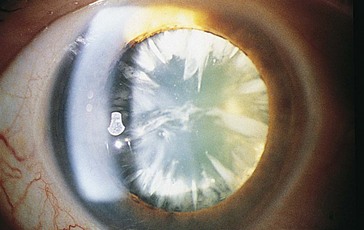
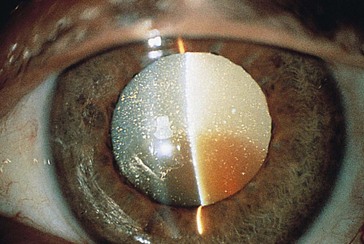
Cataracts
Acquired Cataracts
Classified by location or etiology
Cortical
lens fiber fragments, degenerated protein, liquefaction
Nuclear sclerosis
Posterior subcapsular (PSC)
Traumatic and toxic cataracts
Cataracts associated with systemic disease
Lens Capsule Abnormalities
Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome (PXS)
Material produced by lens epithelial cells and extruded through lens capsule
Appears to be an ocular sign of systemic elastosis; also found in conjunctiva, skin, lung, and liver
Usually elderly, Caucasian females; increased incidence in Scandinavians and with increasing age
Ectopia Lentis
Findings
decreased vision, astigmatism, monocular diplopia, iridodonesis, phacodenesis, malpositioned lens
Homocystinuria (AR)
Surgery
Nd : YAG Laser
Vitreolysis
Disrupt anterior vitreous face in aphakic and pseudophakic eyes with malignant glaucoma
Cataract Surgery
IOL Calculations (see Ch. 1, Optics)
Most accurate formulas according to axial length
A scan
Ultrasound waves travel faster through lens (1640 m/s) than either aqueous or vitreous (1532 m/s)
To correct any AL, use the formula: ALcorrected = ALmeasured × (Vcorrect/Vmeasured)
Average measurements
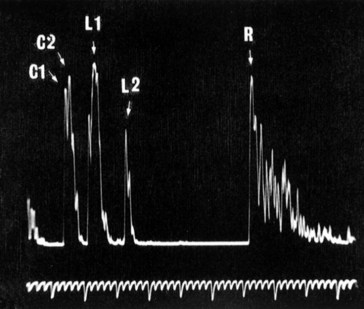
Contact A scan
5 spikes corresponding to beam reflection from interfaces: cornea, anterior lens surface, posterior lens surface, retina, sclera (Figure 10-7)
Keratometry in patient following refractive surgery
Viscoelastic Device (Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Device [OVD])
Variety of clear gel-like materials composed of sodium hyaluronate and chondroitin sulfate
Classification
Examples: Healon, Healon GV, Amvisc, Amvisc Plus, Provisc
Phacodynamics
Vacuum (aspiration level)
negative pressure created at tip by pump (0–500 mmHg); holds material onto occluded tip
Pump systems
Complications of Cataract Surgery
Retrobulbar Hemorrhage
May occur following retrobulbar injection or trauma; risk of CRAO as orbital pressure rises
Central Anesthesia Following Retrobulbar Block
Agent spreads along meningeal cuff of optic nerve to enter CSF
Iris Prolapse During Phaco
Wound too large or too posterior, bottle too high, posterior pressure, suprachoroidal hemorrhage
Expulsive Suprachoroidal Hemorrhage
May occur during intraocular surgery or days later; incidence of 0.5%
Uveitis-Glaucoma-Hyphema (UGH) Syndrome
Due to repeated trauma to angle structures and iris by IOL; scarring and degeneration occur
Anterior Capsular Contraction Syndrome (Capsular Phimosis)
Due to small capsulorhexis with retention of lens epithelial cells
CME (Irvine-Gass Syndrome)
More common with intracapsular (ICCE) than extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE)
50% angiographically for ICCE vs 15% for ECCE
Clinically significant (visual loss) in <1% of patients with ECCE
Review Questions (Answers start on page 369)
Abelson MB. Allergic Diseases of the Eye. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2001.
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Lens and Cataract, vol 11. San Francisco: AAO; 2012.
Boruchoff SA. Anterior Segment Disorder: A Diagnostic Color Atlas. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2001.
Elander RE, Rich LF, Robin JB. Principles and Practice of Refractive Surgery. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1997.
Jaffe NS, Jaffe MS, Jaffe GF. Cataract Surgery and Its Complications, 6th edn. St Louis: Mosby; 1997.
Mackie IA. External Eye Disease. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2003.
Watson P, Hazleman B, Pavesio C. Sclera and Systemic Disorders. Philadelphia: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2003.

 AR,
AR, 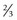 AD
AD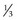 sporadic,
sporadic, 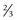 AR
AR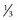 AD,
AD,  sporadic
sporadic sporadic,
sporadic,  AD
AD