Findings identical to calculous cholecystitis (except gallstones)
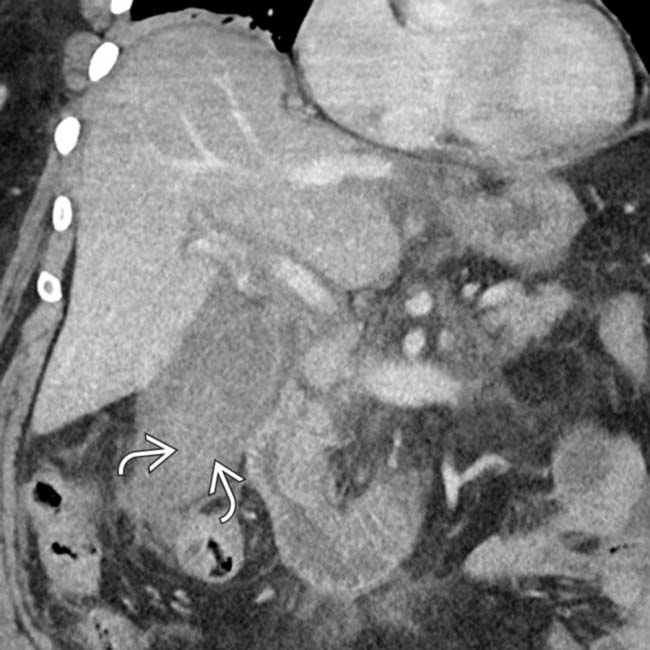
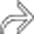 , concerning for gangrenous cholecystitis.
, concerning for gangrenous cholecystitis.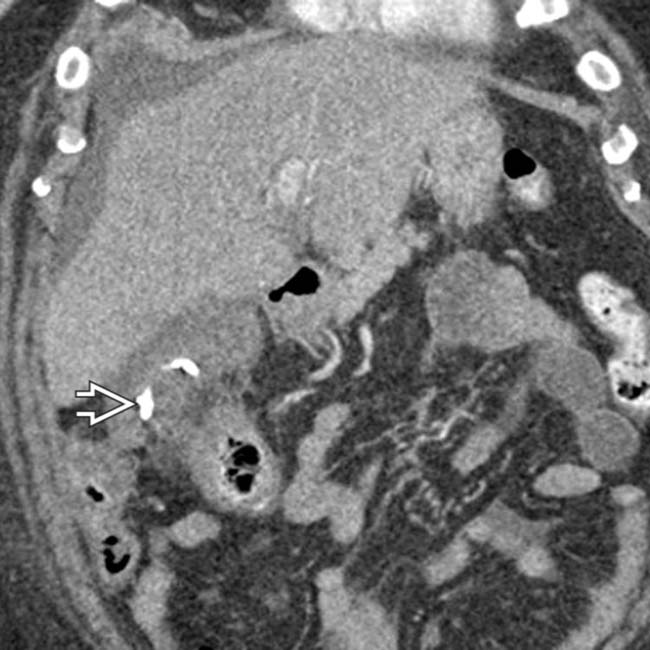
 , a common temporizing measure in critically ill patients too unstable for cholecystectomy.
, a common temporizing measure in critically ill patients too unstable for cholecystectomy.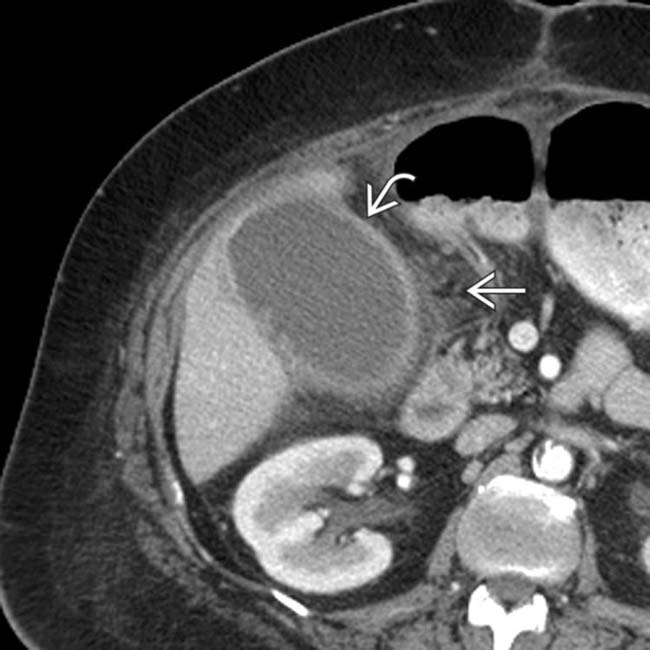
 , and pericholecystic fat infiltration
, and pericholecystic fat infiltration  . No gallstones were identified at ultrasound.
. No gallstones were identified at ultrasound.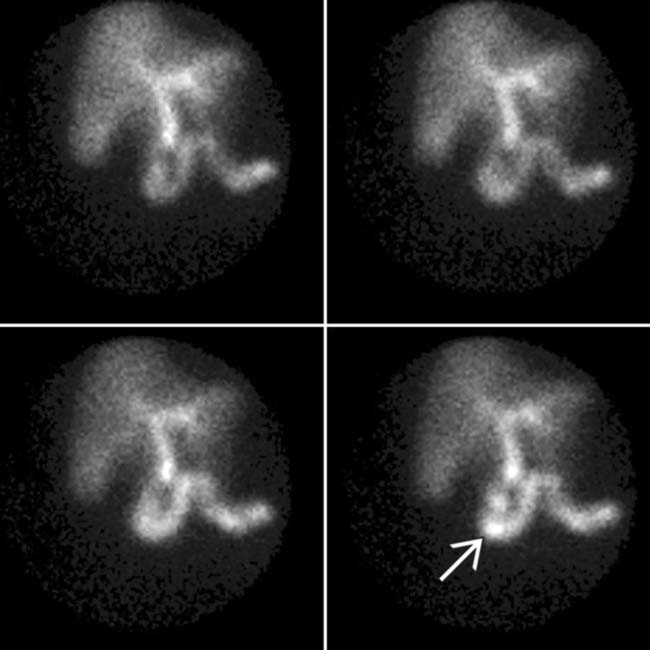
 but no GB activity 30 minutes post tracer administration. No GB activity was shown after morphine administration (an observation that increases exam specificity).
but no GB activity 30 minutes post tracer administration. No GB activity was shown after morphine administration (an observation that increases exam specificity).IMAGING
General Features
Ultrasonographic Findings
• Positive sonographic Murphy sign (pain with insonation over GB that is accentuated with deep breathing)
• Complications
 Gangrenous cholecystitis: Asymmetric wall thickening, intraluminal linear membranes, and echogenic material due to sloughed mucosa and irregularity/ulcerations of GB wall
Gangrenous cholecystitis: Asymmetric wall thickening, intraluminal linear membranes, and echogenic material due to sloughed mucosa and irregularity/ulcerations of GB wall
 Emphysematous cholecystitis: Intramural and intraluminal gas with multiple bright echogenic reflectors and “dirty” posterior acoustic shadowing
Emphysematous cholecystitis: Intramural and intraluminal gas with multiple bright echogenic reflectors and “dirty” posterior acoustic shadowing
 Gangrenous cholecystitis: Asymmetric wall thickening, intraluminal linear membranes, and echogenic material due to sloughed mucosa and irregularity/ulcerations of GB wall
Gangrenous cholecystitis: Asymmetric wall thickening, intraluminal linear membranes, and echogenic material due to sloughed mucosa and irregularity/ulcerations of GB wall
 Emphysematous cholecystitis: Intramural and intraluminal gas with multiple bright echogenic reflectors and “dirty” posterior acoustic shadowing
Emphysematous cholecystitis: Intramural and intraluminal gas with multiple bright echogenic reflectors and “dirty” posterior acoustic shadowing
CT Findings
• Imaging findings are identical to acute calculous cholecystitis (except for absence of gallstones)
• Uncomplicated acalculous cholecystitis
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
PATHOLOGY
General Features
• Not associated with obstruction of cystic duct or GB neck by stones or sludge
• Pathophysiology
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
• Most common signs/symptoms
 and reactive thickening of the adjacent colon
and reactive thickening of the adjacent colon  . Patients recovering from surgical or medical emergencies are at risk for acalculous cholecystitis.
. Patients recovering from surgical or medical emergencies are at risk for acalculous cholecystitis.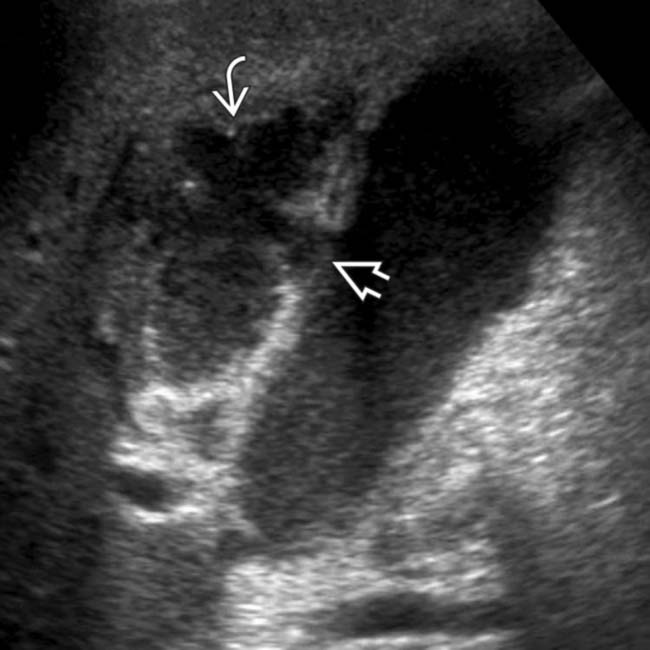
 , and a complex pericholecystic fluid collection
, and a complex pericholecystic fluid collection  . Acalculous cholecystitis was confirmed at surgery.
. Acalculous cholecystitis was confirmed at surgery.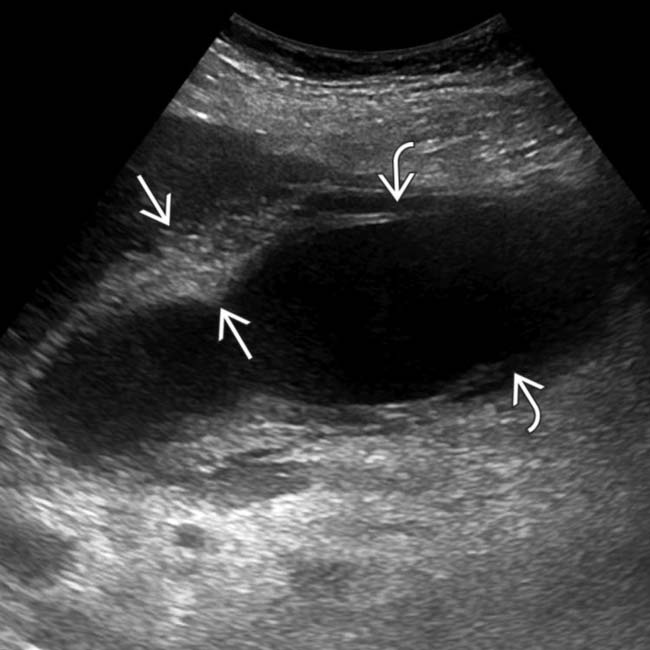
 and a linear echogenic band adjacent to the wall
and a linear echogenic band adjacent to the wall  ; features compatible with mucosal sloughing and acalculous, gangrenous cholecystitis.
; features compatible with mucosal sloughing and acalculous, gangrenous cholecystitis.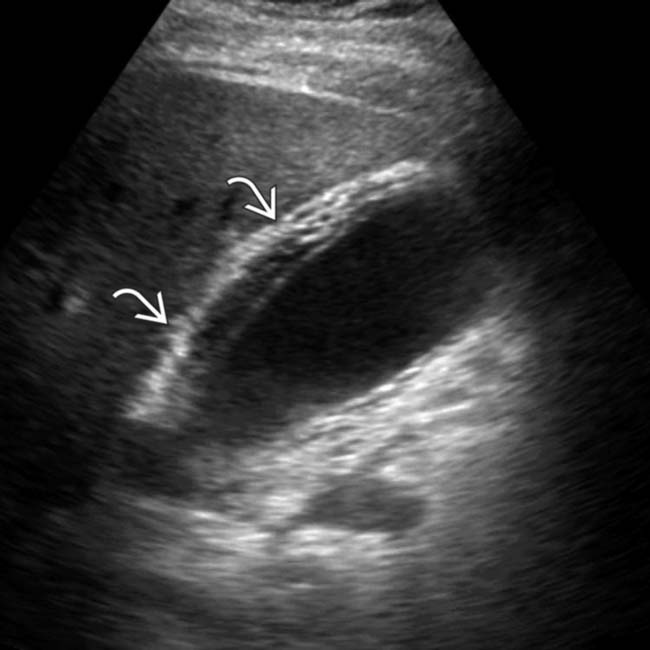
 and no gallstones. A sonographic Murphy sign was elicited. Cholecystectomy revealed gangrenous, acute acalculous cholecystitis.
and no gallstones. A sonographic Murphy sign was elicited. Cholecystectomy revealed gangrenous, acute acalculous cholecystitis.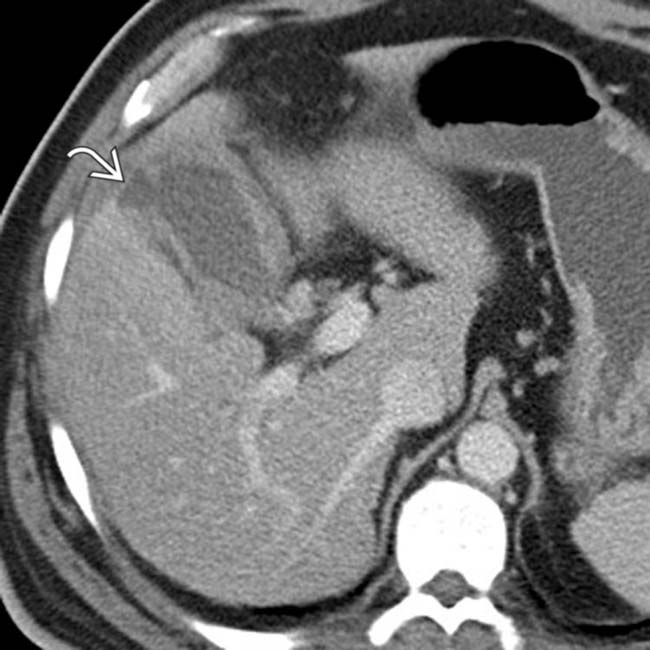
 .
.
 . The appearance is highly suggestive of gangrenous cholecystitis with contained perforation, a diagnosis confirmed at surgery.
. The appearance is highly suggestive of gangrenous cholecystitis with contained perforation, a diagnosis confirmed at surgery.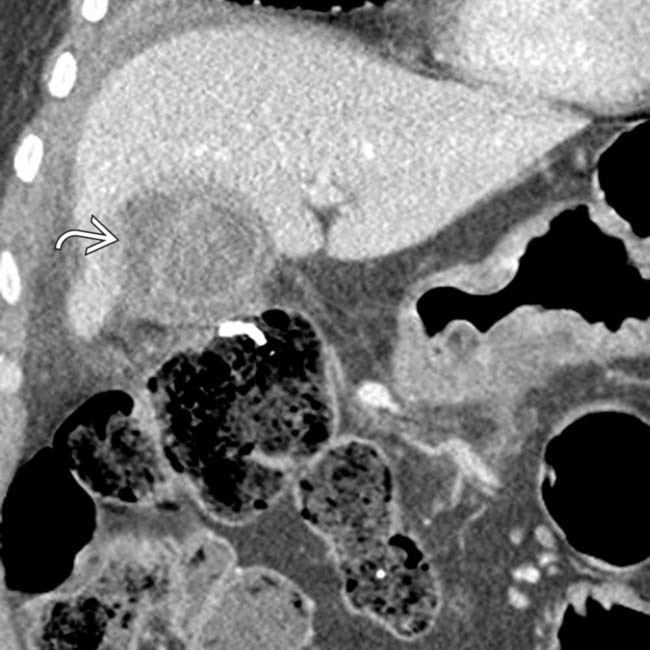
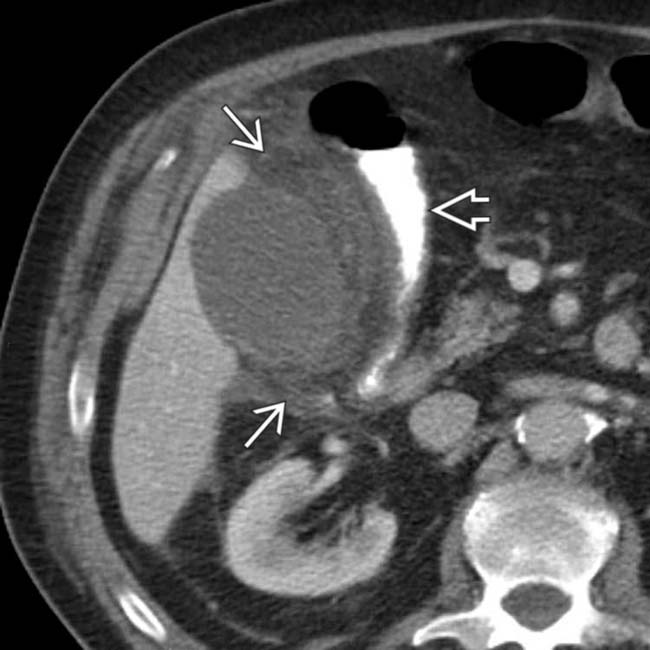
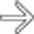
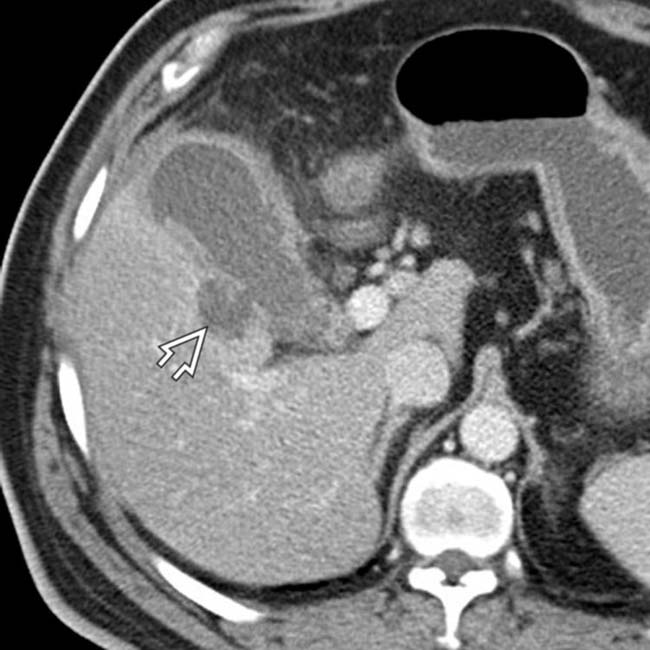
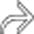 , suggesting perforation. While no discrete defect was seen on CT, gangrenous cholecystitis was confirmed at surgery.
, suggesting perforation. While no discrete defect was seen on CT, gangrenous cholecystitis was confirmed at surgery.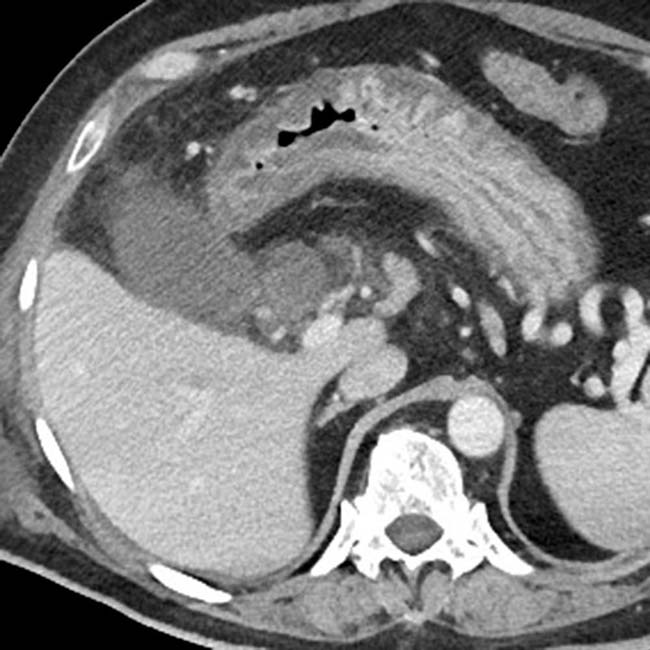
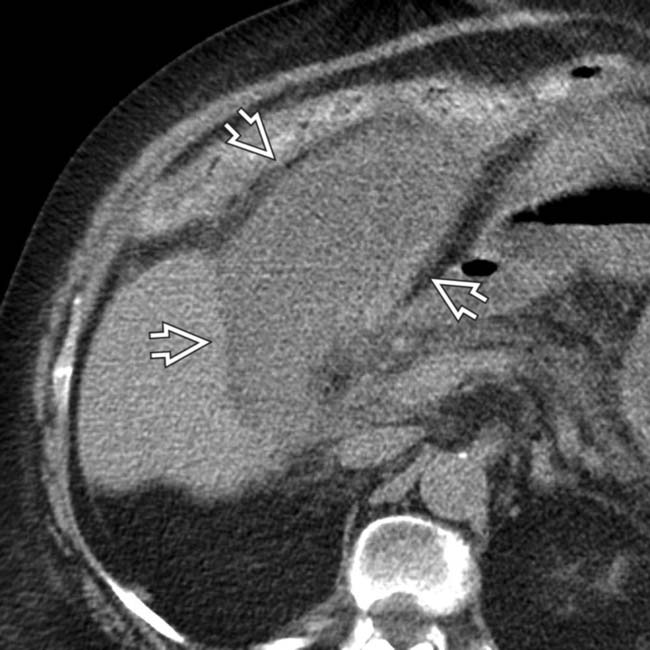
 , irregular wall thickening, and pericholecystic fat infiltration. The patient expired 1 day later.
, irregular wall thickening, and pericholecystic fat infiltration. The patient expired 1 day later.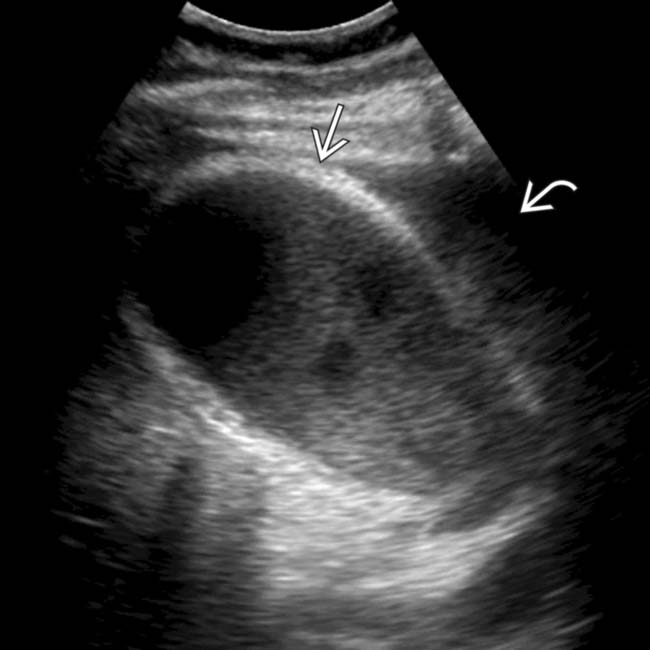
 , and pericholecystic fluid
, and pericholecystic fluid  .
.



































































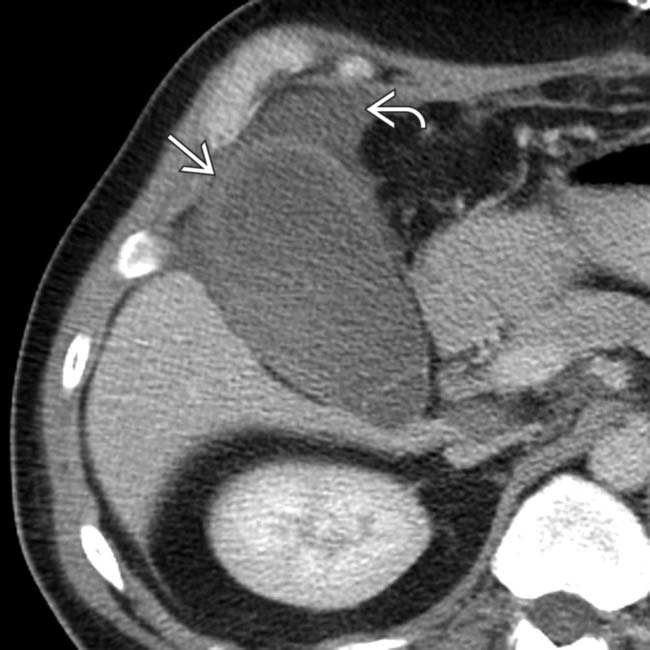
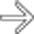
 , and adjacent fluid
, and adjacent fluid  . Ongoing sepsis and persistent GB thickening on follow-up ultrasound exams prompted a cholecystotomy. The aspirate was positive for E. coli and Enterococcus faecalis.
. Ongoing sepsis and persistent GB thickening on follow-up ultrasound exams prompted a cholecystotomy. The aspirate was positive for E. coli and Enterococcus faecalis.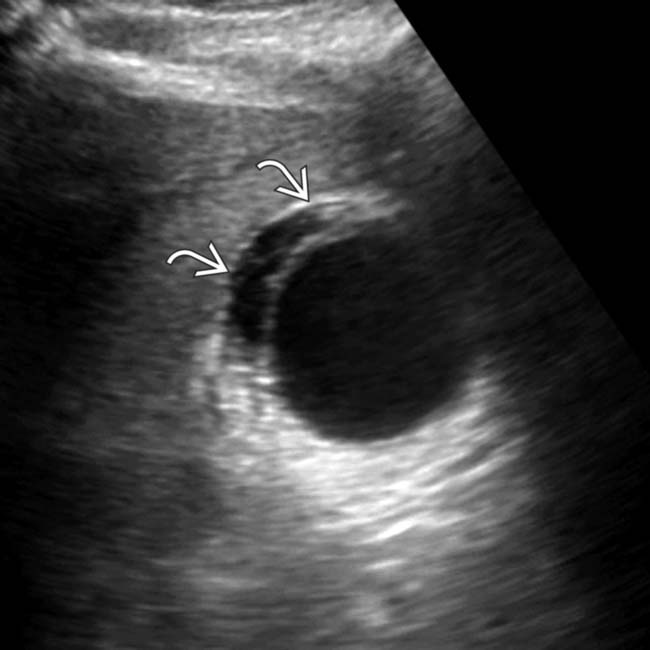
 , found to represent acalculous cholecystitis.
, found to represent acalculous cholecystitis.


