Simple fluid density (0-10 HU) or slightly hyperdense
 “Abscess” suggests a discrete, drainable fluid collection: Differentiate from ill-defined inflammation and fluid that is not drainable (i.e. phlegmon)
“Abscess” suggests a discrete, drainable fluid collection: Differentiate from ill-defined inflammation and fluid that is not drainable (i.e. phlegmon)• US: Complex fluid collection with internal low-level echoes, membranes, or septations
 with gas bubbles
with gas bubbles  and an enhancing capsule
and an enhancing capsule  , findings diagnostic for an abdominal abscess.
, findings diagnostic for an abdominal abscess.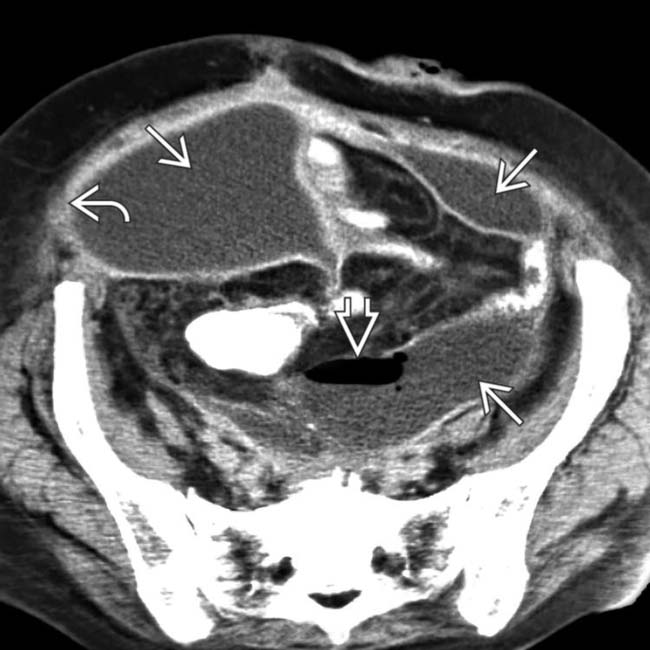
 with prominently enhancing capsules
with prominently enhancing capsules  and mass effect on adjacent structures, representing abdominal abscesses. Note the air-fluid level
and mass effect on adjacent structures, representing abdominal abscesses. Note the air-fluid level  within one of the abscesses.
within one of the abscesses.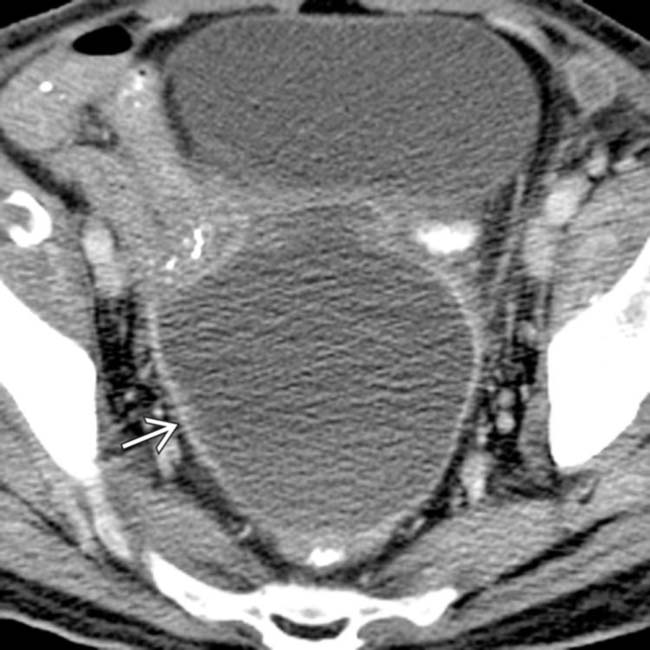
 following hysterectomy. Note the presence of a discrete enhancing rim and mass effect on adjacent loops of bowel and the bladder.
following hysterectomy. Note the presence of a discrete enhancing rim and mass effect on adjacent loops of bowel and the bladder.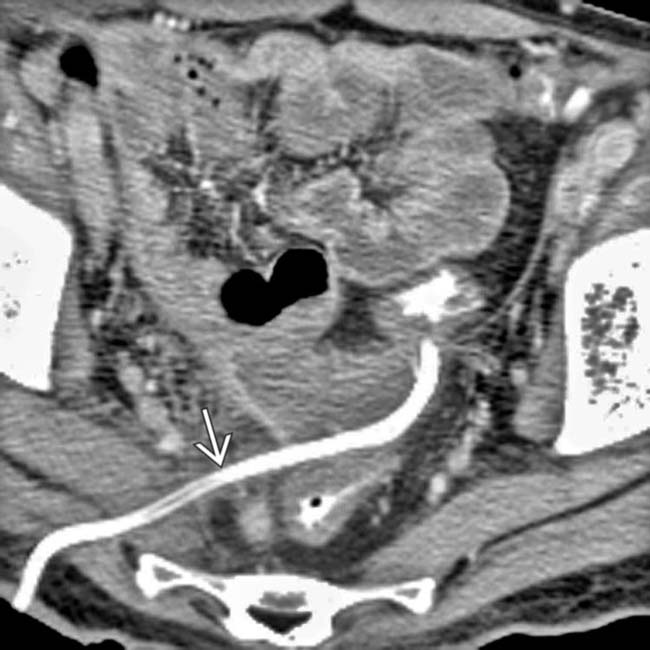
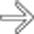 using a transgluteal approach. The abscess has almost completely resolved following drainage.
using a transgluteal approach. The abscess has almost completely resolved following drainage.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• Presence of internal gas (∼ 50% of cases) in absence of intervention highly suspicious for infected collection
Ultrasonographic Findings
• Complex fluid collection with internal low-level echoes, membranes, or septations on US
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Treatment
• Options, risks, complications
 Percutaneous abscess drainage (PAD)
Percutaneous abscess drainage (PAD)
 Contraindications for PAD related to abscess
Contraindications for PAD related to abscess
 Percutaneous abscess drainage (PAD)
Percutaneous abscess drainage (PAD)
– Best candidates have well-defined, encapsulated, fluid-filled abscesses > 3 cm with safe catheter access route
– Drainage can be performed under CT or US guidance, with multiple approaches possible (transcutaneous, transgluteal, transrectal, transvaginal)
 Contraindications for PAD related to abscess
Contraindications for PAD related to abscess
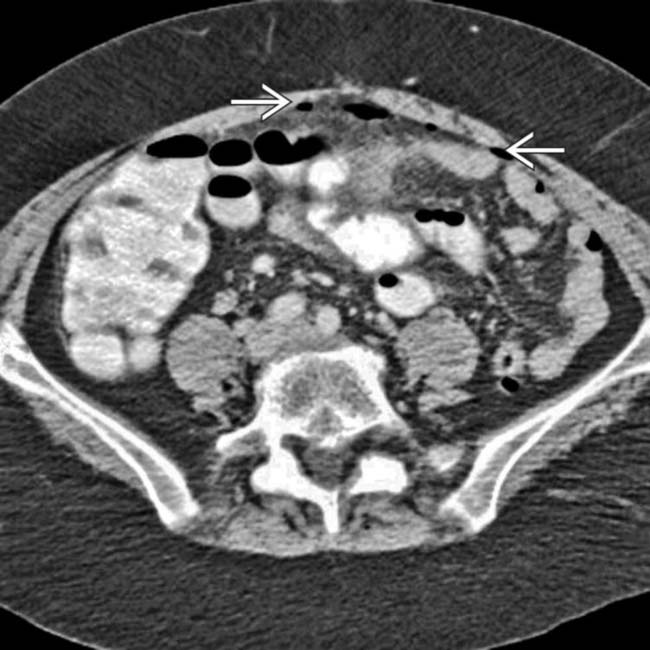
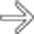 .
.
 immediately adjacent to a segment of sigmoid colon with extensive diverticulosis
immediately adjacent to a segment of sigmoid colon with extensive diverticulosis  , which proved to be the source of the free air and abscesses.
, which proved to be the source of the free air and abscesses.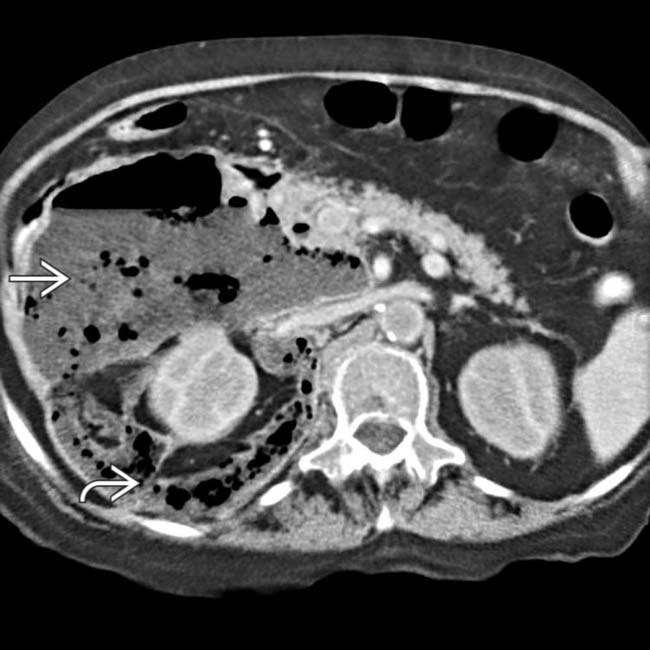
 dissecting through the retroperitoneal spaces, especially the anterior pararenal space and the interfascial plane
dissecting through the retroperitoneal spaces, especially the anterior pararenal space and the interfascial plane  .
.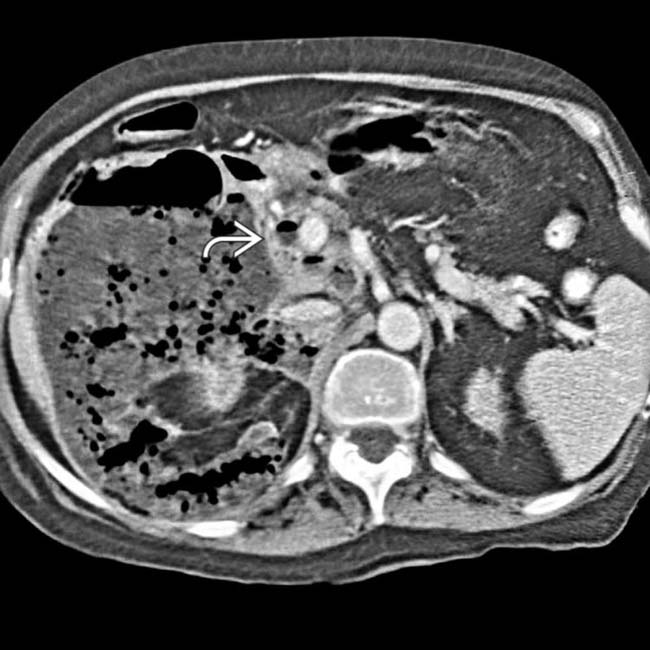
 at the papillotomy site.
at the papillotomy site.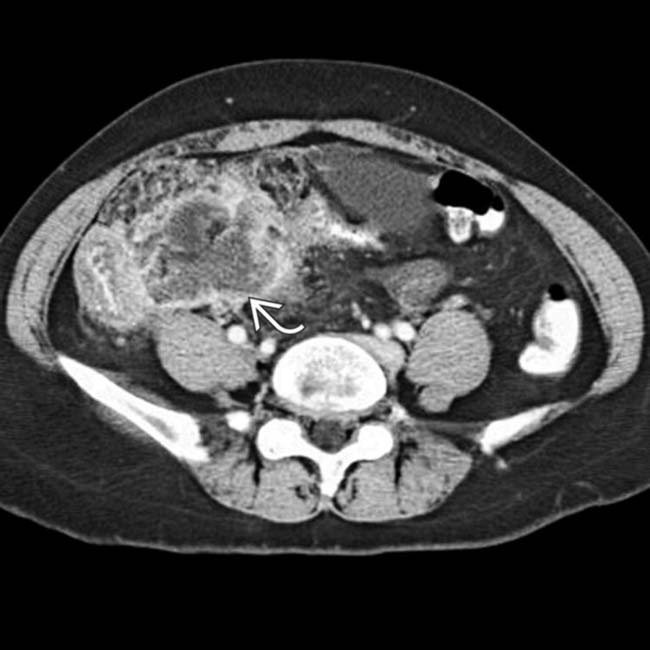
 with mass effect displacing the small bowel, bladder, and uterus.
with mass effect displacing the small bowel, bladder, and uterus.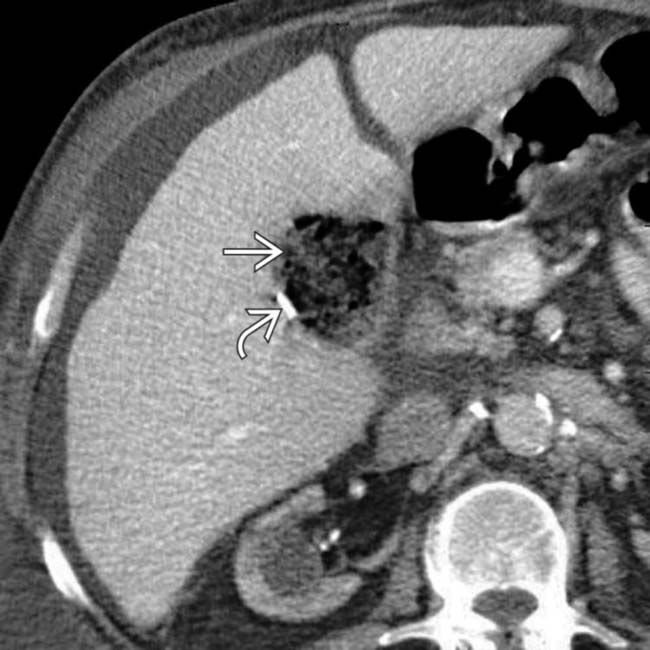
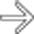
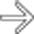
 , but very little fluid, in the cholecystectomy bed. Surgical clips
, but very little fluid, in the cholecystectomy bed. Surgical clips  are also seen. This represents oxidized cellulose (Surgicel), which was placed for hemostasis at surgery, and not an abscess.
are also seen. This represents oxidized cellulose (Surgicel), which was placed for hemostasis at surgery, and not an abscess.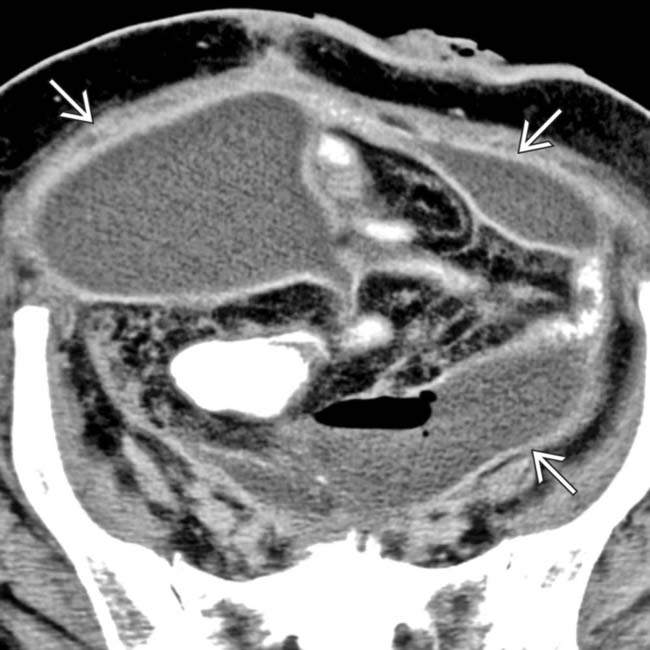
 .
.
 , cecal thickening, and adjacent fat stranding
, cecal thickening, and adjacent fat stranding  .
.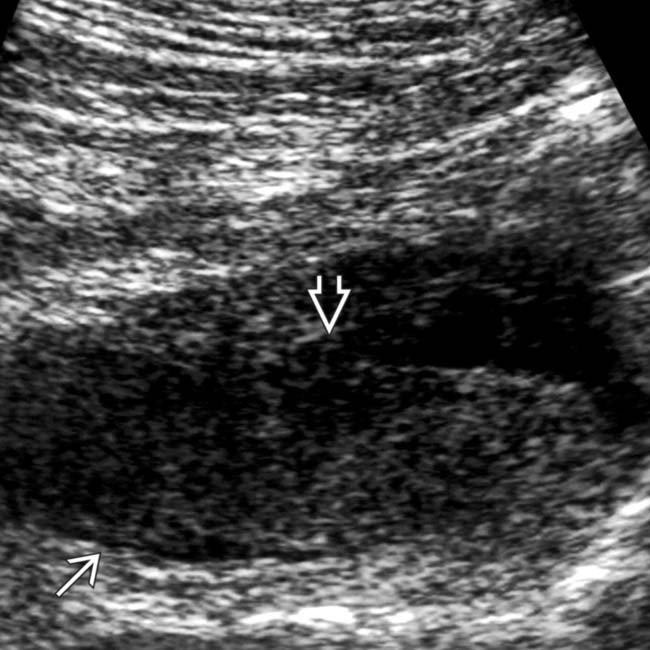
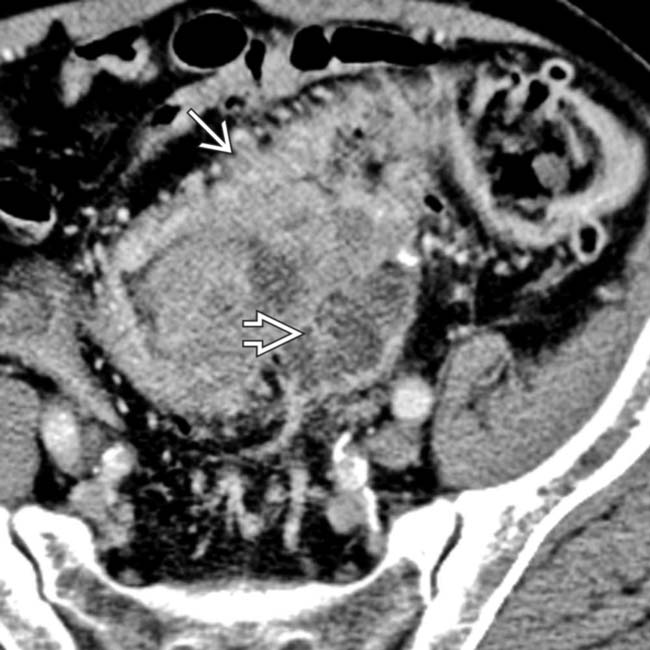
 with fluid-fluid level
with fluid-fluid level  .
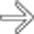
.
 and ill-defined adjacent fluid collection
and ill-defined adjacent fluid collection  .
.
 .
.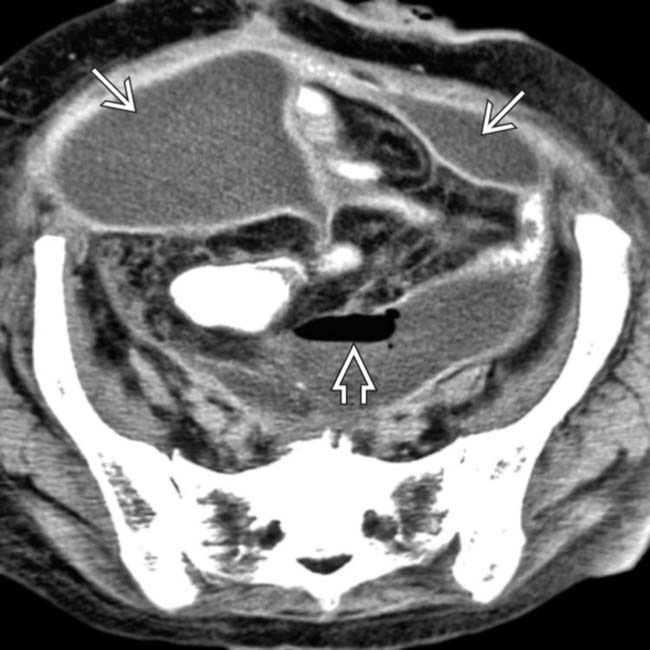
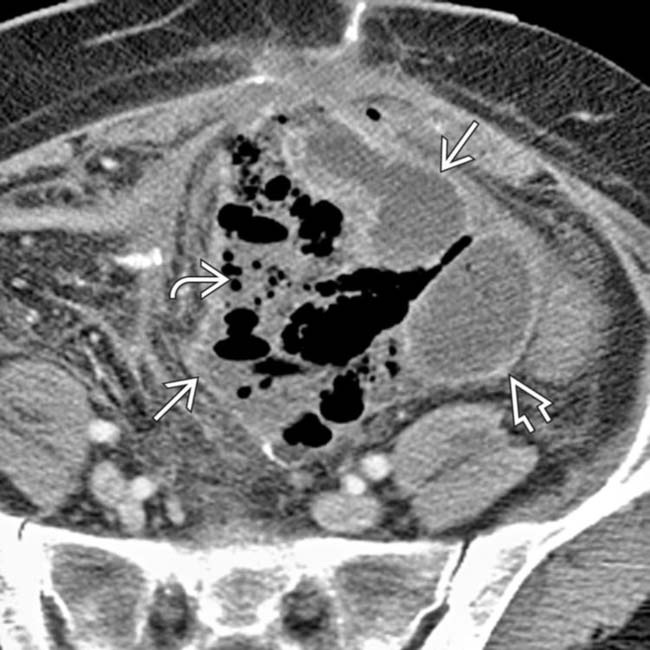
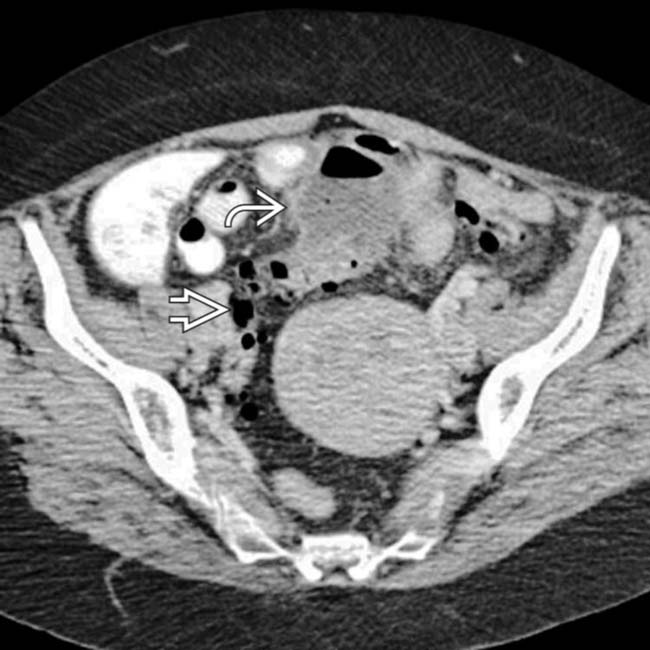
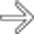
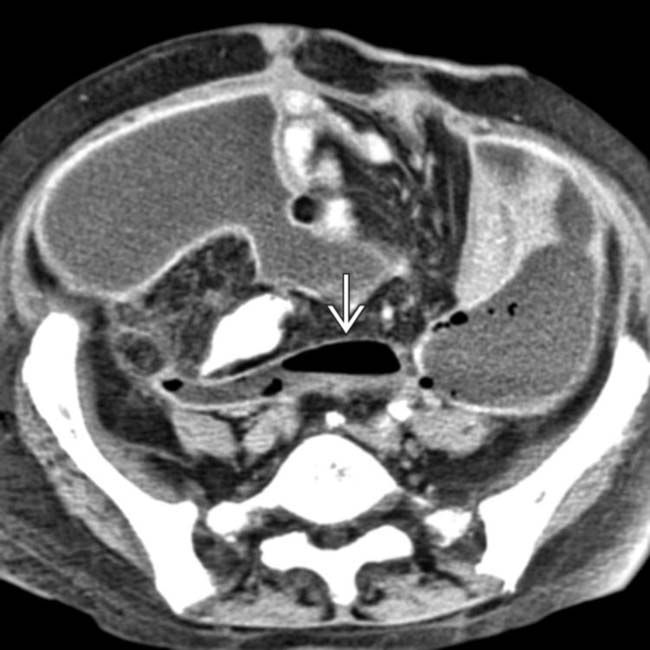
 after bowel resection. Note multiple fluid collections with enhancing rims; gas is seen only in pelvic abscess
after bowel resection. Note multiple fluid collections with enhancing rims; gas is seen only in pelvic abscess  .
.
 , but not in other collections.
, but not in other collections.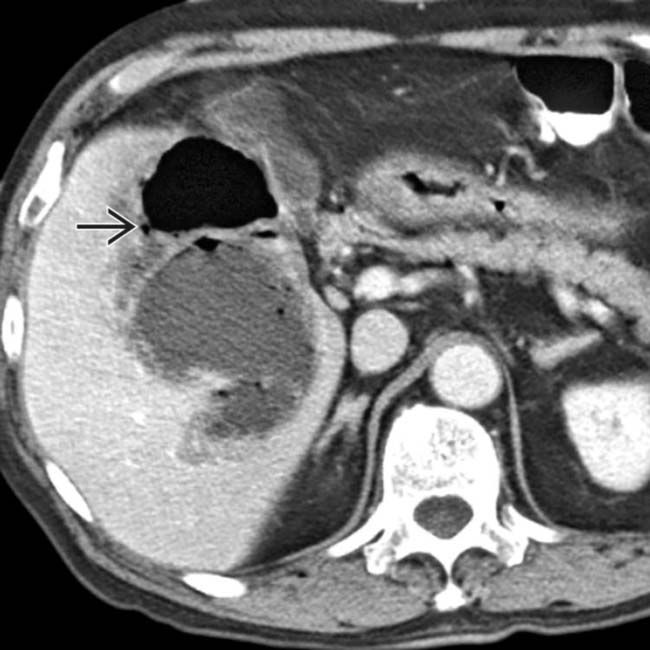
 .
.
 .
.
 surrounding the abscess.
surrounding the abscess.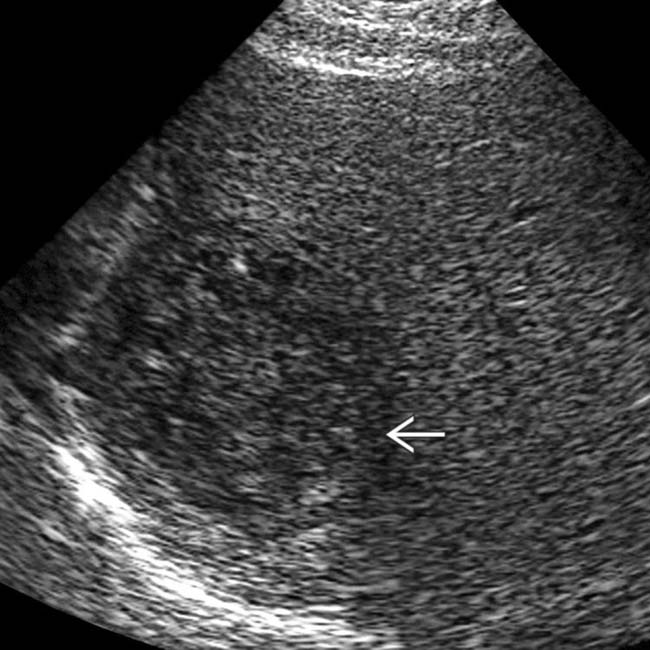
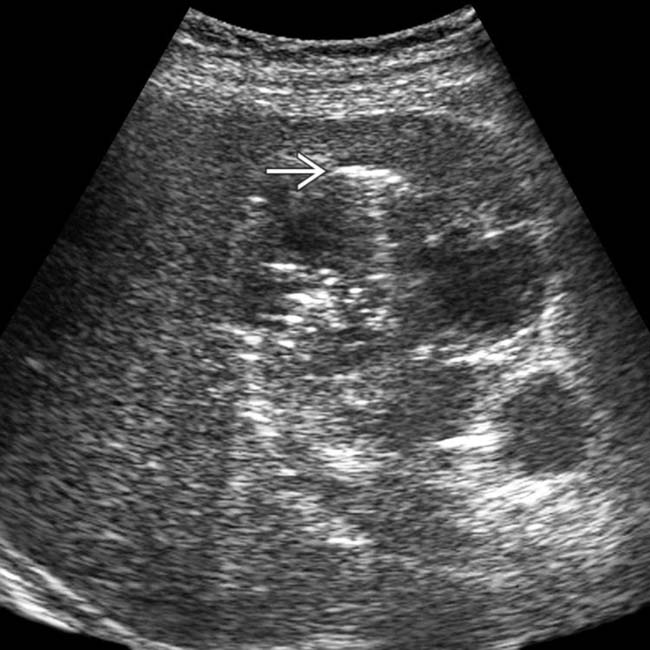
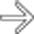
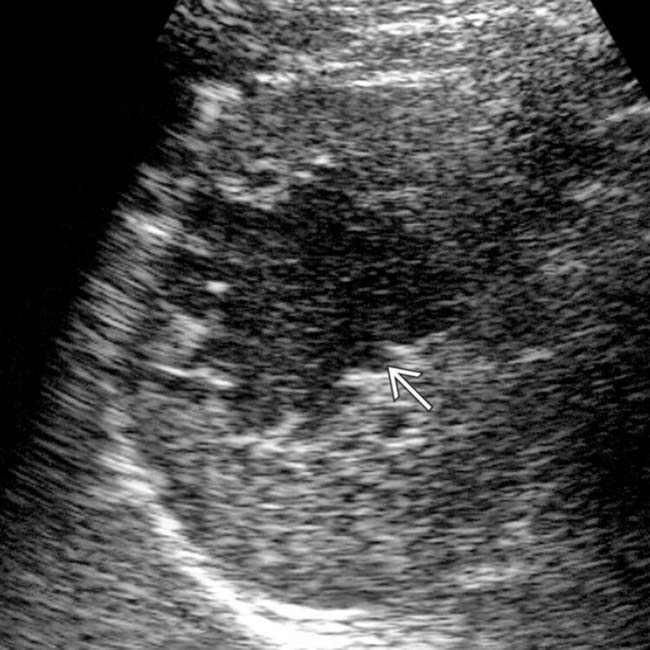
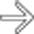 within the hypoechoic mass, and the lack of distal acoustic enhancement.
within the hypoechoic mass, and the lack of distal acoustic enhancement.
 .
.























































 .
.
 .
.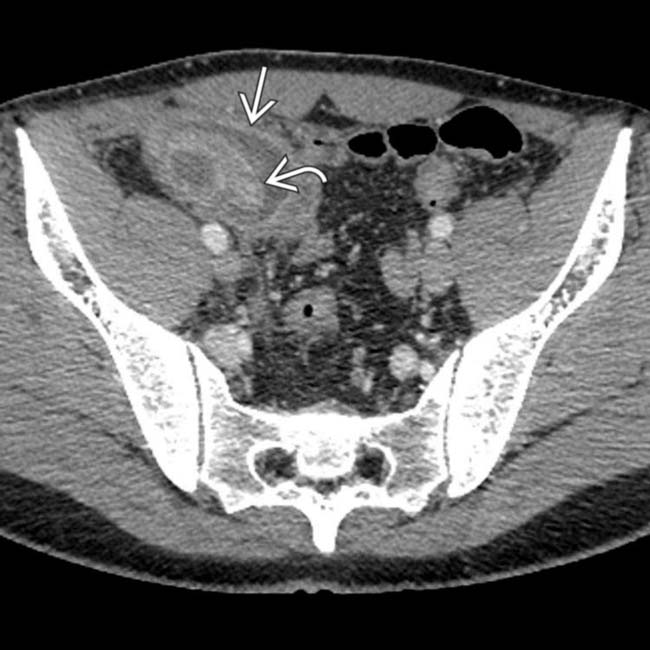
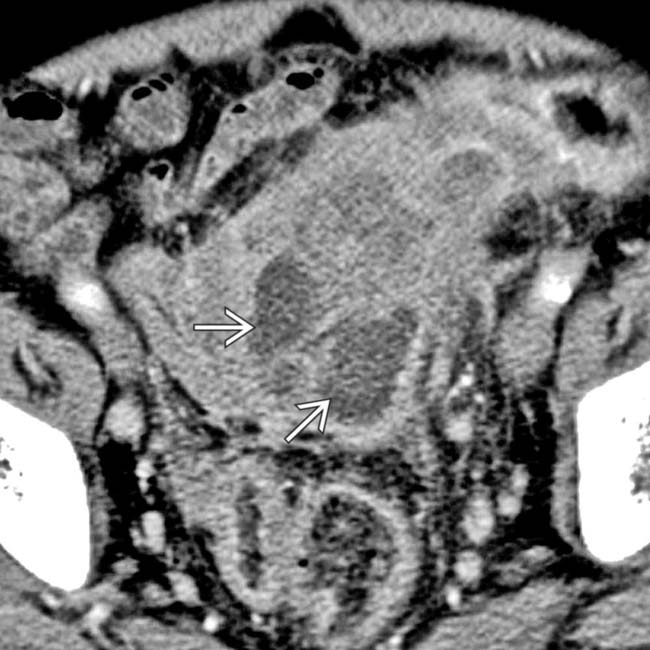
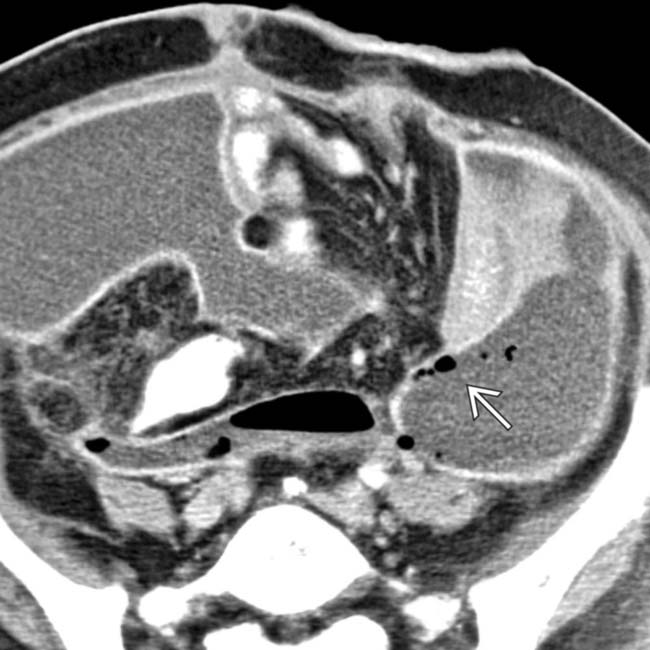
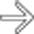 with peripheral rim enhancement in the right lower quadrant. In the midst of the fluid collection is a tubular structure
with peripheral rim enhancement in the right lower quadrant. In the midst of the fluid collection is a tubular structure 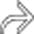 , representing a ruptured appendix.
, representing a ruptured appendix.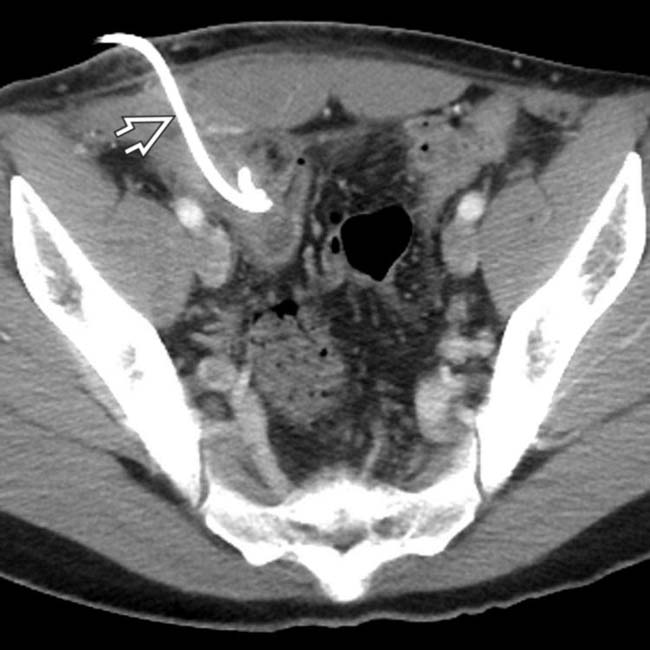
 placed percutaneously in the collection, with near resolution of the fluid within the abscess.
placed percutaneously in the collection, with near resolution of the fluid within the abscess.


