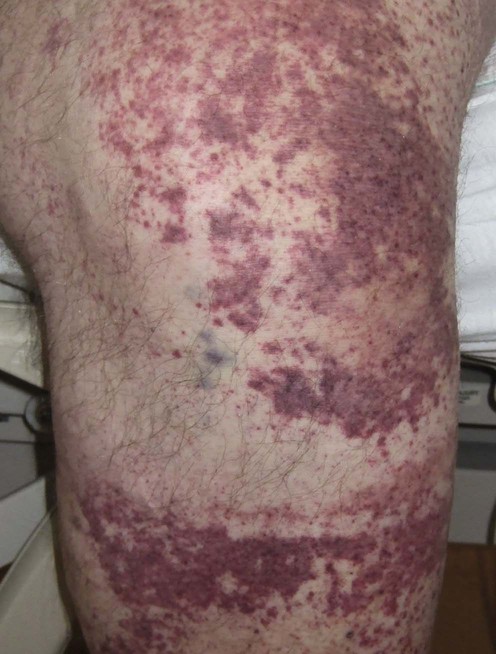
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Specific investigations
First-line therapies
Second-line therapies
Azathioprine. An effective, corticosteroid-sparing therapy for patients with recalcitrant cutaneous lupus erythematosus or with recalcitrant cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
Callen JP, Spencer LV, Burruss JB, Holtman J. Arch Dermatol 1991; 127: 515–22.
Open-label trial involving six patients who had failed to respond to ‘less toxic’ therapies.
Methotrexate in patients with moderate systemic lupus erythematosus (exclusion of renal and central nervous system disease).
Gansauge S, Breitbart A, Rinaldi N, Schwarz-Eywill M. Ann Rheum Dis 1997; 56: 382–5.
Methotrexate use has been reported in a total of 13 patients with CSVV in case reports and series.
Third-line therapies
Other therapies
 Plasma exchange Plasma exchange |
D |
 Intravenous immune globulin Intravenous immune globulin |
E |
 Infliximab Infliximab |
E |
 Minocycline Minocycline |
E |
 Tacrolimus Tacrolimus |
E |
 Tocilizumab Tocilizumab |
E |













 Observation
Observation Removal or withdrawal of the causative agent (e.g., drug)
Removal or withdrawal of the causative agent (e.g., drug) Colchicine
Colchicine Dapsone
Dapsone Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Systemic corticosteroids
Systemic corticosteroids Immunosuppressive/cytotoxic agents: azathioprine (B for negative, C for positive), methotrexate (C), cyclosporine (C), mycophenolate mofetil (C)
Immunosuppressive/cytotoxic agents: azathioprine (B for negative, C for positive), methotrexate (C), cyclosporine (C), mycophenolate mofetil (C) Rituximab (A for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and ANCA-associated vasculitis, E for other vasculitides)
Rituximab (A for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and ANCA-associated vasculitis, E for other vasculitides) Antihistamines
Antihistamines Dietary restriction
Dietary restriction Pentoxifylline
Pentoxifylline