Diffuse GB thickening ± sonographic Murphy sign in setting of acalculous cholecystitis
• MR: Papillary stenosis with tapered narrowing of distal CBD and proximal CBD dilatation
 ± thickening and hyperenhancement of bile duct wall on T1WI C+ images in setting of acute inflammation
± thickening and hyperenhancement of bile duct wall on T1WI C+ images in setting of acute inflammation
 ± thickening and hyperenhancement of bile duct wall on T1WI C+ images in setting of acute inflammation
± thickening and hyperenhancement of bile duct wall on T1WI C+ images in setting of acute inflammation• ERCP: Papillary stenosis with proximal CBD dilation, strictures/ulcerations of CBD, and intrahepatic strictures
 and wall thickening
and wall thickening  . (Courtesy K. Hosseinzadeh, MD.)
. (Courtesy K. Hosseinzadeh, MD.)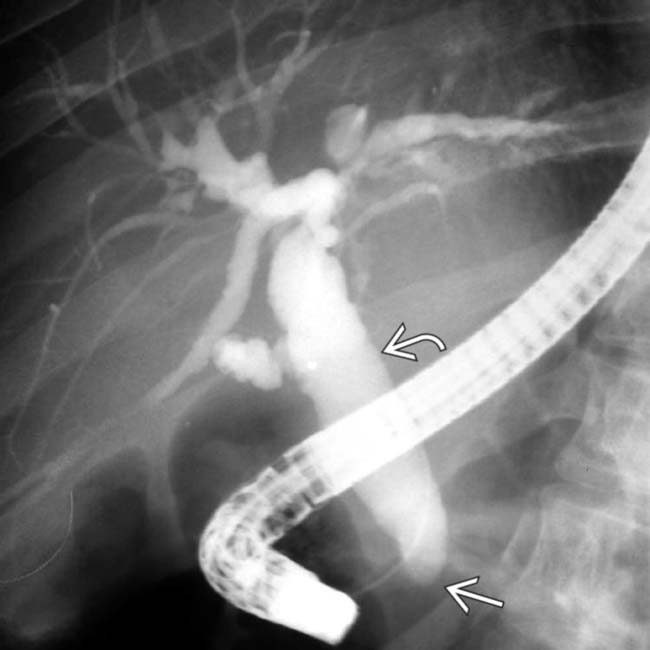
 is dilated, and the distal duct is strictured
is dilated, and the distal duct is strictured  . Intrahepatic biliary strictures in AIDS cholangitis can resemble those seen in PSC.
. Intrahepatic biliary strictures in AIDS cholangitis can resemble those seen in PSC.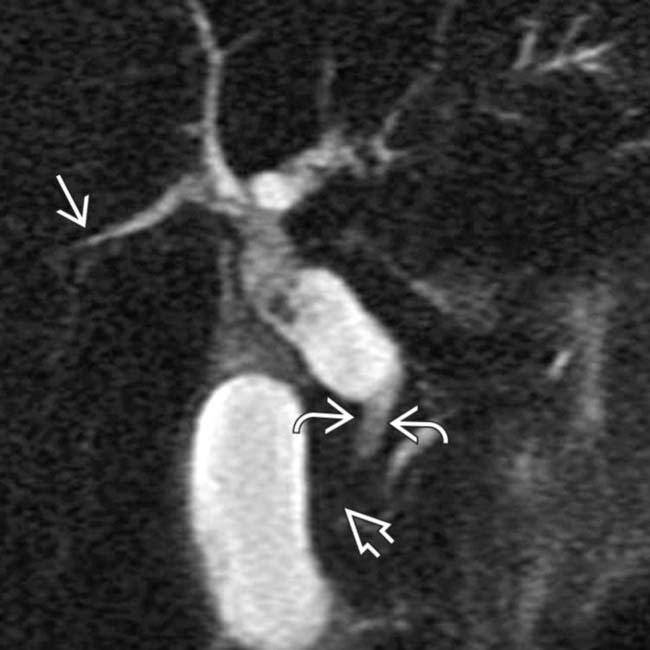
 , extrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation, a narrowed distal CBD
, extrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation, a narrowed distal CBD  , and papillary stenosis
, and papillary stenosis  . This combination is characteristic of AIDS cholangiopathy. (Courtesy V. Kabathina, MD.)
. This combination is characteristic of AIDS cholangiopathy. (Courtesy V. Kabathina, MD.)IMAGING
General Features
MR Findings
• Papillary stenosis with tapered narrowing of distal CBD (without abrupt margins) and proximal CBD dilatation
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
PATHOLOGY
General Features
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
 in CMV acalculous cholecystitis.
in CMV acalculous cholecystitis.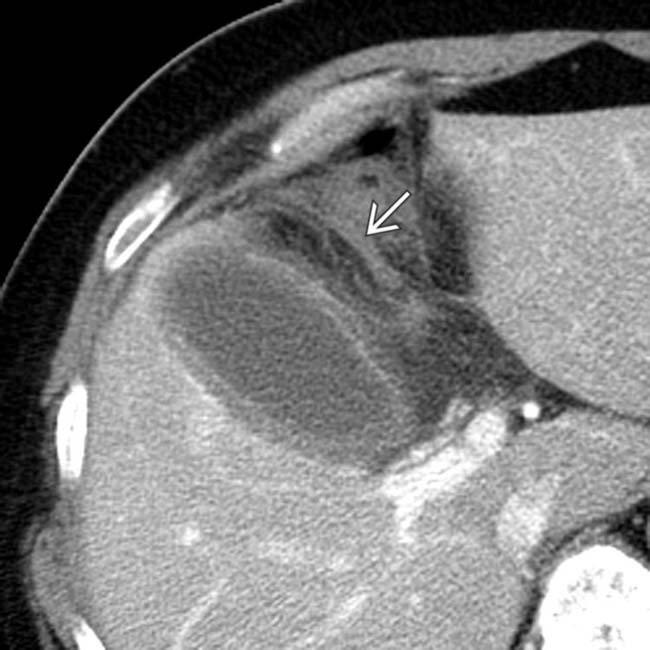
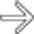 in CMV acalculous cholecystitis.
in CMV acalculous cholecystitis.
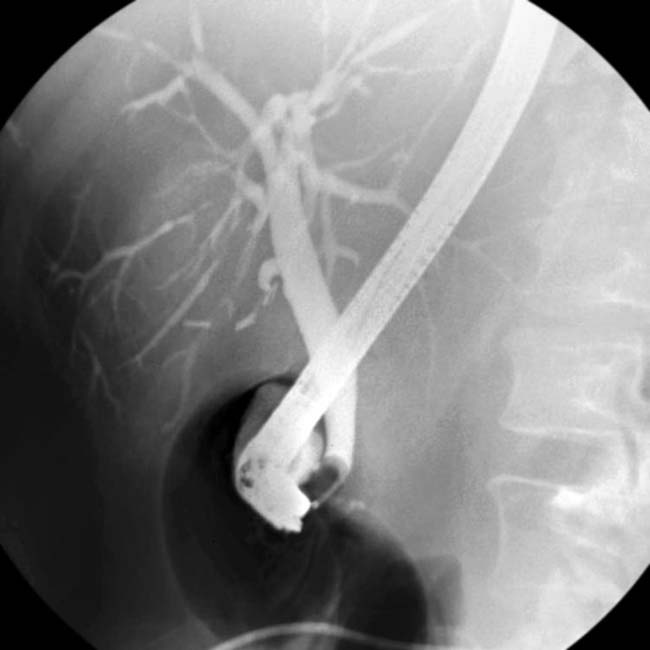
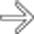
 in ampullary stenosis from Cryptosporidium in AIDS cholangitis.
in ampullary stenosis from Cryptosporidium in AIDS cholangitis.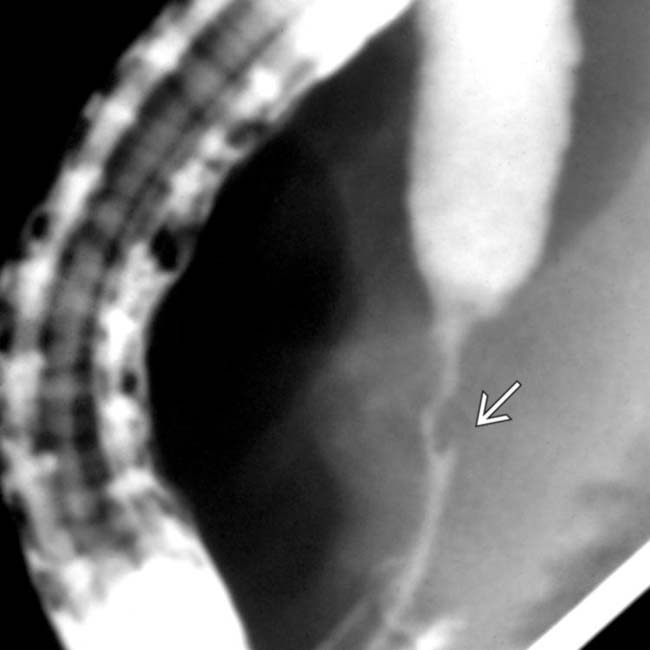
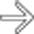 .
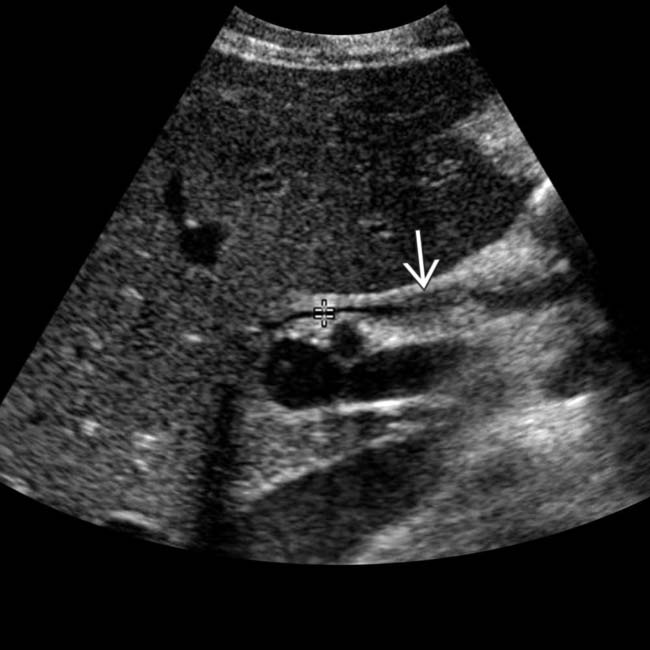
.
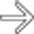 , typical features of AIDS-related cholangiopathy.
, typical features of AIDS-related cholangiopathy.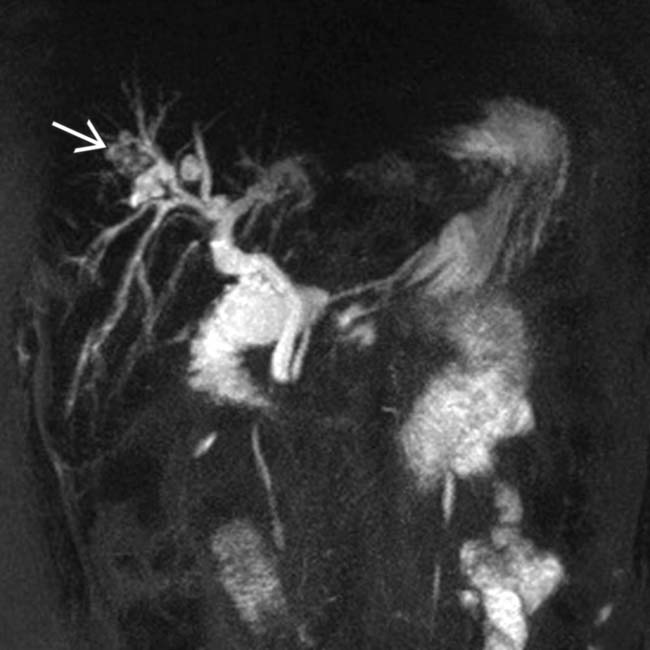
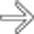 within the intrahepatic ducts. The appearance of the intrahepatic ducts in this case can be seen with any form of sclerosing cholangitis, in this case due to AIDS cholangiopathy. Hepatolithiasis in this case is an unusual feature.
within the intrahepatic ducts. The appearance of the intrahepatic ducts in this case can be seen with any form of sclerosing cholangitis, in this case due to AIDS cholangiopathy. Hepatolithiasis in this case is an unusual feature.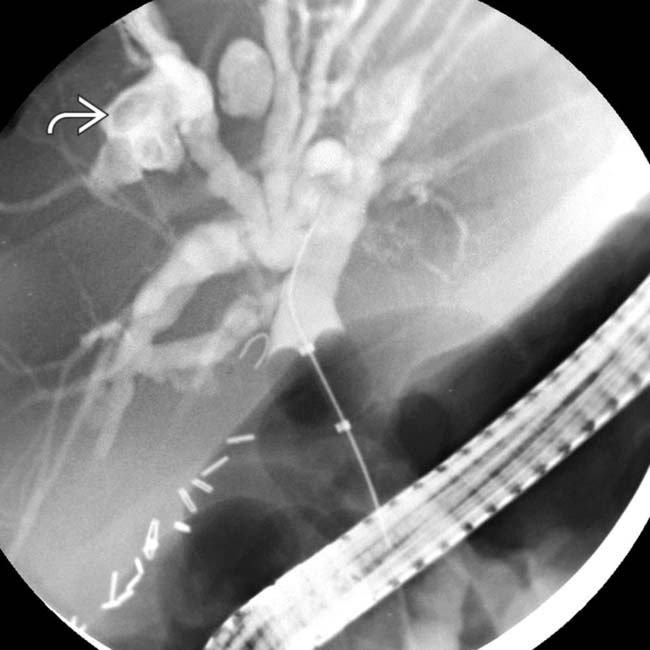
 within a focally dilated bile duct segment.
within a focally dilated bile duct segment.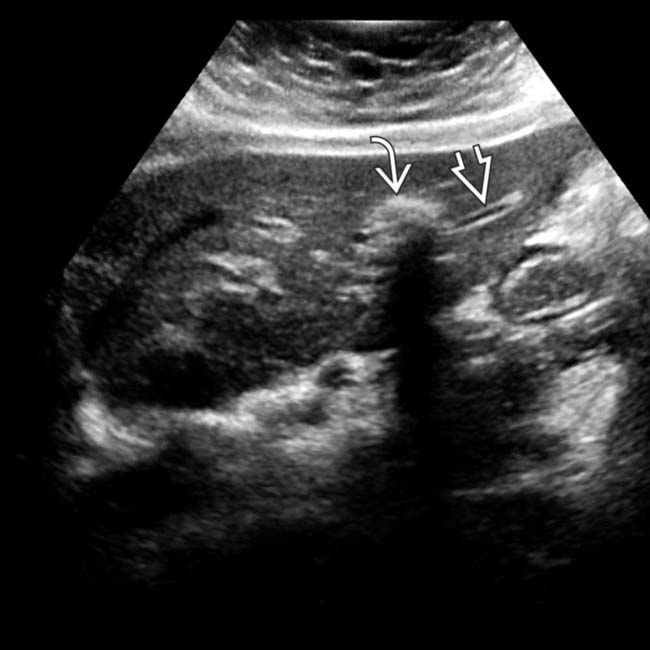
 as well as intrahepatic ductal stones
as well as intrahepatic ductal stones 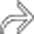 in a patient with AIDS-related cholangiopathy.
in a patient with AIDS-related cholangiopathy.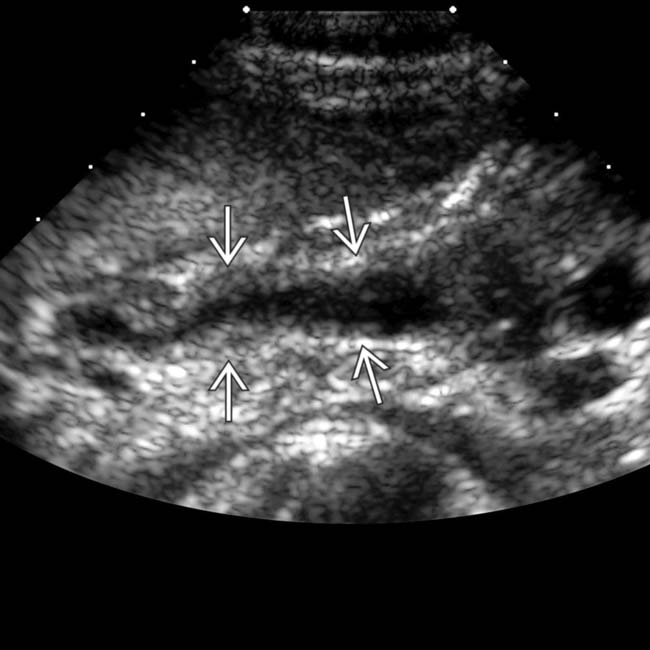
 . (Courtesy K. Hosseinzadeh, MD.)
. (Courtesy K. Hosseinzadeh, MD.)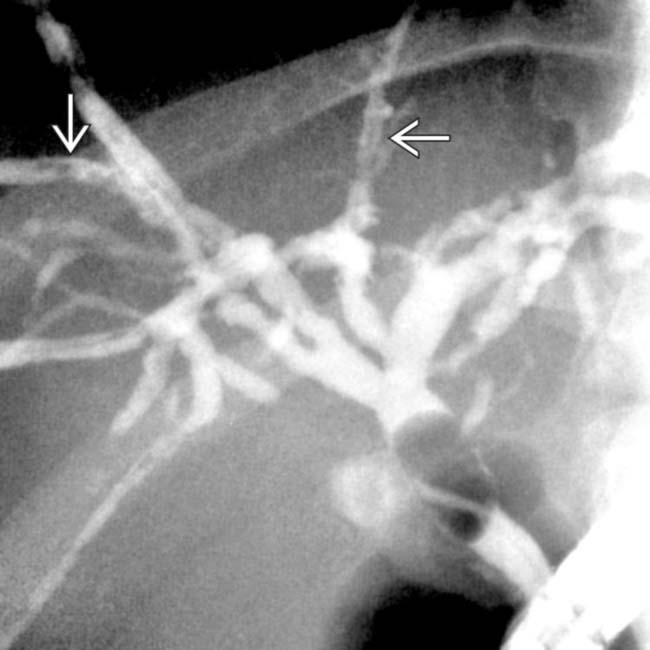
 . Stool cultures were positive for Cryptosporidium.
. Stool cultures were positive for Cryptosporidium.
 .
.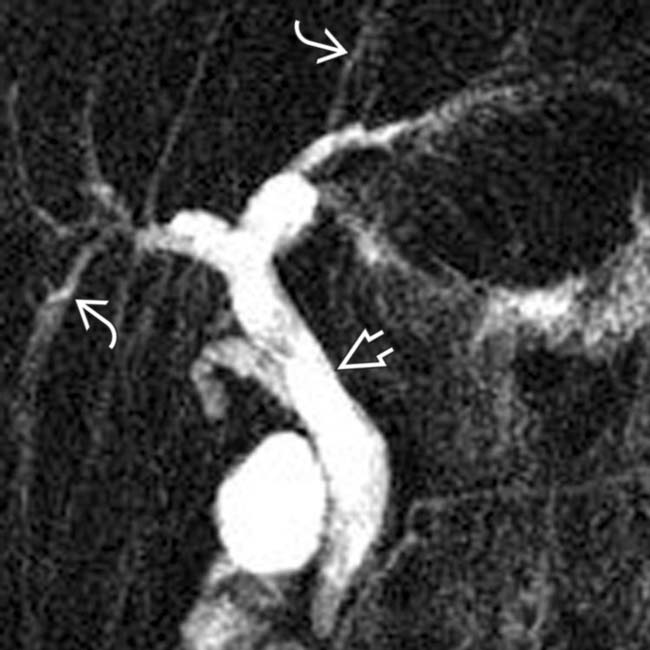
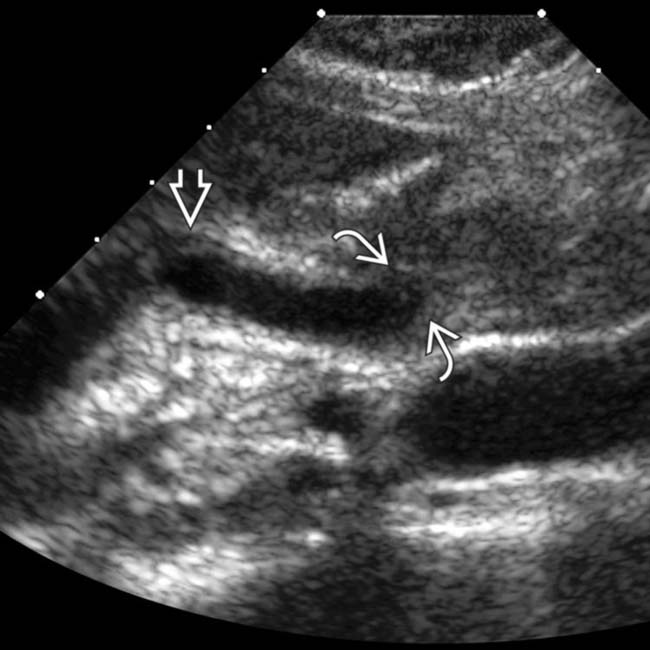
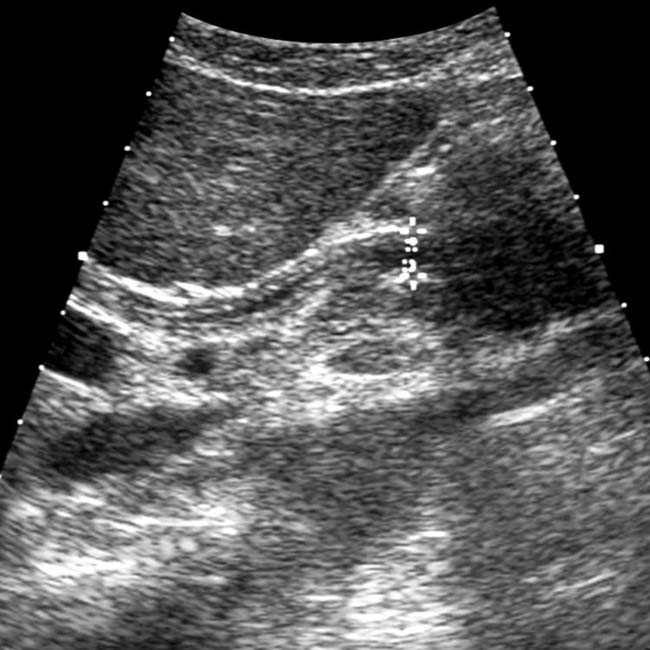
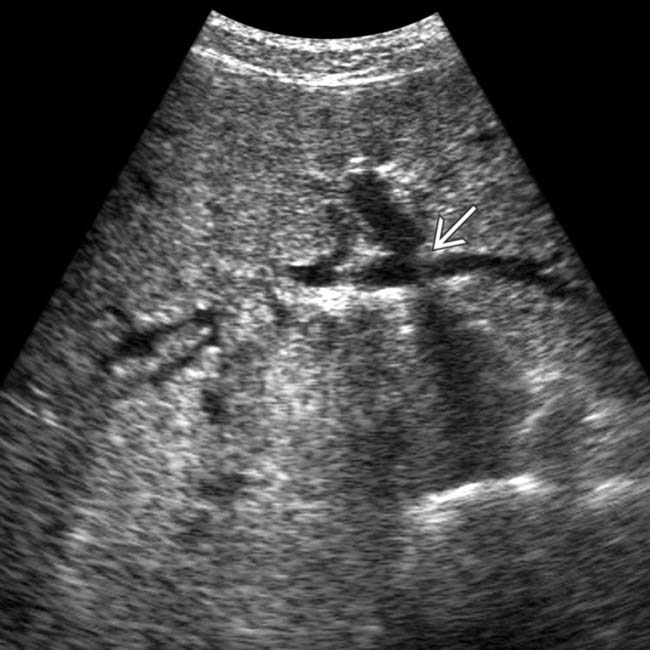
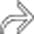 , signifying cholangitis. The dilation of the common bile duct (CBD)
, signifying cholangitis. The dilation of the common bile duct (CBD)  is probably due to a distal CBD stricture.
is probably due to a distal CBD stricture.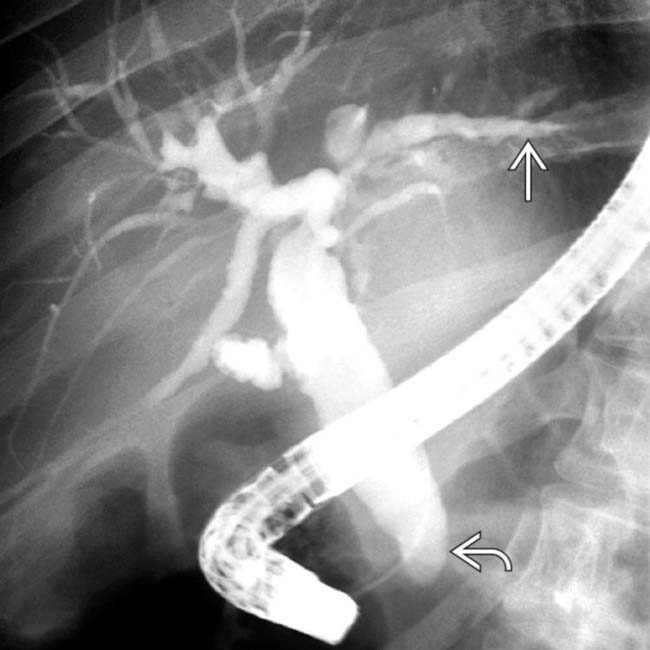
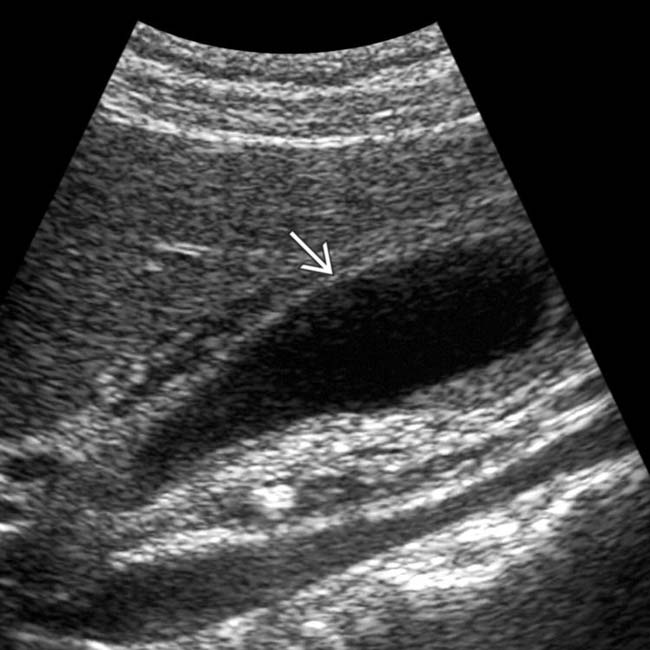
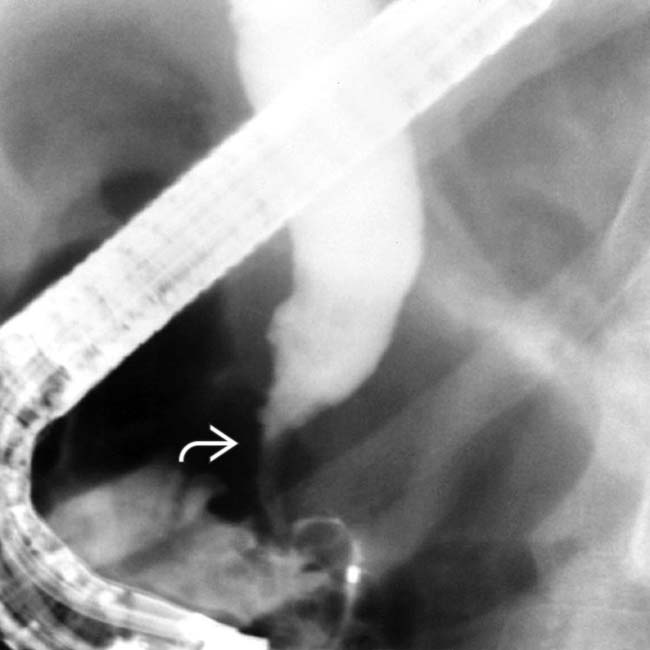
 . Note the grossly dilated CBD with irregular ductal lining and a strictured distal duct
. Note the grossly dilated CBD with irregular ductal lining and a strictured distal duct  .
.





















































 from AIDS cholangitis.
from AIDS cholangitis.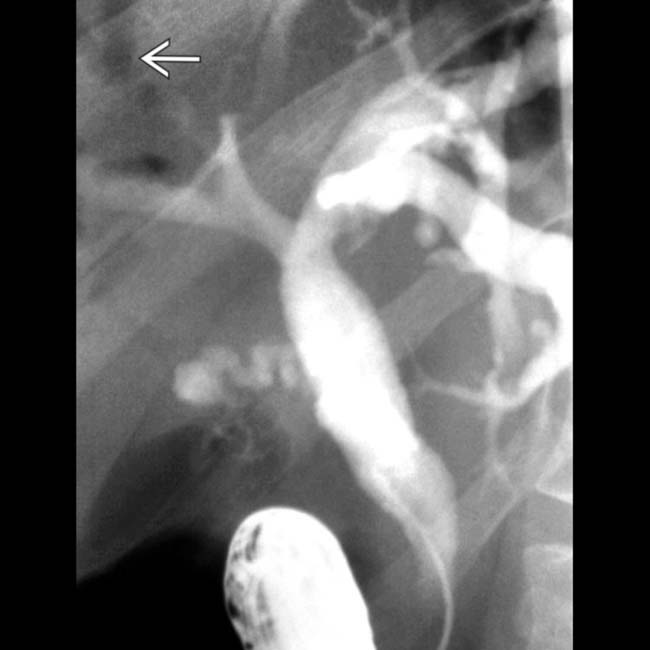
 .
.
 .
.


