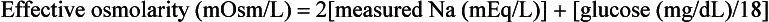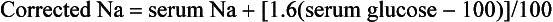Acute and chronic complications of diabetes
1. What are the acute complications of diabetes?
Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia; both are the result of an imbalance between medications (insulin or oral diabetic agents) and the patient’s food intake and exercise.
2. Describe the symptoms of hyperglycemia.
Initial symptoms are increased thirst (polydipsia), increased urination (polyuria), fatigue, and blurry vision. If uncorrected, hyperglycemia may eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS). Rather than distinct entities, DKA and HHS represent a spectrum of a disease process characterized by varying degrees of insulin deficiency, overproduction of counterregulatory hormones, and dehydration. In some situations, features of both DKA and HHS may occur concurrently.
DKA is a state of uncontrolled catabolism triggered by a relative or absolute deficiency in circulating insulin. The DKA triad is hyperglycemia (blood glucose [BG] usually > 250 mg/dL), metabolic acidosis (pH < 7.35), and ketonuria. Insulin deficiency is accompanied by a reciprocal elevation in counterregulatory hormones (glucagon, epinephrine, growth hormone, and cortisol), which causes increased glucose production by the liver (gluconeogenesis) and catabolism of fat (lipolysis). Lipolysis provides the substrate (free fatty acids) for the uncontrolled production of ketones by the liver. The production of ketones then leads to metabolic acidosis.
Any disorder that alters the balance between insulin and counterregulatory hormones can precipitate DKA. A minority of cases occurs in people not previously diagnosed with diabetes, but most cases (up to 80%) occur in people with previous diagnoses. DKA is most often associated with type 1 diabetes; however, it may also occur in older patients with type 2 diabetes, particularly when associated with a major intercurrent illness.
5. What illnesses may trigger DKA?
Infection and myocardial infarction are the illnesses most commonly known to trigger DKA. Even localized infections, such as urinary tract infections and prostatitis, have precipitated DKA. Other triggers are severe emotional stress, trauma, medications (i.e., corticosteroids), and hormonal changes (i.e., preovulation) in women. Nonadherence and improper insulin self-management during an intercurrent illness are other common causes of DKA. Both represent a lack of knowledge and may be remediated through appropriate education (sick day rules to frequently measure glucose/ketones) or psychological intervention.
6. What are the signs and symptoms of DKA?
Nausea and vomiting, generalized abdominal pain, dehydration, rapid (Kussmaul) respirations, and a sweet (acetone) odor on the breath represent the classic clinical picture. In addition, patients may have an altered mental status and symptoms due to their possible precipitating illness.
DKA should be suspected if the patient presents with marked hyperglycemia (BG > 250 mg/dL) and metabolic acidosis (pH < 7.35). An elevated anion gap (> 13 mEq/L) is usually, but not always, present. The finding of elevated ketones in the blood or urine confirms the diagnosis.
8. Is the ketone test result always positive with DKA?
No. If blood or urine ketone results are negative and DKA is strongly suspected, treatment with fluids and insulin should still be initiated. During the course of treatment, the blood and urine ketones test results will become positive. This “delay” in positivity for measured ketones is due to a limitation of the laboratory test for ketones, which detects only acetoacetate. The predominant ketone in untreated DKA is beta-hydroxybutyrate. As DKA is treated, acetoacetate becomes the predominant ketone, causing the test for ketones to turn positive.
9. What lab tests are recommended in the first hour of treatment for DKA?
 Baseline electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and glucose measurements, anion gap calculation, urinalysis, urine and blood ketone measurements, and electrocardiogram (ECG) should be performed.
Baseline electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and glucose measurements, anion gap calculation, urinalysis, urine and blood ketone measurements, and electrocardiogram (ECG) should be performed.
 An arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis should be obtained if the patient appears ill or tachypneic or if the serum bicarbonate is very low (< 10 mEq/L).
An arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis should be obtained if the patient appears ill or tachypneic or if the serum bicarbonate is very low (< 10 mEq/L).
 Fluid intake, urine output, and progression of laboratory changes should be recorded.
Fluid intake, urine output, and progression of laboratory changes should be recorded.
 Further lab testing should be based on findings of suspected triggers (i.e., infection, myocardial infarction).
Further lab testing should be based on findings of suspected triggers (i.e., infection, myocardial infarction).
10. Summarize the strategy for fluid and potassium administration in the first hour.
 Fluids: Normal saline given at 15 mL/kg/h (approximately 1 L/h for a 70-kg individual).
Fluids: Normal saline given at 15 mL/kg/h (approximately 1 L/h for a 70-kg individual).
 Potassium: If T waves on the ECG are peaked or normal, no potassium replacement is initially necessary. If T waves are low or U waves are seen, 40 mEq potassium chloride (KCl) should be added to each liter of intravenous (IV) fluids.
Potassium: If T waves on the ECG are peaked or normal, no potassium replacement is initially necessary. If T waves are low or U waves are seen, 40 mEq potassium chloride (KCl) should be added to each liter of intravenous (IV) fluids.
11. How should insulin treatment be started with DKA?
An initial IV bolus of 10 to 20 units of regular insulin should be followed by a continuous infusion of 0.5 units/mL of regular insulin mixed in normal saline at a rate of 5 to 10 units per hour (0.1 unit/kg/h).
12. Summarize the strategy for clinical assessment, and fluid and potassium administration in the second hour of treatment.
 Fluids: Continue normal saline at approximately 1 L/h.
Fluids: Continue normal saline at approximately 1 L/h.
 Potassium: Adjust or add KCl to IV fluids to maintain serum potassium at 4 to 5 mEq/L.
Potassium: Adjust or add KCl to IV fluids to maintain serum potassium at 4 to 5 mEq/L.
 Monitor vital signs (including respiratory rate), level of consciousness, hydration status, and urine output.
Monitor vital signs (including respiratory rate), level of consciousness, hydration status, and urine output.
 Repeat measurements of electrolytes, BG, and urine and blood ketones. Calculate anion gap.
Repeat measurements of electrolytes, BG, and urine and blood ketones. Calculate anion gap.
13. How should insulin be adjusted during treatment?
If the serum glucose drops to less than 250 mg/dL, fluids should be changed to a 5% to 10% dextrose–containing solution. The insulin infusion rate may be doubled if the serum glucose does not decline after the first hour. The optimal rate of glucose decline is 100 mg/dL/h. The glucose level should not be allowed to fall to less than 250 mg/dL during the first 4 to 5 hours of treatment.
14. Summarize the basic strategy after the second hour of treatment.
 Assess the patient and repeat previously discussed lab tests hourly.
Assess the patient and repeat previously discussed lab tests hourly.
 Fluids: Adjust the rate of infusion according to the level of hydration. Consider changing to 0.45% normal saline if the patient is euvolemic and hypernatremic.
Fluids: Adjust the rate of infusion according to the level of hydration. Consider changing to 0.45% normal saline if the patient is euvolemic and hypernatremic.
 Potassium: Continue to adjust to a goal serum value of 4 to 5 mEq/L.
Potassium: Continue to adjust to a goal serum value of 4 to 5 mEq/L.
 Insulin: Continue IV infusion as long as acidosis is present; supplement with dextrose as necessary.
Insulin: Continue IV infusion as long as acidosis is present; supplement with dextrose as necessary.
15. When can the insulin infusion be discontinued?
When the anion gap corrects to normal, the pH is 7.3 or greater, or the serum bicarbonate is 18 mEq/L or greater, the patient can be given a subcutaneous dose of regular insulin or a short-acting insulin analog (lispro, aspart, glulisine) to cover a meal. The infusion should be stopped 30 minutes after the subcutaneous insulin is given. If the patient is unable to eat, give 5 units of regular or a short-acting insulin analog, continue the IV dextrose solution, and give supplemental short-acting insulin every 4 hours on the basis of the glucose level.
16. What other interventions may be necessary in the treatment of DKA?
If the initial serum phosphorus is less than 1.0 mg/dL, consider giving 10 to 20 mEq/h potassium phosphate in the IV fluids.
Bicarbonate (in the form of sodium bicarbonate) replacement is not recommended unless other causes of severe acidosis are present (e.g., sepsis, lactic acidosis) or the arterial pH is less than 6.9. If used, sodium bicarbonate should be diluted in the IV fluids and given over 1 hour.
17. What is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome?
Formerly known as hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome or coma, and described first in 1957 by Sament and Schwartz, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS) is a constellation of hyperglycemia, hyperosmolarity, and altered level of consciousness, most typically in the absence of acidosis.
18. Who is at risk for HHS and why?
Elderly patients, with or without a history of type 2 diabetes, are at particular risk for HHS because of a higher rate of impaired thirst perception and increased prevalence of impaired renal function. Precipitating factors, such as infection, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular events, pancreatitis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and use of exogenous medications, may also be present.
19. What are the signs of HHS?
 Marked hyperglycemia (BG > 600 mg/dL)
Marked hyperglycemia (BG > 600 mg/dL)
 Hyperosmolarity (serum Osm > 320 mOsm/L)
Hyperosmolarity (serum Osm > 320 mOsm/L)
Hyperglycemia, once triggered, leads to glycosuria, osmotic diuresis, hyperosmolarity, cellular dehydration, hypovolemia, shock, coma, and, if untreated, death.
20. Why is ketoacidosis typically not seen in HHS?
Although glucose levels are generally higher in HHS than in DKA, the residual insulin secretory capacity of type 2 diabetics likely prevents severe acidosis and ketosis in HHS. The presence of circulating insulin or lower levels of counterregulatory hormones (or both) prevents lipolysis and significant ketone production. Lactic acidosis may be seen, however.
21. What are the symptoms of HHS?
Polyuria and polydipsia often occur days to weeks before manifestation of HHS. Patients are unable to drink enough to match a brisk osmotic diuresis, exacerbating the hyperglycemia. The imbalance of fluid intake and output eventually results in impairment of renal function, decrease in glucose excretion, and further worsening of hyperglycemia. Profound dehydration is typical. Fever is not part of the syndrome and, if present, suggests an infectious component. Focal neurologic defects may be seen in patients, including bilateral or unilateral hyporeflexia or hyperreflexia, seizures, hemiparesis, aphasia, presence of Babinski sign, hemianopsia, nystagmus, visual hallucinations, acute quadriplegia, and dysphagia.
22. What is the most common presenting symptom of HHS?
Altered mental status occurs in approximately 90% of cases and is the most common reason that patients are brought to the hospital. An effective osmolarity higher than 340 mOsm/L is required for coma to be attributed to HHS and is present in 10% of patients upon presentation. Effective osmolarity refers to the true osmolarity seen by the cells and is calculated by means of the following equation:
23. What is the hallmark laboratory finding in patients with HHS?
Marked hyperglycemia (BG > 600 mg/dL and often > 1000 mg/dL) is characteristic: The serum sodium concentration is often factitiously low. To correct for the hyperglycemia, the following formula is used:
Other laboratory abnormalities include elevated BUN and creatinine, hypertriglyceridemia, and leukocytosis.
24. What is the first step in treating HHS?
Aggressive volume resuscitation is imperative and should be addressed before insulin administration to avoid intracellular fluid shifts (from falling glucose levels) that may worsen systemic perfusion. The fluid deficit is typically severe—on the order of 9 to 12 L. In patients with renal insufficiency or cardiac disease, central venous access may be necessary to monitor the response to therapy, and patients with altered mental status may require an indwelling urinary catheter.
25. Should isotonic or hypotonic fluids be used?
There is controversy regarding this issue; however, isotonic (0.9%) saline at a rate of approximately 1 to 2 L over the first hour is generally recommended. After the first hour, fluids may be changed on the basis of the serum sodium concentration: If serum Na is between 145 and 165 mEq/L, a change to half-normal saline (0.45%) may be considered; if serum Na is lower than 145 mEq/L, isotonic saline should be continued. Replacement of one half of the calculated fluid deficit over the initial 5 to 12 hours is recommended, with the balance of the deficit replaced over the subsequent 12 hours.
26. What role does insulin play in the treatment of HHS?
Continuous IV insulin infusion, as previously described for DKA, is helpful to reduce glucose levels at a predictable rate. Patients may be transitioned directly from IV to subcutaneous insulin as described for DKA. Because the presence of HHS suggests a significant insulin deficiency, most patients require discharge after being started on an insulin regimen, with the appropriateness of oral agents determined in the outpatient setting.
27. Describe the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
To be defined as hypoglycemia-induced, Whipple’s triad (low blood glucose, symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms by raising blood glucose) must be present. Symptoms can be divided into adrenergic and neuroglycopenic symptoms (Table 2-1), with different symptoms manifesting at progressively lower blood glucose levels. Adrenergic symptoms originate with the autonomic nervous system and include norepinephrine-mediated palpitations, tremor, anxiety and acetylcholine-mediated sweating, hunger, and paresthesias. Neuroglycopenic symptoms can include weakness, visual changes, behavior changes, confusion, seizure, loss of consciousness, and, if untreated, death; these symptoms represent the effects of low glucose levels on the central nervous system. Typical signs are pallor, diaphoresis, and tremor.
TABLE 2-1.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF HYPOGLYCEMIA
| Adrenergic | Diaphoresis |
| Palpitations | |
| Tremor | |
| Arousal/anxiety | |
| Pallor | |
| Hypertension | |
| Neuroglycopenic | Cognitive impairment |
| Fatigue | |
| Dizziness/faintness | |
| Visual changes | |
| Paresthesias | |
| Hunger | |
| Inappropriate behavior | |
| Focal neurologic deficits | |
| Seizures | |
| Loss of consciousness | |
| Death |
Adapted from Cryer PE, Gerich JE: Hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: insulin excess and defective glucose counterregulation. In Rifkin H, Porte E, editors: Ellenberg and Rifkin’s diabetes mellitus: theory and practice, ed 4, New York, 1990, Elsevier, pp 526–546.
28. Discuss therapy-related causes of hypoglycemia in diabetes.
It is impossible to mimic the peaks and troughs of a normal insulin secretory pattern with subcutaneous insulin injections, and even a perfectly designed insulin regimen can lead to hypoglycemia when the patient decreases food intake, delays a meal, or exercises even slightly more than usual. Menstruating women can experience hypoglycemia at the time of menses because of a rapid fall in estrogen and progesterone. Elderly patients given a sulfonylurea for the first time may respond with severe hypoglycemia.
29. What other conditions may contribute to the development of hypoglycemia?
In addition to therapy-related factors, disorders such as those listed in Table 2-2 may precipitate hypoglycemia.
TABLE 2-2.
CAUSES OF FASTING (POSTABSORPTIVE) HYPOGLYCEMIA
1. Drugs: insulin, sulfonylureas, alcohol
2. Critical organ failure: renal, hepatic, cardiac failure; sepsis; inanition
3. Hormonal deficiencies: cortisol and/or growth hormone; glucagon + epinephrine
5. Endogenous hyperinsulinism: beta-cell tumor (insulinoma); functional beta-cell hypersecretion; autoimmune hypoglycemia; ? ectopic insulin secretion
From Cryer PE, Gerich JE: Hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: insulin excess and defective glucose counterregulation. In Rifkin H, Porte E, editors: Ellenberg and Rifkin’s diabetes mellitus: theory and practice, ed 4, New York, 1990, Elsevier, pp 526-546.
30. What is “hypoglycemia unawareness”?
Defective counterregulation is often associated with hypoglycemia unawareness, in which the patient reports an absence of the normal adrenergic warning symptoms of hypoglycemia. In contrast, the predominant signs and symptoms are due to decreased delivery of glucose to the brain (neuroglycopenic symptoms). The cognitive impairment associated with neuroglycopenia may prevent the patient from responding appropriately to self-treat the hypoglycemia. The result may be a traumatic automobile accident, seizure, coma, or death.
31. Can hypoglycemia unawareness be prevented?
Studies suggest that hypoglycemia unawareness may be the body’s maladaptation to previous episodes of hypoglycemia. A single episode of hypoglycemia has been shown to reduce autonomic and symptomatic responses to hypoglycemia on the following day in normal subjects and in patients with type 1 diabetes. In contrast, meticulous prevention of hypoglycemia has been shown to reverse the defective counterregulation and reestablish the adrenergic symptoms after 3 months. Thus, meticulous attention to prevent hypoglycemia in patients without established autonomic neuropathy may be beneficial in reversing hypoglycemic unawareness.
32. How is hypoglycemia treated?
Mild hypoglycemia (BG 50-60 mg/dL) should be treated with 15 g of simple carbohydrate, such as 4 oz of unsweetened fruit juice or nondietetic soft drink. For more profound hypoglycemia, 15 to 20 g of simple carbohydrate should be ingested quickly, followed by 15 to 20 g of a complex carbohydrate, such as crackers or bread. All diabetic patients should be taught how to treat their hypoglycemia appropriately.
33. What should be done if the patient is unconscious?
Patients who are unconscious should not be given oral liquids. More viscous sources of sugar (e.g., honey, glucose gels, cake icing in a tube) can be carefully placed inside the cheek or under the tongue. Alternatively, 1 mg of glucagon may be injected intramuscularly. Glucagon indirectly raises the blood glucose level by increasing hepatic glucose production (glycogenolysis). In the hospital setting, IV dextrose (50% dextrose injection [D50]) is usually more accessible than glucagon and results in a prompt return of consciousness.
34. Discuss the role of education in treating hypoglycemia.
Instruction in the use of glucose gels and glucagon should be an essential part of training for all individuals living with insulin-treated diabetic patients. Patients and family members should be instructed not to overtreat hypoglycemia, particularly if it is mild. Overtreatment leads to subsequent hyperglycemia. Patients should also be instructed to test the blood glucose level when symptoms occur to confirm hypoglycemia whenever feasible. If testing is not possible, it is best to treat first. Patients taking diabetes medication should be instructed to test their glucose level before driving a vehicle. If the glucose level is lower than a preset level (e.g., < 125 mg/dL), the patient should be instructed to ingest a small source of carbohydrate before driving.
35. Summarize the common long-term complications of diabetes mellitus.
The chronic complications of diabetes can be divided into two broad categories: microvascular complications and macrovascular complications. Microvascular complications are considered relatively specific to diabetes; they are associated with pathologic endothelial changes, such as basement membrane thickening and increased vascular permeability, and can cause damage to the eyes (retinopathy), kidneys (nephropathy), and peripheral nerves (neuropathy). Macrovascular complications encompass an increased susceptibility to large blood vessel damage (atherosclerosis) and its ensuing complications.
36. What basic mechanism underlies the development of long-term diabetic complications?
Hyperglycemia is the major force underlying the microvascular complications of diabetes and has been implicated in the excessive risk for atherosclerosis seen in patients with insulin resistance. However, it is difficult to ascribe all of these observations to glucotoxicity alone.
37. How does chronic hyperglycemia affect cellular function?
 Nonenzymatic mass-action glycation of proteins: These proteins ultimately form advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs), which are associated with altered protein function. AGEs have been found in the connective tissue of blood vessels and in the renal glomerular matrix and have been shown to modify low-density lipoprotein (LDL) composition.
Nonenzymatic mass-action glycation of proteins: These proteins ultimately form advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs), which are associated with altered protein function. AGEs have been found in the connective tissue of blood vessels and in the renal glomerular matrix and have been shown to modify low-density lipoprotein (LDL) composition.
 Enzymatic conversion of glucose to sorbitol by aldose reductase in the eyes and peripheral nerves: Because the cellular clearance of sorbitol is extremely slow, it accumulates as an osmotically active molecule. This accumulation is also associated with neuronal myoinositol depletion.
Enzymatic conversion of glucose to sorbitol by aldose reductase in the eyes and peripheral nerves: Because the cellular clearance of sorbitol is extremely slow, it accumulates as an osmotically active molecule. This accumulation is also associated with neuronal myoinositol depletion.
 Excess intracellular glucosamine: Another product of glucose, intracellular glucosamine has been linked to endothelial dysfunction and to impaired insulin action.
Excess intracellular glucosamine: Another product of glucose, intracellular glucosamine has been linked to endothelial dysfunction and to impaired insulin action.
 Activation of protein kinase C (PKC) by glucose: Thought to be due to depressed nitric oxide production and increased endothelin-1 activity, activation of PKC has been shown to mediate retinal and renal blood flow abnormalities and to increase endothelial cell permeability.
Activation of protein kinase C (PKC) by glucose: Thought to be due to depressed nitric oxide production and increased endothelin-1 activity, activation of PKC has been shown to mediate retinal and renal blood flow abnormalities and to increase endothelial cell permeability.
 Hyperglycemia-driven oxidative stress: The resulting activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) has been tied to glycemic injury and may serve, in part, to increase substrate flux into AGE, polyol, and glucosamine formation and to promote PKC activation.
Hyperglycemia-driven oxidative stress: The resulting activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) has been tied to glycemic injury and may serve, in part, to increase substrate flux into AGE, polyol, and glucosamine formation and to promote PKC activation.
38. Describe the characteristics of diabetic retinopathy.
Significant diabetic retinopathy may progress without symptoms. The initial visible lesions are microaneurysms that form on the terminal capillaries of the retina. Increased capillary permeability is manifested by the leaking of proteinaceous fluid, causing hard exudates. Dot-and-blot hemorrhages result from leaking of red blood cells. These findings by themselves do not lead to visual loss and are categorized as nonproliferative retinopathy (Table 2-3).
TABLE 2-3.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF DIABETIC EYE DISEASE
| Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy | Retinal microaneurysms |
| Occasional blot hemorrhages | |
| Hard exudates | |
| One or two soft exudates | |
| Preproliferative diabetic retinopathy | Presence of venous beading |
| Significant areas of large retinal blot hemorrhages | |
| Multiple cotton-wool spots (nerve fiber infarcts) | |
| Multiple intraretinal microvascular abnormalities | |
| Proliferative diabetic retinopathy | New vessels on the optic disc (NVD) |
| New vessels elsewhere on the retina (NVE) | |
| Preretinal or vitreous hemorrhage | |
| Fibrous tissue proliferation | |
| High-risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy | NVD with or without preretinal or vitreous hemorrhage |
| NVE with preretinal or vitreous hemorrhage | |
| Diabetic macular edema | Any thickening of retina < 2 disc diameters from center of macula |
| Any hard exudates < 2 disc diameters from center of macula with associated thickening of the retina | |
| Any nonperfused retina inside the temporal vessel arcades | |
| Any combination of the above |
From Centers for Disease Control: The prevention and treatment of complications of diabetes mellitus, Atlanta, 1991, Division of Diabetes Translation, Department of Health and Human Services.
Proliferative retinopathy (see Table 2-3) develops when the retinal vessels are further damaged, causing retinal ischemia. The ischemia triggers new, fragile vessels to develop, a process termed neovascularization. These vessels may grow into the vitreous cavity and may bleed into preretinal areas or vitreous, causing significant vision loss. Loss of vision also may result from retinal detachment secondary to the contraction of fibrous tissue, which often accompanies neovascularization. Diabetic macular edema occurs when fluid from abnormal vessels leaks into the macula. It is detected with indirect funduscopy as the finding of a thickened retina near the macula and is commonly associated with the presence of hard exudates.
39. How common is diabetic retinopathy and how is it managed?
If glucose levels are not controlled, up to 70% of type 1 diabetics may experience proliferative retinopathy over their lifetime. Among type 2 diabetics, 21% may have significant nonproliferative and even proliferative retinopathy or macular edema at the time of diagnosis. This may be due to the long undiagnosed period of hyperglycemia that often occurs in people with type 2 diabetes.
Vision-threatening retinopathy can be managed with retinal photocoagulation, surgery (principally vitrectomy), and intraocular injections of anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) compounds or steroids. Fenofibrate may also help.
40. What are the risk factors for development of diabetic retinopathy?
 Diabetic nephropathy is strongly associated with proliferative retinopathy in type 1 diabetes and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes.
Diabetic nephropathy is strongly associated with proliferative retinopathy in type 1 diabetes and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes.
41. How serious a problem is diabetic nephropathy, and how can its progression be slowed?
Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States. Its progression follows a predictable pattern characterized into stages I through V (Table 2-4).
TABLE 2-4.
STAGING OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
| STAGE | ESTIMATED GFR (ML/MIN) | FINDINGS |
| 1 | 90 | Asymptomatic, ± HTN, renal hypertrophy, possible increase in GFR (GFR > 125 mL/min confers high risk of progression) |
| 2 | 60-89 | ± Edema, ± HTN, glomerular histologic changes |
| 3 | 30-59 | Edema, HTN, anemia, microalbuminuria (urinary albumin excretion 30-300 mg/day) |
| 4 | 15-29 | Edema, fatigue, dyspnea, HTN, electrolyte abnormalities, proteinuria (urinary albumin excretion > 300 mg/day or total protein excretion > 500 mg/day) |
| 5 | < 15 | Anorexia, dyspnea, HTN, encephalopathy, end-stage renal disease |
Improved blood pressure and glucose control, the use of either an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) or the reduction of dietary protein intake can slow the rate of progression of renal failure in patients with nephropathy.
42. What is the risk that nephropathy will develop in a diabetic person?
Older epidemiologic studies suggest that patients with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes are at highest risk for nephropathy, which affects 30% of these patients. The risk of nephropathy is about 10 times less for patients with type 2 diabetes, but because of the higher prevalence of type 2 diabetes, this group currently outnumbers type 1 patients with end-stage renal disease. One explanation for the difference in risk for nephropathy between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that the development of proteinuria in people with type 2 diabetes is associated with increased mortality.
43. What factors affect the development of diabetic nephropathy?
In addition to glycemic control, genetic factors play a key role in determining risk for diabetic nephropathy. Genes coding for essential hypertension appear to increase the risk. Known risk factors for diabetic nephropathy are as follows:
44. Name the types of diabetic neuropathies.
There are four principal types: distal symmetric polyneuropathy, diabetic amyotrophy, diabetic mononeuropathy, and autonomic neuropathy. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy is the most common form and is slowly progressive. Amyotrophy manifests as pain and weakness in the thighs and may spontaneously improve. Mononeuropathy may affect both cranial and spinal nerves. Forms of autonomic neuropathy include gastroparesis and orthostatic hypotension.
45. Summarize the symptoms of distal symmetric polyneuropathy.
The disorder is usually discovered on physical examination by finding loss of vibratory sense in the toes and loss of ankle reflexes. Light touch and pinprick sensations are subsequently lost. Common associated symptoms are paresthesias and numbness of the feet, especially at night. The paresthesias may evolve to severe knifelike or burning pain, which can be disabling.
46. Explain the basic pathophysiology of distal symmetric polyneuropathy.
Pathologically, the nerves show axonal degeneration. Sensory loss or pain in the hands may also occur, but more commonly it is a manifestation of an entrapment neuropathy, such as carpal tunnel syndrome. Entrapment neuropathies are common in patients with diabetes and may result from increased susceptibility of these nerves to external pressure.
47. What causes the foot problems in patients with diabetes?
Loss of proprioceptive nerve fibers can result in an abnormal gait, leading to “pressure spots” on the foot that are signaled by the presence of thick calluses. If untreated, the calluses may ulcerate and become infected. Neuropathy, vascular disease, and predisposition to infection are the primary pathogenic components in the increased incidence of foot injury and amputation in diabetic patients.
48. How common is diabetic autonomic neuropathy? How does it affect survival rates?
Depending on the sophistication of testing used, up to 90% of people with diabetes have some degree of autonomic dysfunction. However, less than 50% of affected people are symptomatic. Patients with clinically significant autonomic neuropathy have a 10-year survival rate less than 50%. Both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems may be affected by diabetic neuropathy, and because these neuropathies initially damage nerves with the longest axons, patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy also have readily apparent peripheral neuropathy.
49. Describe the classic signs of diabetic autonomic neuropathy.
Unexplained resting tachycardia and postural hypotension (with absence of fever, hypoglycemia, hyperthyroidism, etc.) are characteristic. Gastrointestinal symptoms are due to lack of peristalsis in the stomach (gastroparesis) or intestine and include early satiety, bloating, nausea, belching, abdominal distension, constipation, and diarrhea. Urinary retention or overflow incontinence may indicate autonomic neuropathy involving the urinary bladder. Erectile dysfunction is also a common symptom of autonomic neuropathy in diabetic men.
50. How is diabetic autonomic neuropathy diagnosed?
Lack of R-R variation on an electrocardiogram during deep breathing or the Valsalva maneuver can be used to confirm the diagnosis. Postural hypotension can be diagnosed by documenting a fall in upright blood pressure without a concurrent increase in pulse rate. Gastroparesis is diagnosed by the demonstration of prolonged gastric emptying using standardized radiolabeled meals; however, even mild hyperglycemia (BG > 150 mg/dL) at the time of the test may functionally slow gastric emptying. Urinary and erectile problems are diagnosed by careful history taking.
51. How is painful diabetic neuropathy treated?
Multiple medications have been tried, with mixed success. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids, and the serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). The most effective medications among those currently available appear to be pregabalin (Lyrica; starting dose 50 mg three times daily [TID] with titration to 100 mg TID, if tolerated), gabapentin (Neurontin; starting dose 300 mg twice daily with titration to 600 mg TID, as necessary), and the SNRI duloxetine (Cymbalta; dose 60 mg daily).
52. What are the risks associated with macrovascular disease in diabetes?
Patients with diabetes are at a twofold to fourfold higher risk for both cardiovascular disease (CVD) and peripheral vascular disease than the nondiabetic population. Women with diabetes have as high a risk for CVD as men. The commonly identified risk factors for CVD—smoking, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension—also adversely affect CVD risk in people with diabetes. As a consequence, three out of four people with diabetes will die from CVD.
53. How can macrovascular disease be prevented in the diabetic population?
Cardiovascular risk factor reduction should be initiated at the first visit and pursued as aggressively in diabetic patients as in patients with known coronary artery disease. Aggressive blood pressure control is strongly supported by later randomized controlled trials, with a target blood pressure less than 130 (systolic)/80 (diastolic) mm Hg. Some studies have suggested that ACE inhibitors may be more effective than other antihypertensive agents in preventing CVD events and are currently the antihypertensive agents of choice. Control of hyperlipidemia should be pursued just as aggressively; the recommended goal for LDL cholesterol is less than 100 mg/dL (< 70 mg/dL in high-risk patients). Improving glycemic control typically causes a significant reduction in triglyceride levels and modest reduction in LDL cholesterol. If goals for lipids are not achieved through glycemic control, diet, and exercise, then antihyperlipidemic drug therapy should be considered. The hydroxyl methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors (statins) are the drug class of choice. Smoking cessation should be strongly encouraged, as should exercise and weight loss (if the patient is overweight). Low-dose aspirin therapy is also recommended in high-risk individuals, but there is considerable controversy about the effectiveness of this intervention.
54. Does aggressive lipid-lowering therapy improve cardiac outcomes in diabetic patients?
Yes. A bevy of studies have proved the benefit of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in reducing the cardiovascular burden associated with diabetes by approximately 50%. On the basis of these studies, aggressive lipid-lowering therapy should be advocated in all diabetic patients, particularly those with known coronary artery disease.
55. How important is glycemic control in preventing the chronic complications of diabetes mellitus?
As discussed in Chapter 1, the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) involving people with type 1 diabetes and the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) using subjects with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes have established that improving glycemic control effectively reduces the risk of development of microvascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular outcomes were also significantly reduced in the long-term follow-up of subjects in both studies. However, several later trials involving people with long-standing type 2 diabetes (ACCORD [Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes], ADVANCE [Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron MR Controlled Evaluation], and VADT [VA Diabetes Trial]) have suggested a limited role for tight glucose control in preventing the cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes. It must be kept in mind that both the DCCT and the UKPDS were conducted prior to the introduction of statins as well as ACE inhibitors and ARBs and the current standards of percutaneous coronary interventions. In addition, there was a significant reduction in microvascular complications. Indeed, the diminution in microvascular complications in the ADVANCE trial and VADT was clearly related to both the duration of diabetes prior to study entry and the degree of hyperglycemia as represented by the initial hemoglobin A1C value. Without question, management of diabetes must be focused early in the disease.
56. Does improved glycemic control in hospitalized patients affect outcome?
Adults with diabetes are six times more likely to be hospitalized than those without diabetes, and once hospitalized, they have a higher risk of mortality and a 30% longer length of stay. Under any circumstances, poorly controlled diabetes is a catabolic condition, and in hospitalized patients with diabetes who are under physiologic stress, catabolism is certainly detrimental. In addition, leukocytes and immune function are impaired by hyperglycemia. An early single-center study comparing very tight glucose management (BG range 80-110 mg/dL) with usual care (BG range 180-200 mg/dL) in patients in surgical intensive care units (ICUs) reported reductions in in-hospital mortality by 34%, sepsis by 46%, hemodialysis rate by 44%, transfusions by 50%, and critical illness–related polyneuropathy by 44%. Subsequently, several prospective and observational trials documented mixed results, and this issue was compounded by several meta-analyses that offered mixed conclusions about very tight glucose control in the ICU setting. A multicenter trial, Normoglycemia in Intensive Care Evaluation—Survival Using Glucose Algorithm Regulation (NICE-SUGAR), compared tight glucose control (BG target 81-108 mg/dL) with usual therapy (BG target < 180 mg/dL) with the primary end point being mortality at 90 days from study entry. Mortality was unexpectedly increased by 14% in the intensively managed group. Also, there was no difference in secondary end points, including length of stay, rate of organ failure, and mechanical ventilation. As a result, the current consensus is to view blood glucose no greater than 180 mg/dL as the threshold for starting intravenous insulin in the ICU setting and establishing a blood glucose target between 140 and 180 mg/dL.
The data are less robust in patients hospitalized in non–critical care settings, but a meta-analysis has suggested that improved glycemic control significantly reduces the risk of infection and likely lowers the risk of hypoglycemia. Consensus statements have established treatment targets for non–critical care patients: preprandial BG less than 140 mg/dL and random BG level less than 180 mg/dL.
, The ACCORD Study Group. Long-term effects of intensive glucose lowering on cardiovascular outcomes. N Engl J Med 2011;364:818–828.
, The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2560–2572.
, American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—-2012. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(Suppl 1):S11–S63.
Antionetti, DA, Klein, R. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1227–1239.
Chong, MS, Hester, J, Diabetic painful neuropathy. current and future treatment options. Drugs 2007;67:569–585.
Chrysant, SG, The ALLHAT study. results and clinical implications. Q J Med 2003;96:771–772.
Collins, R, Armitage, J, Parish, S, et al. MRC/BHF heart protection study of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin in 5963 people with diabetes: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361:2005–2016.
, DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Intensive diabetes therapy and glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2011;365:2366–2376.
, The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2643–2653.
Duckworth, W, Abrira, C, Moritz, T, et al. Glucose control and vascular outcomes in veterans with type diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:129–139.
Folwaczny, C, Wawarta, R, Otto, B, et al. Gastric emptying of solid and liquid meals in healthy controls compared with long-term type-1 diabetes mellitus under optimal glucose control. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2003;111:223–229.
Fritsche, A, Stefan, N, Häring, H, et al. Avoidance of hypoglycemia restores hypoglycemia awareness by increasing β-adrenergic sensitivity in type 1 diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134:729–736.
Haffner, SM, Lehto, S, Ronnemaa, T, et al. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:229–234.
Hasler, WL, Gastroparesis. symptoms, evaluation, and treatment. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2007;36:619–647.
Hollenberg, NK. Treatment of the patient with diabetes mellitus and risk of nephropathy. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:125–130.
Kitabchi, A, Wall, BW, Management of diabetic ketoacidosis. diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. Crit Care Clin 2001;17:75–106.
Murad, MH, Coburn, J, Coto-Yglesias, F, et al, Glycemic control in non-critically ill hospitalized patients. a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:49–58.
, The NICE-SUGAR Study Investigators. Intensive versus conventional glucose control in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1283–1297.
Pyörålå, K, Pederson, TR, Kjekshus, J, et al, Cholesterol lowering with simvastatin improves prognosis of diabetic patients with coronary heart disease. a subgroup analysis of the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Diabetes Care 1997;20:614–620.
Reusch, JEB, Diabetes, microvascular complications, and cardiovascular complications. what is it about glucose. J Clin Invest 2003;112:986–988.
Ritz, E, Orth, SR. Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1127–1133.
Russell, M, Silverman, A, Fleg, JL, et al. Achieving lipid targets in adults with type 2 diabetes—the SANDS Study. J Clin Lipidol. 2010;4:435–443.
Sarafidis, PA. Antihypertensive therapy in the presence of proteinuri. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:12–26.
Simó, R, Hernández, C. Advances in the medical treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1556–1562.
Umpierrez, GE, Hellman, R, Korytowski, MT, et al, Management of hyperglycemia in hospitalized patients in non-critical care setting. an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:16–38.
Van den Berghe, G, Wouters, P, Weekers, F, et al. Intensive insulin therapy in the surgical intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1301–1308.
Vinik, AI, Mehrabyan, A. Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Compr Ther. 2003;29:130–145.