Usually unilocular, well-defined cyst with sharp margin and thin imperceptible wall
 Less commonly, imaging features can overlap with neoplastic pancreatic cysts, and lesions can demonstrate more complexity (multiloculation, calcifications, etc.)
Less commonly, imaging features can overlap with neoplastic pancreatic cysts, and lesions can demonstrate more complexity (multiloculation, calcifications, etc.)
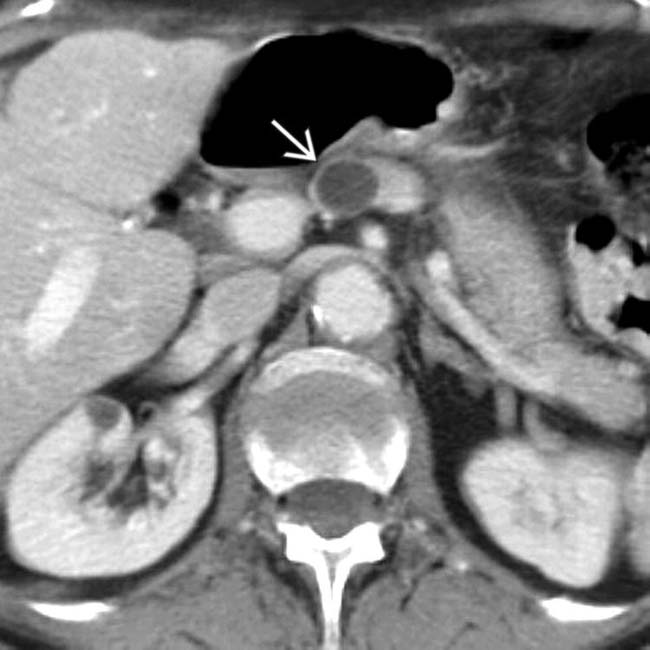
 in the pancreatic neck.
in the pancreatic neck.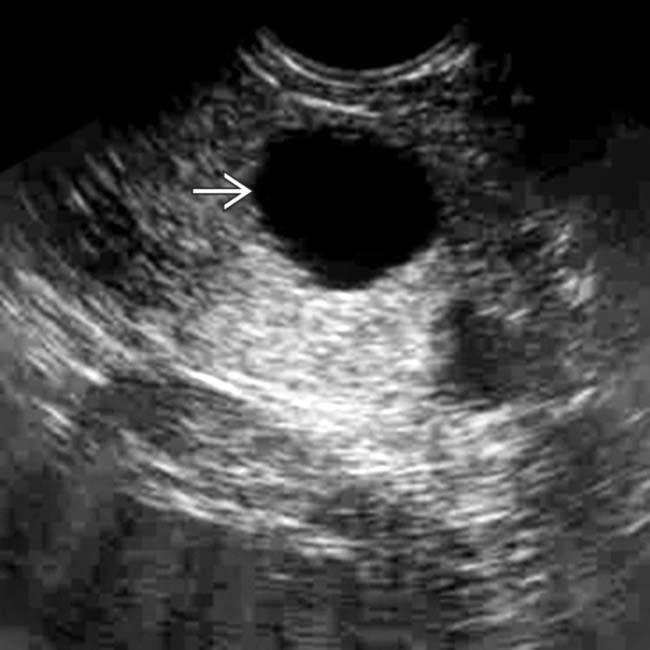
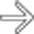
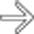
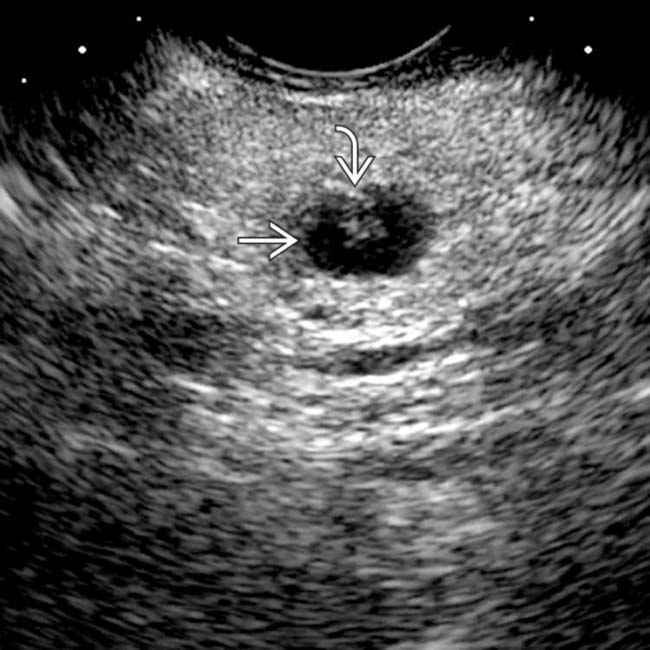
 in the neck of the pancreas. There is no mural nodularity or other sign of complexity. Aspiration demonstrated clear serous fluid with no elevated tumor markers. It was elected to follow this cyst with sonography. It has remained stable for several years and is presumably a nonneoplastic simple cyst.
in the neck of the pancreas. There is no mural nodularity or other sign of complexity. Aspiration demonstrated clear serous fluid with no elevated tumor markers. It was elected to follow this cyst with sonography. It has remained stable for several years and is presumably a nonneoplastic simple cyst.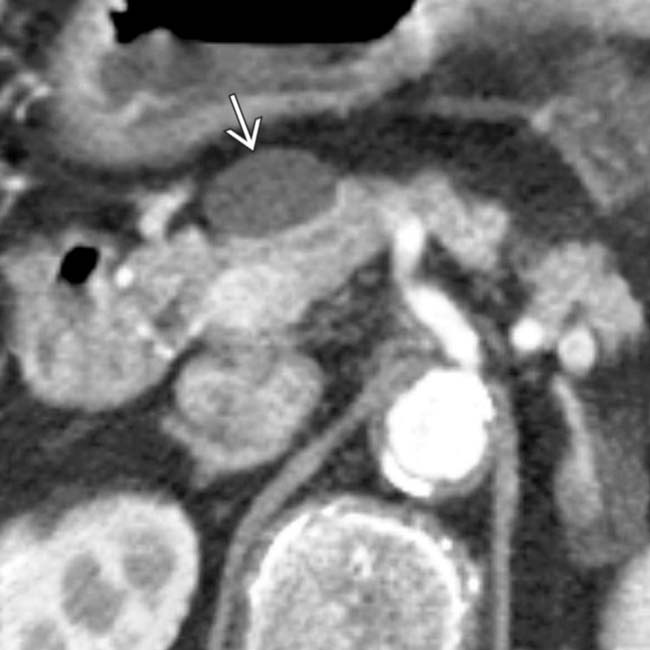
 in the pancreatic head/neck. The wall of the cyst is imperceptible and there are no internal septations or other signs of complexity.
in the pancreatic head/neck. The wall of the cyst is imperceptible and there are no internal septations or other signs of complexity.
 . Needle aspiration of the cyst demonstrated clear serous fluid with no malignant cells or elevated tumor markers, consistent with a nonneoplastic, simple cyst.
. Needle aspiration of the cyst demonstrated clear serous fluid with no malignant cells or elevated tumor markers, consistent with a nonneoplastic, simple cyst.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• Imaging features can show some variability, since this category encompasses several histopathologically distinct types of nonneoplastic cysts
• Less commonly, imaging features can overlap with neoplastic pancreatic cysts, and lesions can demonstrate more complexity (multiloculation, calcifications, etc.)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pancreatic Pseudocyst
PATHOLOGY
General Features
Staging, Grading, & Classification
• While generally grouped together into a category of nonneoplastic pancreatic cysts, these cysts can be further subdivided into multiple distinct histopathologic subtypes
 Mucinous nonneoplastic cysts: Mucinous epithelium, no cellular atypia, and no communication with pancreatic duct
Mucinous nonneoplastic cysts: Mucinous epithelium, no cellular atypia, and no communication with pancreatic duct
 Mucinous nonneoplastic cysts: Mucinous epithelium, no cellular atypia, and no communication with pancreatic duct
Mucinous nonneoplastic cysts: Mucinous epithelium, no cellular atypia, and no communication with pancreatic duct
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
 . The well-defined, simple-appearing cyst
. The well-defined, simple-appearing cyst  in the pancreas almost certainly represents a nonneoplastic pancreatic cyst, very common in VHL patients.
in the pancreas almost certainly represents a nonneoplastic pancreatic cyst, very common in VHL patients.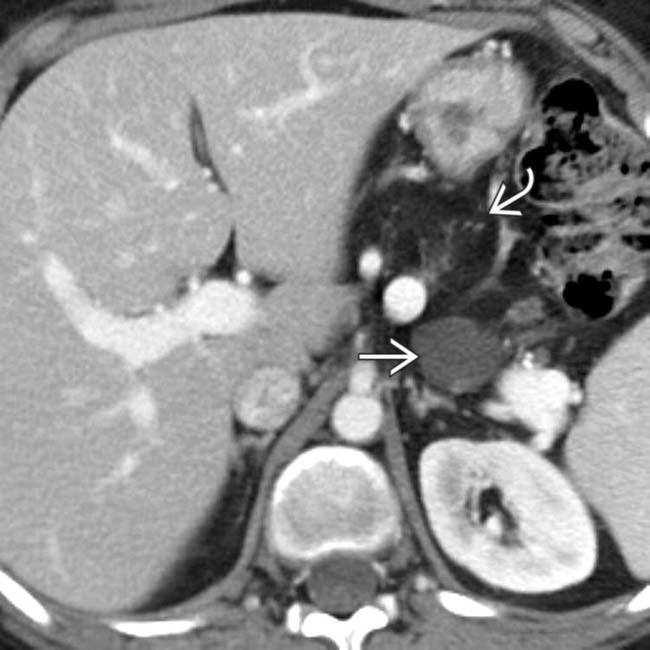
 , characteristic of pancreatic involvement with this disease. Notice also the thin-walled retention cyst in the tail of the pancreas
, characteristic of pancreatic involvement with this disease. Notice also the thin-walled retention cyst in the tail of the pancreas  .
.
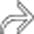 in the pancreatic head. Nonneoplastic cysts are a common finding in cystic fibrosis patients.
in the pancreatic head. Nonneoplastic cysts are a common finding in cystic fibrosis patients.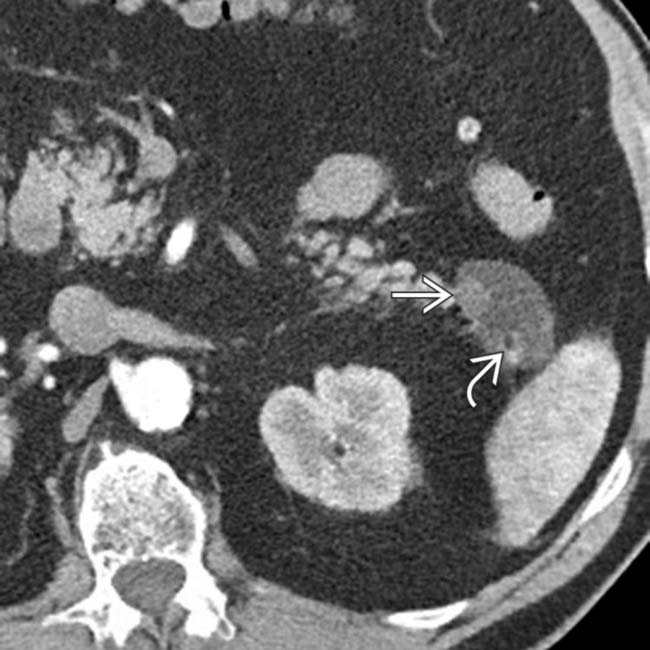
 and a small focus of internal fat density
and a small focus of internal fat density 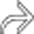 . This was found to be a lymphoepithelial cyst at resection, as these lesions can sometimes demonstrate internal fat.
. This was found to be a lymphoepithelial cyst at resection, as these lesions can sometimes demonstrate internal fat.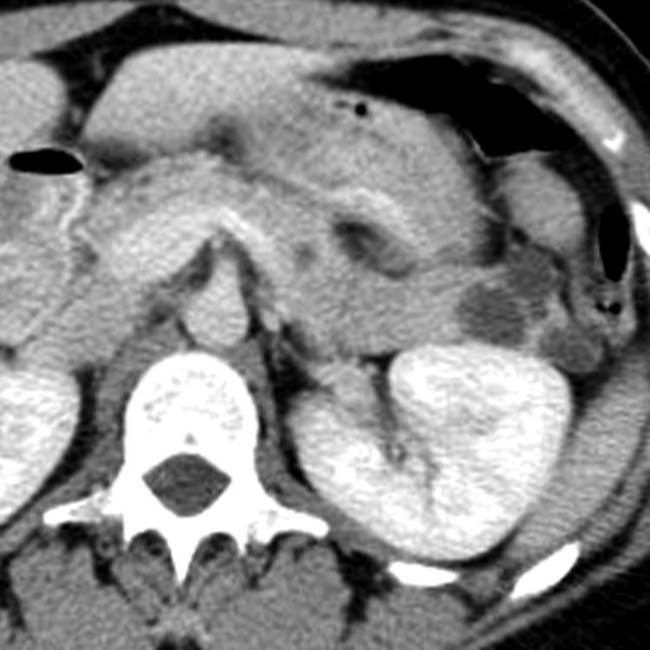
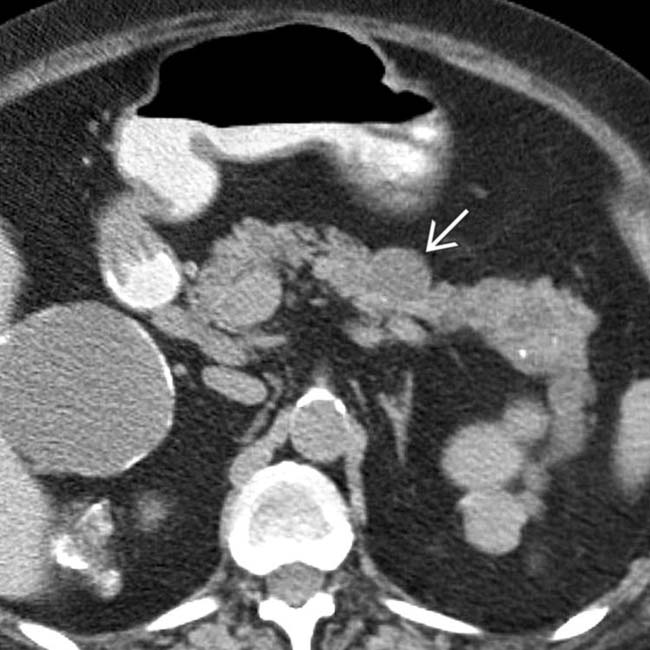
 .
.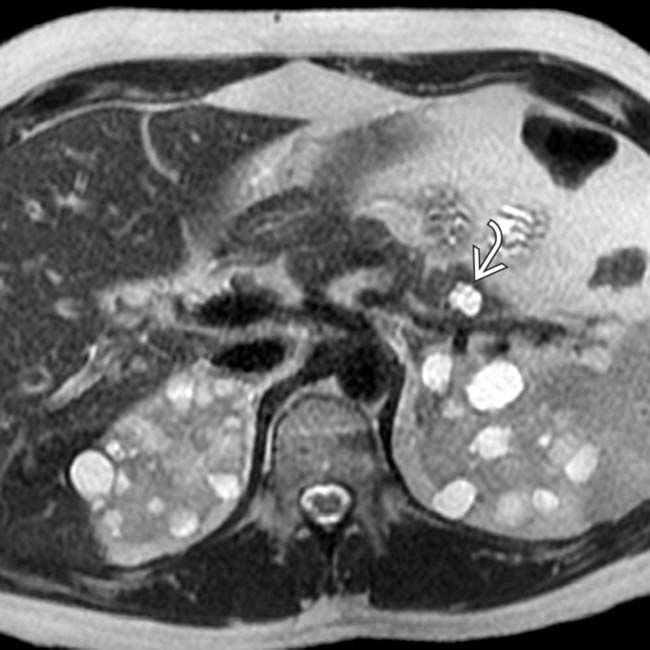
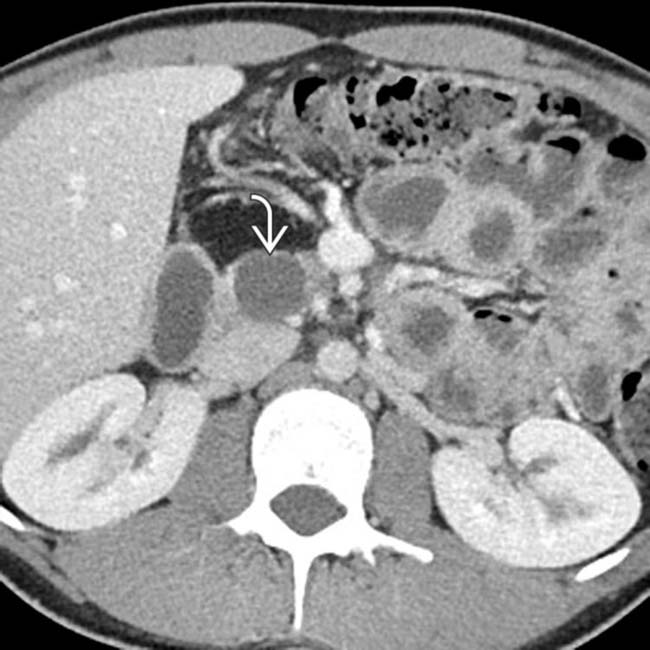
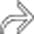 in the pancreas, compatible with the patient’s VHL.
in the pancreas, compatible with the patient’s VHL.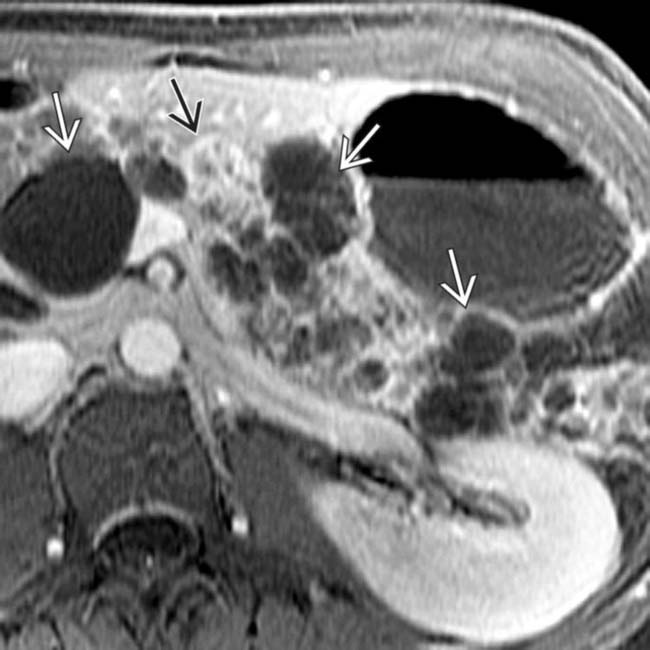
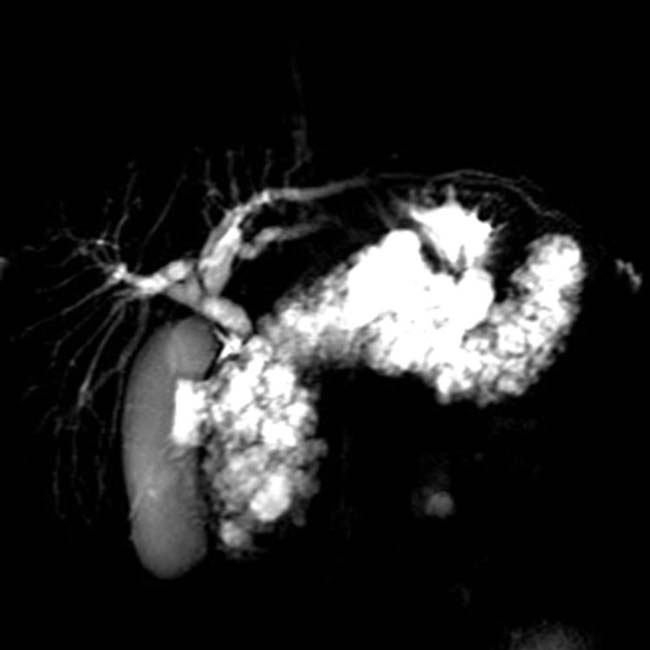
 . In addition, note the small hypervascular neuroendocrine tumor
. In addition, note the small hypervascular neuroendocrine tumor  in the body of the pancreas.
in the body of the pancreas.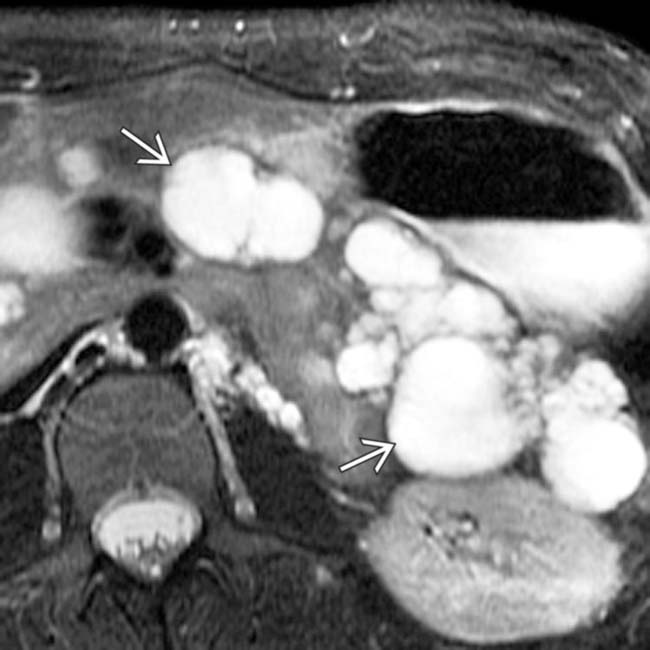
 characteristic of pancreatic cystosis in this disease.
characteristic of pancreatic cystosis in this disease.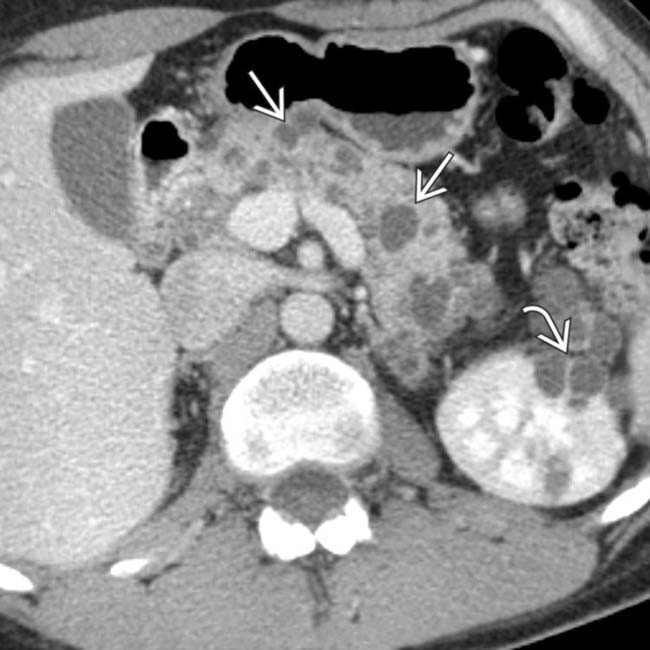
 as well as multiple renal cysts
as well as multiple renal cysts  .
.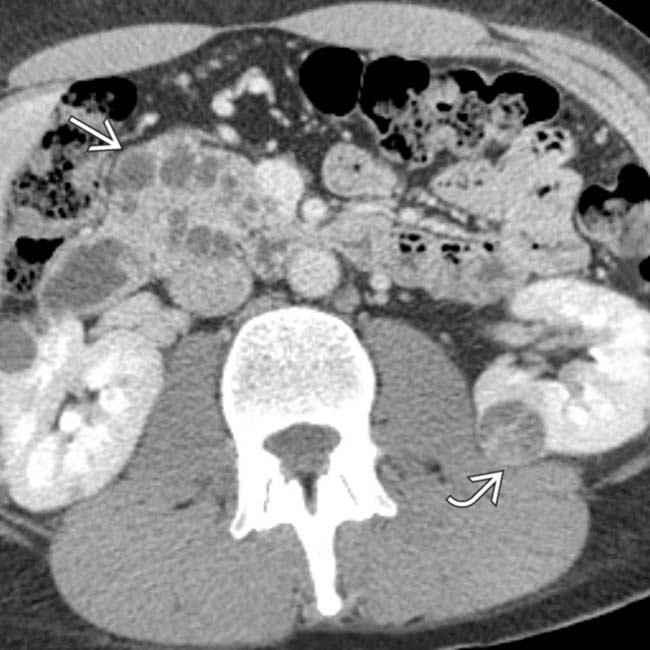
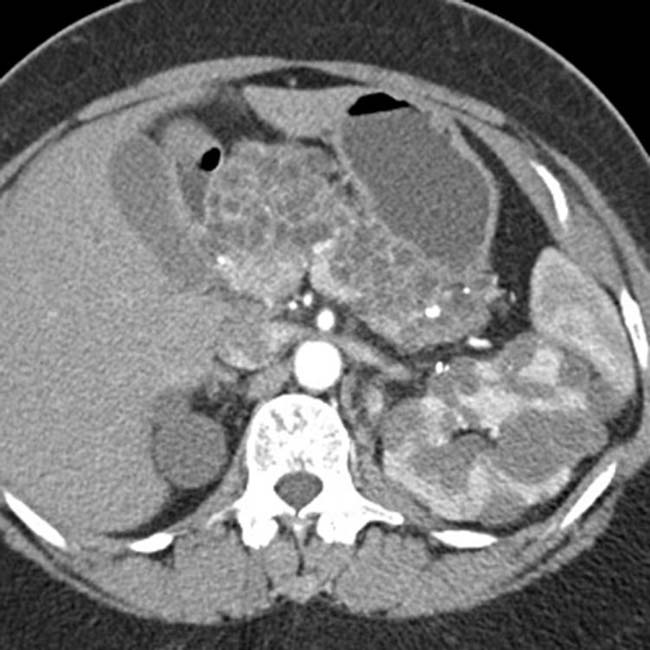
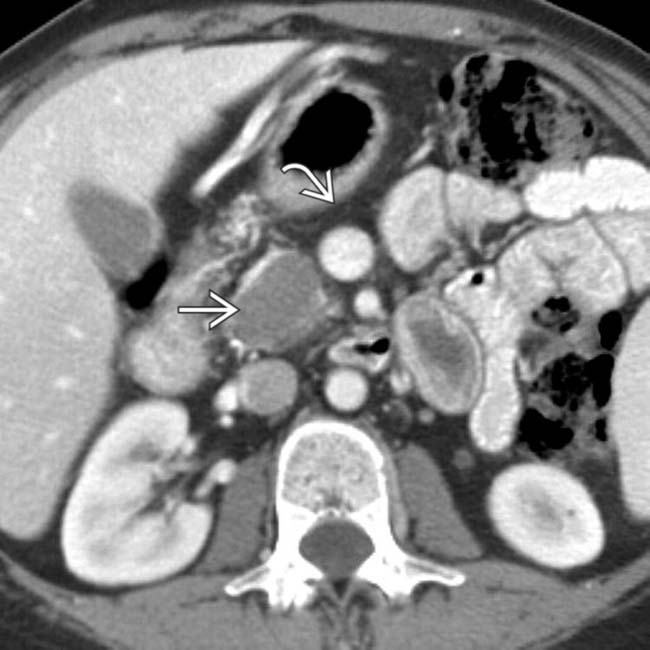
 in the pancreatic head. In addition, there is a small cystic renal cell carcinoma in the left kidney
in the pancreatic head. In addition, there is a small cystic renal cell carcinoma in the left kidney  .
.
 as well as a simple-appearing cyst
as well as a simple-appearing cyst  .
.
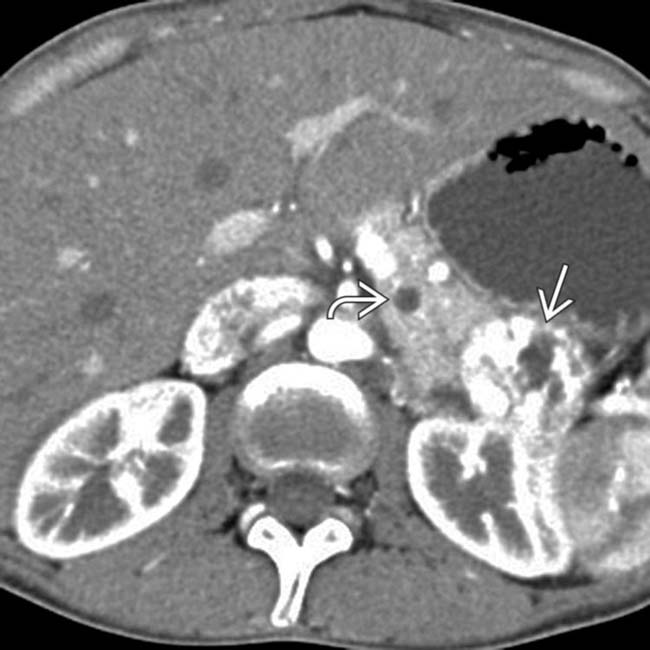
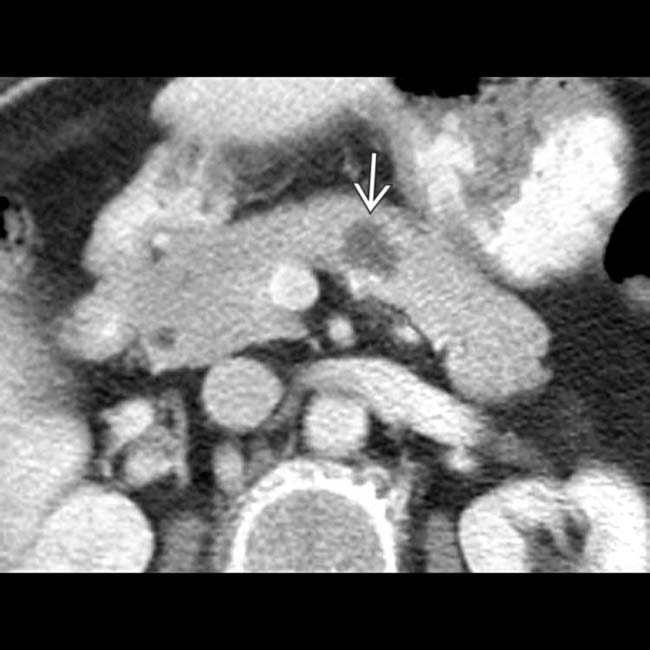
 with a small mural nodule
with a small mural nodule  . Needle aspiration yielded clear fluid with borderline elevated CEA and cellular atypia. This was interpreted as equivocal for malignancy, and a laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy was performed. The excised specimen showed an epithelial lining and was classified as a true cyst of the pancreas.
. Needle aspiration yielded clear fluid with borderline elevated CEA and cellular atypia. This was interpreted as equivocal for malignancy, and a laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy was performed. The excised specimen showed an epithelial lining and was classified as a true cyst of the pancreas.



































 in the pancreatic body.
in the pancreatic body.


