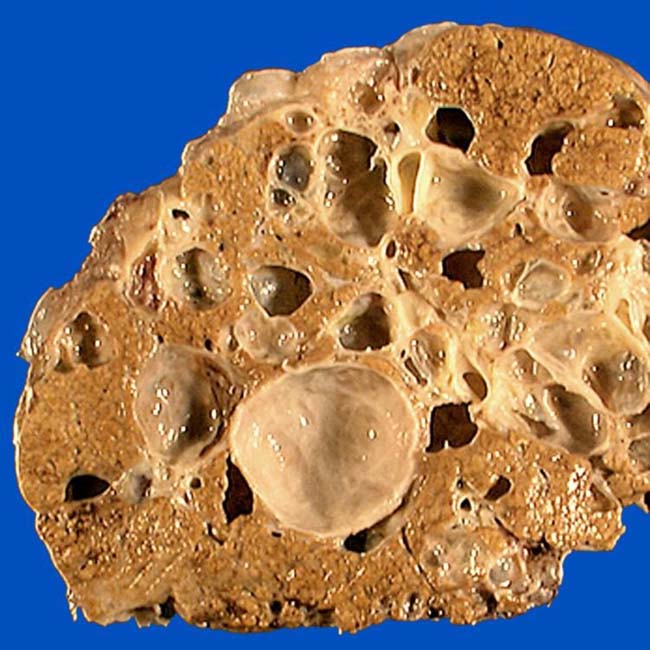
± cysts in kidneys and other organs
• Cyst contents often greater than water density/intensity due to hemorrhage (infection less common)

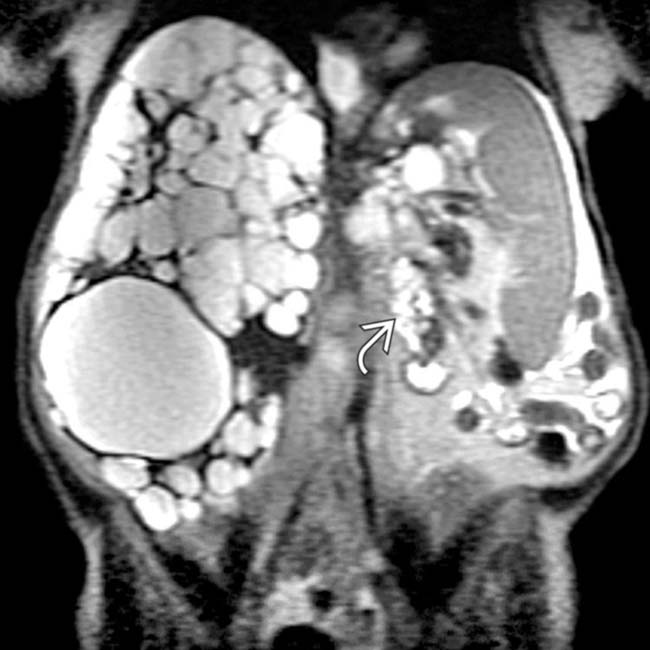
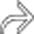 within the left kidney are also visible.
within the left kidney are also visible.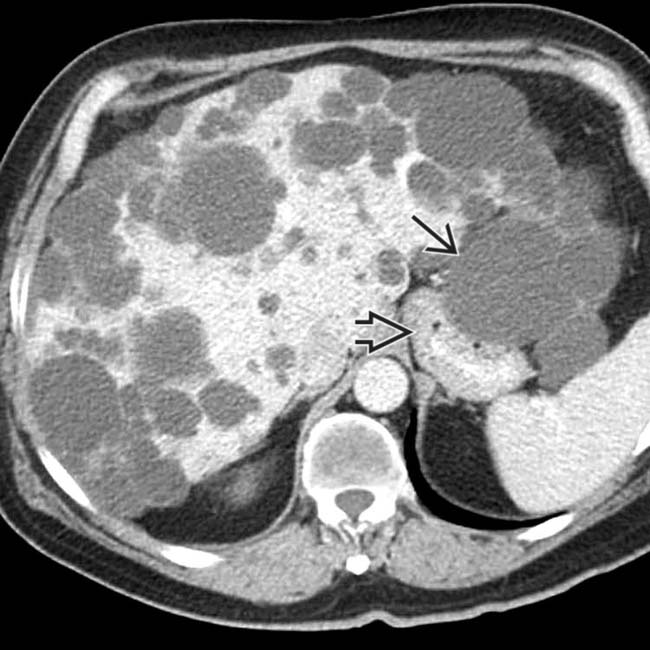
 by a dominant cyst
by a dominant cyst  from the left hepatic lobe, which was subsequently marsupialized at surgery with resolution of symptoms.
from the left hepatic lobe, which was subsequently marsupialized at surgery with resolution of symptoms.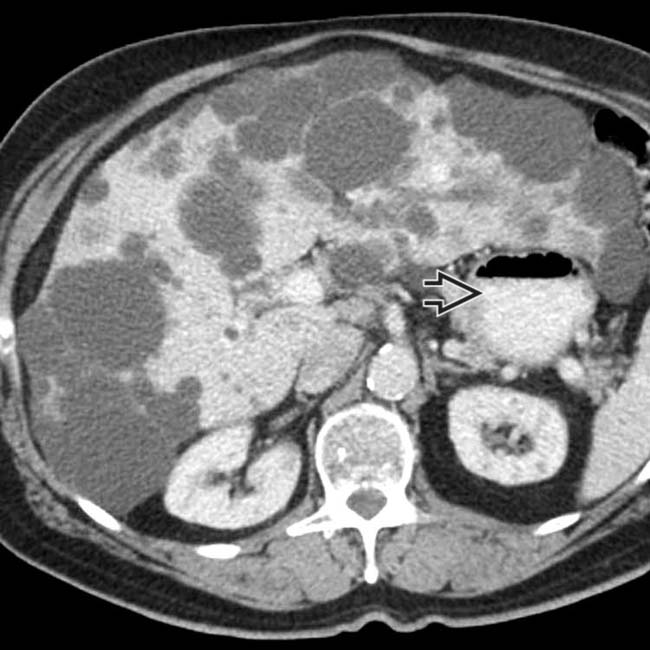
 . The symptoms of early satiety also resolved.
. The symptoms of early satiety also resolved.CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
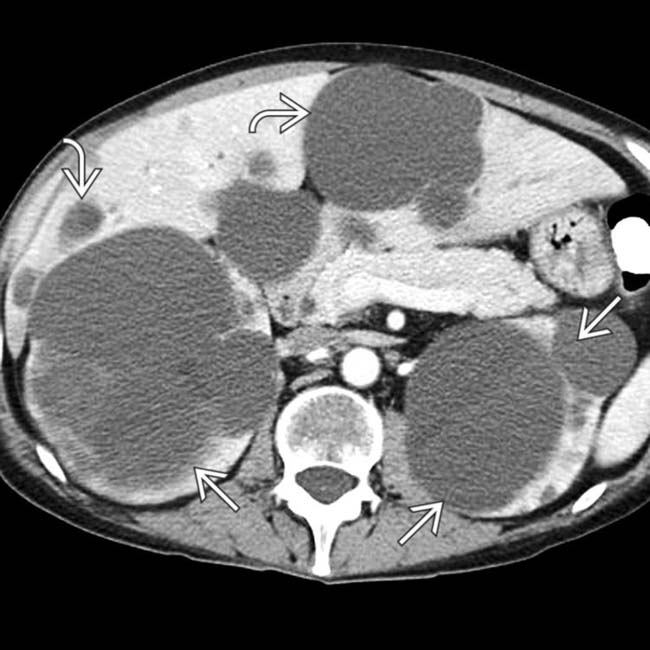
 and in the liver
and in the liver  . Women with polycystic liver disease (PLD) tend to develop larger cysts than men, attributed by some to a hormonal effect on cyst development.
. Women with polycystic liver disease (PLD) tend to develop larger cysts than men, attributed by some to a hormonal effect on cyst development.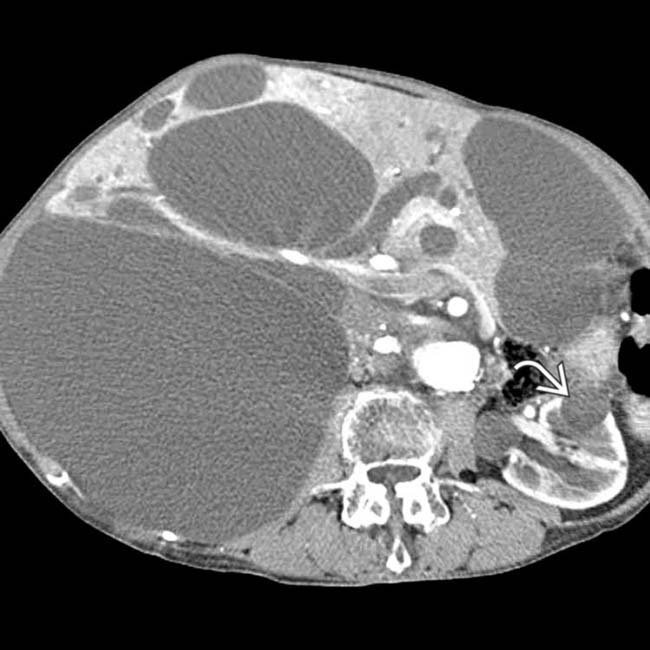
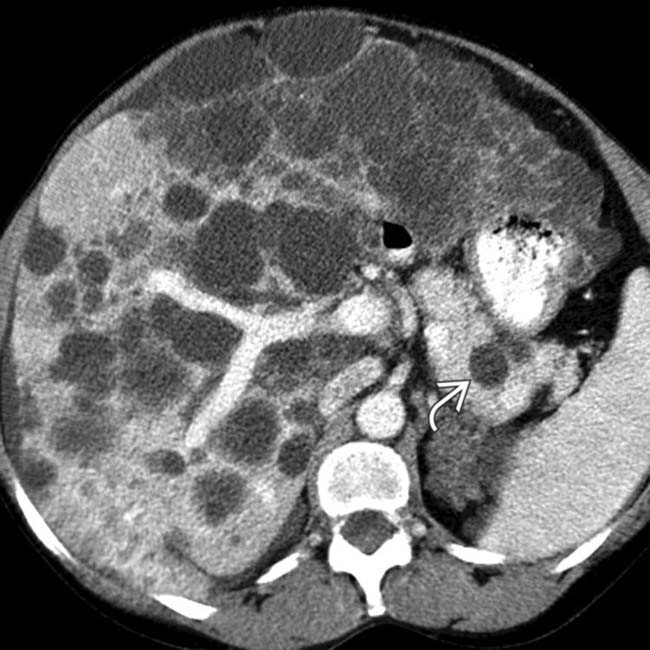
 are evident. The right kidney was displaced caudally and was hydronephrotic due to compression of the renal pelvis (not shown).
are evident. The right kidney was displaced caudally and was hydronephrotic due to compression of the renal pelvis (not shown).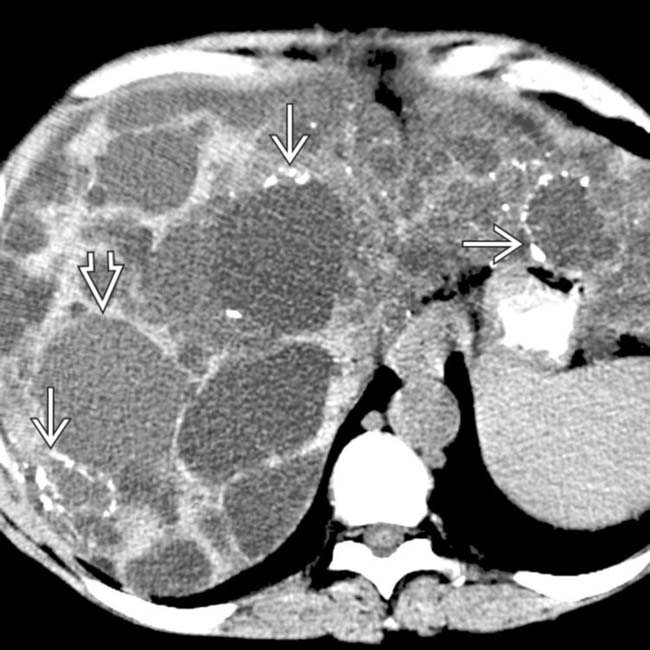
 have higher than water density contents and others have peripheral calcification in cyst walls
have higher than water density contents and others have peripheral calcification in cyst walls 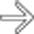 due to prior episodes of intracystic hemorrhage.
due to prior episodes of intracystic hemorrhage.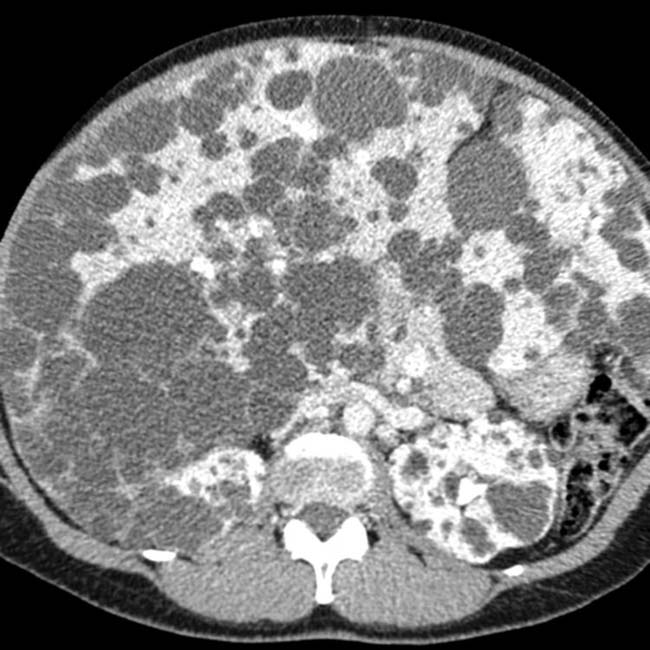
 , as one would expect for simple fluid content, while others are of intermediate intensity. At least 1 has septations and heterogeneous contents
, as one would expect for simple fluid content, while others are of intermediate intensity. At least 1 has septations and heterogeneous contents  from prior hemorrhage.
from prior hemorrhage.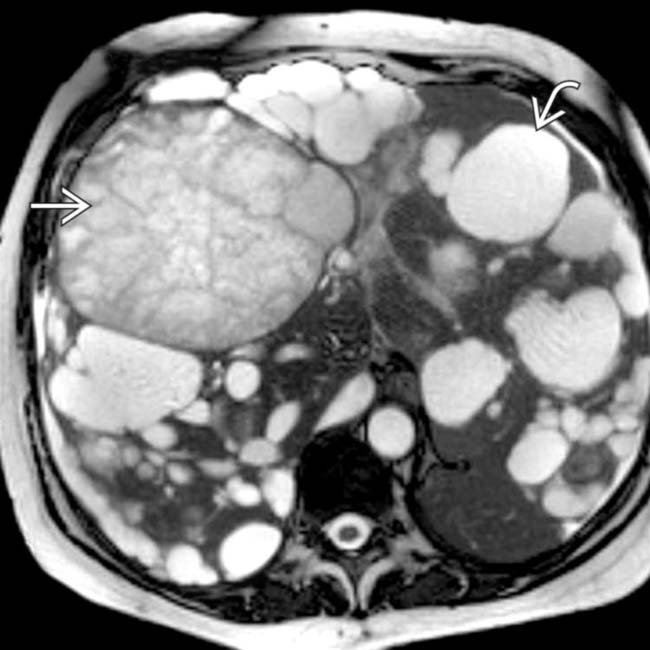
 and complex cysts having heterogeneous contents
and complex cysts having heterogeneous contents  .
.
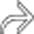 are also seen.
are also seen.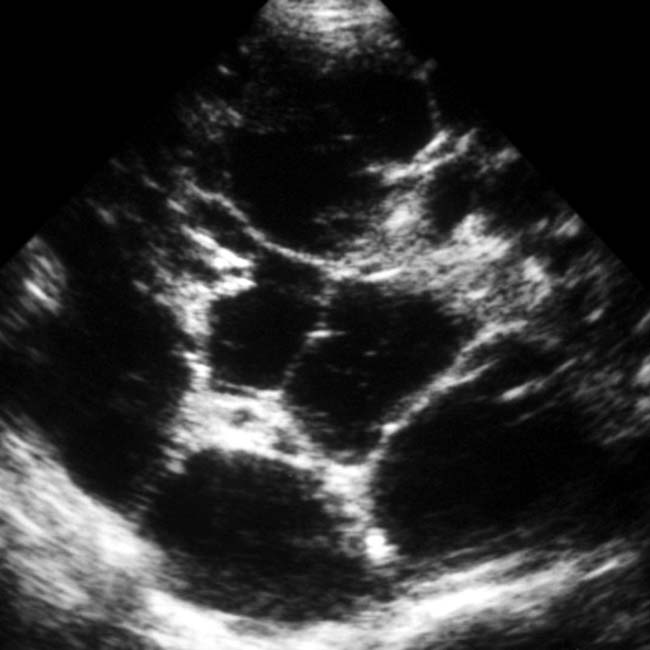





































































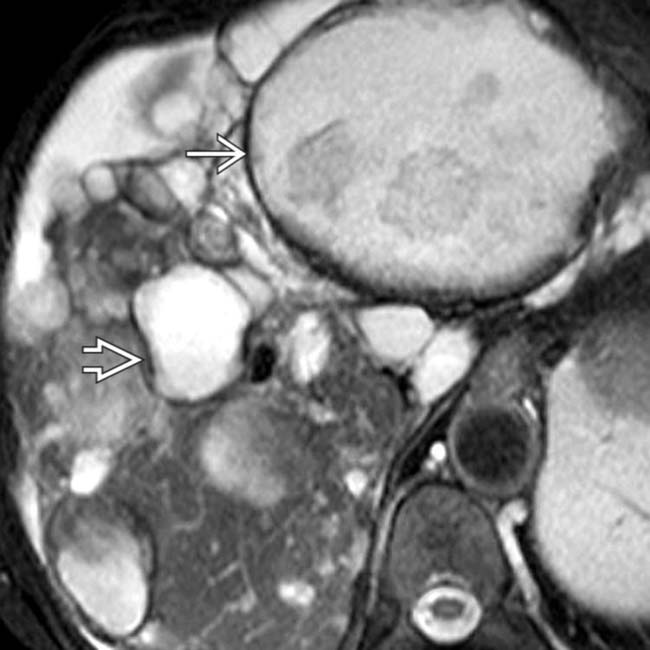
 in a patient with ADPLD as less hyperintense than its neighboring uncomplicated cyst
in a patient with ADPLD as less hyperintense than its neighboring uncomplicated cyst  .
.

