Chapter 11 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in Skeletally Immature Patients
INTRODUCTION
Prior to the mid-1980s, mid-substance anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries in the skeletally immature athlete were believed to be rare.25 More recently, ACL injury has been reported in 10% to 65% of pediatric knees with acute hemarthroses.19,42 Although the true incidence and prevalence of ACL tears in the pediatric population have not been established, these injuries are now being recognized with increasing frequency.42,44 Explanations for this apparent change may include improved ability to diagnose injury by physical examination and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as well as changes in the activity patterns of young athletes. The puzzling question facing clinicians centers on whether youngsters of today are training and conditioning to the point that the ACL has become more susceptible to injury.
Previously, the concern for iatrogenic growth disturbance in children prevented the routine use of anatomic ACL reconstruction that has proved successful in adults. Alternative surgical treatment options include primary repair, extra-articular reconstruction, and transepiphyseal intra-articular reconstruction. Even though these injuries are occurring with increasing frequency, no unanimity exists concerning the appropriate and safest treatment. There are no long-term studies to help determine the optimal management approach. The few studies that have followed skeletally immature patients to physeal closure after transphyseal ACL reconstruction have documented growth comparable with that of age-matched controls without surgery.1,27,39
INDICATIONS
Graf and associates11 reported poor results at 15 months after injury, with new meniscal tears and episodes of instability in seven of eight skeletally immature patients who did not undergo reconstruction or activity limitations after ACL injury. Similarly, in a series of 18 skeletally immature patients examined an average of 51 months after complete ACL tear, Mizuta and colleagues35 found that all patients had symptoms, 6 had meniscal tears, and 11 had developed radiographic changes. Janarv and coworkers16 found that 10 of 23 skeletally immature patients treated with rehabilitation eventually needed reconstruction. McCarroll and associates29 reported superior results with surgical management of complete ACL tears in prepubescent and junior high school patients compared with patients receiving conservative treatment. Of 16 prepubescent patients treated nonoperatively, 9 ceased sports participation, 4 sustained at least one reinjury, and only 3 were able to return to sport. In a separate group of 75 junior high school athletes with mid-substance tears, McCarroll and colleagues30 reported that 37 of 38 patients who were initially treated nonoperatively had instability and 27 (71%) developed meniscal tears. Overall, 92% (55 of 60) of those treated with reconstruction returned to play.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
In the pubescent patient in whom a final growth spurt is anticipated, a soft tissue graft can be used. The exact risk of growth plate injury is unknown but can be extrapolated from the literature on trauma and fractures involving the growth plates around the knee.8 If parents are unwilling to accept the risk of growth plate injury, reconstruction should be delayed until the physes are closed.
CLINICAL EVALUATION
History
A tear of the ACL can result from an impact to the knee or, more commonly, a noncontact twisting or landing injury. The timing of injury, either acute or chronic, should be noted. Knee effusion, pain, and ability to bear weight are important factors in diagnosing an ACL tear. An audible pop heard at the time of injury may be reported. An acute hemarthrosis, particularly in the first 6 to 12 hours after injury, should raise concern for ACL injury. Stanitski and coworkers42 found that 47% of preadolescents with a knee effusion had an ACL injury.
Physical Examination
The most important component in diagnosing pediatric knee injuries is the physical examination.41 The presence of an effusion should be noted. Palpation of the joint line and physeal plates should be performed. Active and passive motion should be documented. Varus and valgus laxity should be checked in full extension and at 30° of flexion. Lachman testing should be assessed for magnitude. Pivot shifting may be quite uncomfortable in the acute setting and is not recommended. If the Lachman examination is positive acutely, the pivot shift test can be deferred until the examination under anesthesia if surgical intervention is chosen. Findings should always be compared with those in the contralateral knee. The patient should be assessed for generalized laxity with the degree of knee hyperextension noted.
PREOPERATIVE PLANNING
Skeletal Maturity
The patient’s level of skeletal maturity should be defined preoperatively. It is generally assumed that girls grow until age 14 ± 1 years and boys until age 16 ± 1 years2; however, age may not be the best indicator of potential growth. Peak growth velocity occurs between the ages of 10 to 11 years for girls and 13 to 14 years for boys. Closure of the triradiate cartilage, which can be seen on a standard radiograph of the pelvis, typically marks the end of peak growth velocity.26 The patient can be assessed physiologically for signs of development, as noted by Tanner and Davies.43 Age at onset of menses can be useful in females. After menarche, girls enter a deceleration phase of growth and typically reach skeletal maturity 18 months later. Family height can be used as an approximate estimate of growth potential as well. The patient can be assessed radiographically to determine skeletal maturity using the Risser sign on the pelvis.37 The Risser sign is a radiographic measurement based on ossification of the iliac apophysis, beginning on the lateral aspect and progressing medially. Divided into four quadrants, the Risser sign proceeds from 0 (no ossification) to Risser 4, in which all four quadrants show ossification of the apophysis. Patients with Risser 0 or 1 have a significant amount of growth remaining, and the Risser 4 patient is skeletally mature. Bone age is another method to determine skeletal maturity by obtaining a radiograph of the hand and wrist and comparing it with the standards in the Gruelich and Pyle atlas.12 The “rule of thirds” suggests that the distal femur and proximal tibia grow an average of 0.9 cm and 0.6 cm, respectively, per year of growth remaining.32 Limb lengths and bilateral lower extremity alignment should be measured and any differences noted.
Associated Intra-articular Pathology
Previous studies have shown that 20% to 100% of pediatric patients who sustain ACL injuries have a concomitant meniscal injury.11,34 Millett and associates34 found that the incidence of medial meniscus tears increases significantly with chronic ACL insufficiency. Of the 22 patients who underwent surgery more than 6 weeks after injury, 72% had associated meniscal tears. If unstable meniscus tears exist, aggressive management is indicated. Every attempt should be made to salvage the meniscus in children and adolescents. Meniscectomy in this age group carries an even more ominous prognosis.18 Manzione and colleagues28 evaluated the results of partial and total meniscectomy in 20 patients with a mean age of 15 years (range, 5–15 yr). At 6-year follow-up, 16 knees had grade I osteoarthritis and 4 had grade II or III changes. Osteochondral injuries may require débridement, drilling, and/or stabilization at the time of ACL reconstruction.
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Primary Repair
DeLee and Curtis7 reported on three patients who underwent primary ACL repair through sutures tied across the physis. At 21 months follow-up, all had clinical laxity and two of the three had episodes of giving-way. Engebretsen and coworkers10 reviewed eight patients 3 to 8 years after primary repair and found that all experienced a decrease in activity level and five of the eight demonstrated instability on clinical examination. Grontvedt and associates13 also noted that primary repair of the ACL in the skeletally immature patient had poor results, similar to those found in adults.
Physeal-Sparing Techniques
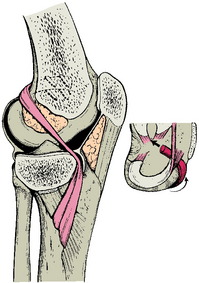
Early reports of physeal-sparing intra-articular reconstruction describe using a hamstring autograft left attached distally, passed into the knee under the anterior portion of the medial meniscus, and fixed to the lateral femoral condyle with staples in the over- the-top position on the femur6 (Fig. 11-1). This technique is nonanatomic and does not reproduce the normal knee ligament kinematics. In a report of nine patients at 36.5 years follow-up, all had a 1+ Lachman and 1+ anterior drawer test. Six of nine patients returned to sports, but with bracing and precautions. No growth disturbances were reported.6
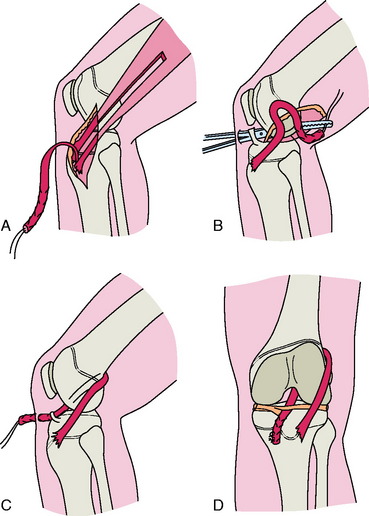
More recently, Kocher and colleagues21 described Micheli and coworkers’ technique,33 which uses a combined intra- and extra-articular reconstruction and an autogenous iliotibial band (ITB) without violation of the physes. An incision is made obliquely from the lateral joint line to the superior border of the ITB. The ITB graft is harvested free proximally and left attached to Gerdy’s tubercle distally and tubularized with a whipstitch. Arthroscopy of the knee is then performed through standard portals. The free end of the graft is brought into the knee in the over-the-top position posteriorly. A second incision is made over the proximal medial tibia. Dissection is carried down to the periosteum, and a curved clamp is passed from this incision into the joint under the intermeniscal ligament. The graft is then brought through the knee, under the intermeniscal ligament anteriorly, and out through the tibial incision. The graft is fixed to the femur with the use of sutures to the lateral femoral condyle at the insertion of the lateral intermuscular septum with the knee in 90° of flexion and external rotation. On the tibial side, the graft is sutured to the periosteum of the proximal tibia just distal to the physis with the knee flexed 20°, and tension is applied to the graft (Fig. 11-2).
Critical Points OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Micheli and coworkers33 reported the results of 17 patients with an average chronologic age of 11 years and a mean bone age of 10 years (range, 2–13 yr) who underwent the physeal-sparing reconstruction described previously. The mean follow-up was 66 months. All knees were subjectively and objectively stable by KT-1000 testing. No child developed a growth disturbance.
A study of Micheli and coworkers’ technique33 by Kocher and associates20 reported on 44 skeletally immature patients (Tanner stage 1 or 2) with a mean chronologic age of 10.3 years and a mean skeletal age of 10.1 years. Functional outcome, graft survival, and growth disturbance were evaluated at a mean of 5.3 years (range, 2–15.1 yr) after surgery. Lachman examination was normal in 23 patients, nearly normal in 18 patients, and abnormal in 1. Two patients required revision reconstruction for graft failure at 4.7 and 8.3 years postoperatively. No patient had an angular deformity or limb length discrepancy clinically or radiographically. The authors strongly recommend this technique for Tanner stage 1 and 2 patients requiring ACL reconstruction.
Transepiphyseal Reconstruction
Critical Points AUTHORS’ PREFERRED TECHNIQUES
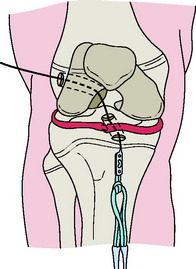
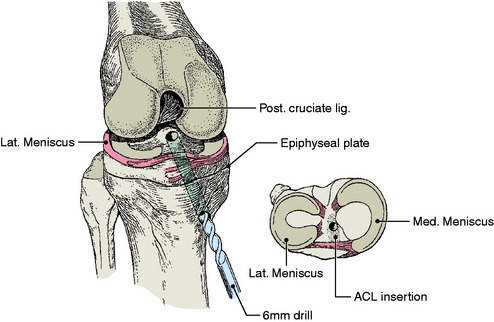
The affected leg is positioned with the hip flexed approximately 20°. Fluoroscopy is positioned on the side of the operating room table opposite the injured knee, and the femoral and tibial growth plates are visualized in both planes prior to preparing and draping. An oblique incision is made over the hamstring tendons. The semitendinosus and gracilis tendons are harvested and then doubled. Arthroscopy of the knee is accomplished in a standard fashion. With the C-arm in the lateral position, the point of the guidewire is positioned on the skin over the lateral femoral condyle, corresponding to the location of the footprint of the ACL. A small lateral incision is made, and the ITB is split longitudinally. The guidewire is advanced across the femoral epiphysis; the C-arm is used to confirm that the guidewire is not angulated in the anteroposterior or inferosuperior planes. The guidewire is visualized in the intercondylar notch arthroscopically, entering the joint at the proximal femoral footprint. A second guidewire is then inserted into the anteromedial tibia at the level of the epiphysis. The guidewire is advanced, clearing the tubercle anteriorly and entering the joint at the free edge of the lateral meniscus on the tibia (center of the footprint of the ACL). Tendon sizers are used to measure the diameter of the tendon graft, and the smallest appropriate reamer and EndoButton are chosen. The EndoButton and tendons are pulled up through the tibia and out the femoral hole with a suture. An EndoButton washer is placed over the EndoButton and the graft is placed under tension, pulling the EndoButton and washer to the surface of the lateral femoral condyle. With the knee in 10° of flexion, the graft is secured distally over a screw and post placed medial to the tubercle and distal to the tibial physis (Fig. 11-3).
Two series have been reported using transepiphyseal ACL reconstruction in skeletally immature patients. Guzzanti and coworkers15 reported the results of this technique in five preadolescent patients (Tanner stage 1) with ACL injuries. The hamstring graft was left attached to the tibia, a transepiphyseal tibial tunnel was used, and the graft was looped over a staple placed at the femoral attachment of the ACL. At a minimum follow-up of 4 years, KT-1000 testing revealed an average side-to-side difference of 1.8 mm. Anderson1 reported his results using the technique described previously in a series of 12 patients (Tanner stage 1–3). At a mean follow-up of 4.1 years (range, 2–8.2 yr), KT-1000 testing revealed a mean side-to-side difference of 1.5 mm. In both series, there were no reported growth abnormalities and no subjective or objective evidence of recurrent instability at a minimum of 4 years follow-up.
Partial Transphyseal Reconstruction
Lipscomb and Anderson25 reported a series of 24 (21 males and 3 females) patients aged 12 to 15 years who underwent partial transphyseal reconstruction. Eleven patients had a completely open physis and 13 had a partially open physis. Skeletal age was not recorded. A hamstring autograft was placed across the tibial physis (6.4-mm tunnel) and exited out through the femoral epiphysis. In addition, an extra-articular reconstruction of the lateral side was routinely added to prevent rotational instability. At an average follow-up of 35 months, the side-to- side difference on Lachman testing averaged 1.8 mm and all patients denied swelling or giving-way. One patient developed a 2.0-cm limb length inequality as a result of stapling across the femoral and tibial physes.
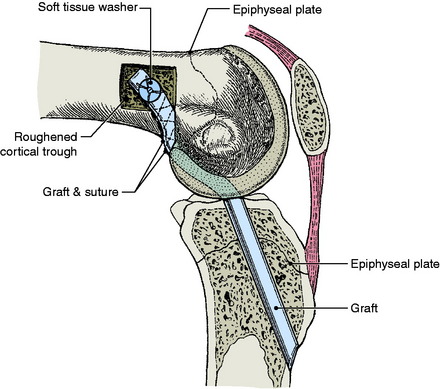
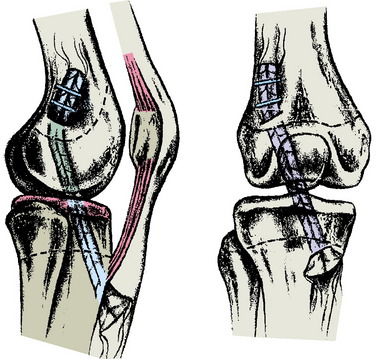
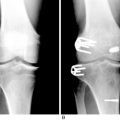
Andrews and colleagues3 performed an ACL reconstruction in eight adolescents using either a (7-mm) fascia lata or Achilles tendon allograft placed centrally across the tibial physis and secured to the femur in the over-the-top position. At skeletal maturity, there were no detected limb length discrepancies (Figs. 11-4 and 11-5).
Lo and coworkers27 reported on five patients with an average age of 12.9 years (range, 8–14 yr) who underwent partial transphyseal reconstruction using either a hamstring or a patella tendon autograft passed centrally through the tibial physis (6 mm) to an over-the-top position on the femur. At an average follow-up of 7.4 years, scanograms revealed no angular deformities or leg length discrepancies.
Transphyseal Reconstruction
Aronowitz and associates5 reported on 19 skeletally immature patients ages 11 to 15 years who underwent allograft reconstruction through drill holes in the distal femur and proximal tibia (Fig. 11-6). All patients had a skeletal age of at least 14 years. At an average of 25 months after surgery (range, 12–60 mo), there were no significant leg length discrepancies or angular deformities determined by scanogram and anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the femur and tibia. The mean Lysholm knee score was 97 (range, 94–100) and the mean KT-1000 arthrometer side-to- side difference was 1.7 mm (range, 0.0–3.0). All patients were satisfied with the results of surgery, and 16 of 19 patients returned to the same sport they were participating in before the injury.
McIntosh and colleagues31 reported on 16 patients (11 males and 5 females) who underwent transphyseal ACL reconstruction. Each patient was followed until skeletal maturity, with a mean clinical follow-up of 41.1 months (range, 24–112 mo). At last follow-up, the mean leg length discrepancy measured 0.62 cm (range, 0.2–1.5 cm). Clinical or radiographic evidence of malalignment was not present in any patient. At follow-up, the mean modified Lysholm score was 98.8 (range, 94–100) and the majority of patients (87.5%) had returned to their previous level of activity.
Shelbourne and coworkers39 reported a series of 16 patients with open growth plates who underwent transphyseal ACL reconstruction using a patellar tendon autograft. At the time of surgery, 7 patients were Tanner stage 3 and 9 were Tanner stage 4. The authors noted that the surgical technique was meticulous for placing the bone plugs proximal to the physes and not overtensioning the graft. Clinical follow-up (mean, 3.4 yr after surgery) showed that no patients had growth plate disturbances, angular deformities, or leg length discrepancies. All patients returned to competitive sports after surgery.
Most recently, Kocher and associates23 reported on 61 knees in 59 skeletally immature pubescent adolescents (Tanner stage 3) who underwent transphyseal ACL reconstruction using hamstring autograft and metaphyseal fixation. Functional outcome, graft survival, and growth disturbances were evaluated at a mean of 3.6 years after surgery. Two patients required revision for graft failure. The Lachman was normal in 51 knees and nearly normal in 8 knees and no patient had an abnormal pivot shift test. The mean increase in height was 8.2 cm (range, 1.2–25.4 cm) from the time of surgery and no angular deformities or limb length inequalities were detected clinically.
These and other reports consistently support the use of transphyseal ACL reconstruction in Tanner stage 3 and 4 adolescents. Overall, few growth disturbances have been reported after transphyseal reconstruction. Koman and Sanders24 reported a case of a 14-year-old male who developed a distal femoral valgus deformity requiring osteotomy and contralateral epiphysiodesis after transphyseal reconstruction with a semitendinosus autograft. The skeletal age of the patient was unknown. The tibial tunnel diameter was unknown, but a 9-mm femoral tunnel was drilled. Cancellous bone plugs were inserted into both tunnels and the tendon was fixed with a cannulated screw across the lateral femoral condyle.
For prepubescent patients (Tanner 1 and 2), the authors’ preference is to perform an intra-articular extraphyseal reconstruction of the ACL using ITB autograft as described by Micheli and coworkers.33 In the pubescent patient with open growth plates and more than 1 year of growth remaining, a partial transphyseal reconstruction (vertical tunnel across the tibial physis, over-the-top on the femur) using either allograft or hamstring or quadriceps tendon autograft is the authors’ preferred technique. Transphyseal (tibial and femoral) reconstruction using hamstring allograft is reserved for patients with less than 1 year of growth remaining, and bone–patellar tendon–bone autograft is the preferred reconstruction when the physes are closed.
COMPLICATIONS: CAUSES AND PREVENTION
Growth disturbance from physeal injury is usually evident at 2 to 6 months after injury but may not be evident for up to 1 year. Growth disturbance may result from formation of a bony bridge or bar across the physeal cartilage but can also occur without the formation of a bony bridge when injury to the physis slows rather than completely stops growth, resulting in angular deformity. Lipscomb and Anderson25 reported one case of 20 mm of shortening in an immature patient associated with staple fixation of the graft across the physis.
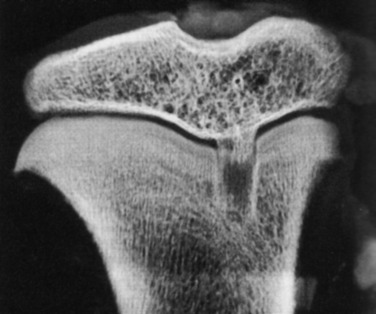
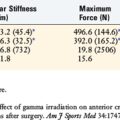
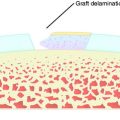
The consequences of violating an active growth plate have been documented in both clinical and experimental reports. Stadelmaier and colleagues40 examined the ability of a soft tissue graft to inhibit formation of a bony bridge within 4.0-mm tunnels drilled across open femoral and tibial growth plates in a canine model using a nontensioned graft. The growth plates were evaluated at 2 weeks and 4 months postoperatively. A bony bridge spanned the growth plate in all nongrafted animals as early as 2 weeks postoperatively (Figs. 11-7 and 11-8), whereas a fascia lata autograft prevented bone formation within the tunnels of all grafted animals and normal growth was maintained (Figs. 11-9 to 11-11). These results have been clinically supported by Andrews and colleagues3 who used a 7-mm allograft centrally placed across the tibial physis and in the over-the-top femoral position in eight patients.

FIGURE 11-8 Photomicrograph of the section seen in Figure 11-7. Note the bony bridge (open arrow) that spans the growth plate (small arrows). (Hematoxylin and eosin x40.)
(From Stadelmaier, D. M.; Arnoczky, S. P.; Dodds, J.; et al.: The effect of drilling and soft tissue grafting across open growth plates. A histologic study. Am J Sports Med 23:431–435, 1995.)

FIGURE 11-10 High-resolution radiograph of the section seen in Figure 11-9. There is no evidence of bony formation across the growth plate in the area of the bone tunnel (outlined by small arrows).
(From Stadelmaier, D. M.; Arnoczky, S. P.; Dodds, J.; et al.: The effect of drilling and soft tissue grafting across open growth plates. A histologic study. Am J Sports Med 23:431–435, 1995.)

FIGURE 11-11 Photomicrograph of the section seen in Figure 11-9. The graft (G) crosses the growth plate, and there is no evidence of any bony formation across the physis (arrows). Note that the growth plate immediately adjacent to the graft-filled tunnel appears normal. (Hematoxylin and eosin x40.)
(From Stadelmaier, D. M.; Arnoczky, S. P.; Dodds, J.; et al.: The effect of drilling and soft tissue grafting across open growth plates. A histologic study. Am J Sports Med 23:431–435, 1995.)
Guzzanti and coworkers14 performed 21 semitendinosus reconstructions in a rabbit model using 2-mm tibial and femoral tunnels. This resulted in damage to 3% of the cross-sectional area of the femoral physis and 4% of the tibial physis. No alteration in growth of the femur was noted; however, 2 tibias developed valgus deformity and 1 tibia became shortened.
Factors such as size and location of the tibial and femoral tunnels have been shown to be important in determining the extent of growth plate damage. However, a safe threshold for physeal tunnels has yet to be determined. A study by Janarv and associates17 concluded that physeal injuries involving 7% to 9% of the cross-sectional area of the physeal plate are enough to cause growth disturbance. For example, in an 8-year-old girl, an 8-mm tunnel would be 3% to 4% of the cross-sectional area of the physis and should not cause growth arrest.
Care should be taken to avoid damage to the tibial tubercle and/or notching and dissection around the distal femoral physis when placing the graft in the over-the-top position. As evidenced by Seil and colleagues,38 damage to the vulnerable perichondral ring is sufficient to cause growth arrest.
In a canine model, Edwards and coworkers9 examined the effect of tensioned soft tissue grafts across the physis and found a substantial rate of distal femoral valgus and proximal tibia varus deformity despite no evidence of a bony bar. Excessive tension (80 N in dogs) across the physis may lead to angular deformities and should be avoided.9 Pressure applied parallel to the direction of growth, such as when tensioning a graft, has also been shown to inhibit longitudinal growth.4
In 2002, the Herodicus Society and the ACL Study Group22 surveyed their members on pediatric ACL reconstruction and complications. Fifteen cases of growth disturbance were reported. There were 8 cases of distal femoral valgus deformity with a physeal bar: 3 cases were associated with hardware crossing the distal physis, 4 with patella tendon–bone plugs crossing the distal femoral physis, and 1 with over-the-top graft placement. There were 2 cases of genu valgum without a physeal bar after lateral extra-articular tenodesis procedures. There were 2 cases of limb length discrepancy: 1 patient developed 2.5 cm of shortening and valgus of the distal femur associated with a 12-mm femoral tunnel and a patellar tendon–bone plug and required contralateral epiphysiodesis. The other case was an 11-year-old girl who underwent transphyseal reconstruction with hamstring autograft through 6-mm tunnels and developed 3.0 cm of overgrowth. There were 3 cases of genu recurvatum after closure of the tibial tubercle apophysis related to either a staple across the physis (2 cases) or a suture to the tibial periosteum (1 case).
Transepiphyseal reconstruction reproduces the anatomy of the ACL more accurately, but it is technically more difficult, making results less predictable. If intra-articular reconstruction with transphyseal drill holes is planned, efforts should be made to minimize the risk of growth abnormality. Transphyseal tunnels should be kept small and centralized in the physis. In younger patients, crossing the growth plate with bone plugs or hardware must be avoided. Animal studies and clinical experience have shown that resection of physeal bars with interposition of soft tissue prevents the reformation of a bony bridge. This lends additional evidence that drill holes filled with tendon graft are less likely to cause growth deformity.36
1 Anderson A.F. Transepiphyseal replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament in skeletally immature patients. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1255-1263.
2 Anderson M., Messner M.B., Green W.T. Distribution of lengths of the normal femur and tibia in children from one to eighteen years of age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46:1197-1202.
3 Andrews M., Noyes F.R., Barber-Westin S.D. Anterior cruciate ligament allograft reconstruction in the skeletally immature athlete. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22:48-54.
4 Arkin A.M., Katz J.F. The effects of pressure on epiphyseal growth; the mechanism of plasticity of growing bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1956;38:1056-1076.
5 Aronowitz E.R., Ganley T.J., Goode J.R., et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in adolescents with open physes. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:168-175.
6 Brief L.P. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction without drill holes. Arthroscopy. 1991;7:350-357.
7 DeLee J.C., Curtis R. Anterior cruciate ligament insufficiency in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;172:112-118.
8 Edwards P.H.Jr., Grana W.A. Physeal fractures about the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995;3:63-69.
9 Edwards T.B., Greene C.C., Baratta R.V., et al. The effect of placing a tensioned graft across open growth plates. A gross and histological analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:725-734.
10 Engebretsen L., Svenningsen S., Benum P. Poor results of anterior cruciate ligament repair in adolescence. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988;59:684-686.
11 Graf B.K., Lange R.H., Fujisaki C.K., et al. Anterior cruciate ligament tears in skeletally immature patients: meniscal pathology at presentation and after attempted conservative treatment. Arthroscopy. 1992;8:229-233.
12 Greulich W., Pyle S., editors. Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist, 2nd ed, Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 1959.
13 Grontvedt T., Engebretsen L., Benum P., et al. A prospective, randomized study of three operations for acute rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. Five-year follow-up of one hundred and thirty-one patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:159-168.
14 Guzzanti V., Falciglia F., Gigante A., et al. The effect of intra-articular ACL reconstruction on the growth plates of rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994;76:960-963.
15 Guzzanti V., Falciglia F., Stanitski C.L. Physeal-sparing intra-articular anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in preadolescents. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31:949-953.
16 Janarv P.M., Nystrom A., Werner S., et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996;16:673-677.
17 Janarv P.M., Wikstrom B., Hirsch G. The influence of transphyseal drilling and tendon grafting on bone growth: an experimental study in the rabbit. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998;18:149-154.
18 Johnson R.J., Beynnon B.D., Nichols C.E., et al. The treatment of injuries of the anterior cruciate ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:140-151.
19 Kloeppel-Wirth S., Koltai J.L., Dittmer H. Significance of arthroscopy in children with knee joint injuries. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1992;2:169-172.
20 Kocher M.S., Garg S., Micheli L.J. Physeal sparing reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament in skeletally immature prepubescent children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:2371-2379.
21 Kocher M.S., Garg S., Micheli L.J. Physeal sparing reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament in skeletally immature prepubescent children and adolescents. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(suppl 1 pt 2):283-293.
22 Kocher M.S., Saxon H.S., Hovis W.D., et al. Management and complications of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in skeletally immature patients: survey of the Herodicus Society and The ACL Study Group. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22:452-457.
23 Kocher M.S., Smith J.T., Zoric B.J., et al. Transphyseal anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in skeletally immature pubescent adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:2632-2639.
24 Koman J.D., Sanders J.O. Valgus deformity after reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament in a skeletally immature patient. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:711-715.
25 Lipscomb A.B., Anderson A.F. Tears of the anterior cruciate ligament in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68:19-28.
26 Little D.G., Song K.M., Katz D., et al. Relationship of peak height velocity to other maturity indicators in idiopathic scoliosis in girls. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:685-693.
27 Lo I.K., Kirkley A., Fowler P.J., et al. The outcome of operatively treated anterior cruciate ligament disruptions in the skeletally immature child. Arthroscopy. 1997;13:627-634.
28 Manzione M., Pizzutillo P.D., Peoples A.B., et al. Meniscectomy in children: a long-term follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 1983;11:111-115.
29 McCarroll J.R., Rettig A.C., Shelbourne K.D. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in the young athlete with open physes. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16:44-47.
30 McCarroll J.R., Shelbourne K.D., Porter D.A., et al. Patellar tendon graft reconstruction for midsubstance anterior cruciate ligament rupture in junior high school athletes. An algorithm for management. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22:478-484.
31 McIntosh A.L., Dahm D.L., Stuart M.J. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in the skeletally immature patient. Arthroscopy. 2006;22:1325-1330.
32 Menelaus M.B. Correction of leg length discrepancy by epiphyseal arrest. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966;48:336-339.
33 Micheli L.J., Rask B., Gerberg L. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in patients who are prepubescent. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;364:40-47.
34 Millett P.J., Willis A.A., Warren R.F. Associated injuries in pediatric and adolescent anterior cruciate ligament tears: does a delay in treatment increase the risk of meniscal tear? Arthroscopy. 2002;18:955-959.
35 Mizuta H., Kubota K., Shiraishi M., et al. The conservative treatment of complete tears of the anterior cruciate ligament in skeletally immature patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77:890-894.
36 Peterson H.A. Partial growth plate arrest and its treatment. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984;4:246-258.
37 Risser J.C. The iliac apophysis; an invaluable sign in the management of scoliosis. Clin Orthop. 1958;11:111-119.
38 Seil R., Pape D., Kohn D. ACL Replacement in Sheep with Open Physes: An Evaluation of Risk Factors. Sardinia, Italy: ACL Study Group, 2004.
39 Shelbourne K.D., Gray T., Wiley B.V. Results of transphyseal anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using patellar tendon autograft in tanner stage 3 or 4 adolescents with clearly open growth plates. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32:1218-1222.
40 Stadelmaier D.M., Arnoczky S.P., Dodds J., et al. The effect of drilling and soft tissue grafting across open growth plates. A histologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23:431-435.
41 Stanitski C.L. Correlation of arthroscopic and clinical examinations with magnetic resonance imaging findings of injured knees in children and adolescents. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26:2-6.
42 Stanitski C.L., Harvell J.C., Fu F. Observations on acute knee hemarthrosis in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993;13:506-510.
43 Tanner J.M., Davies P.S. Clinical longitudinal standards for height and height velocity for North American children. J Pediatr. 1985;107:317-329.
44 Vahasarja V., Kinnuen P., Serlo W. Arthroscopy of the acute traumatic knee in children. Prospective study of 138 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64:580-582.