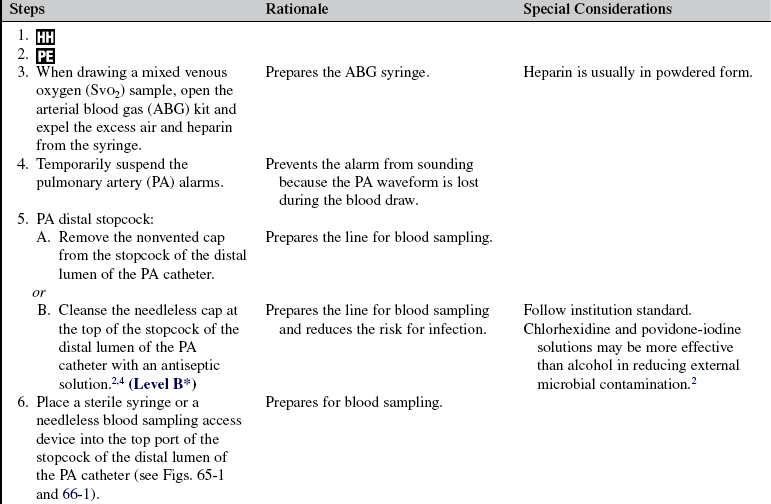
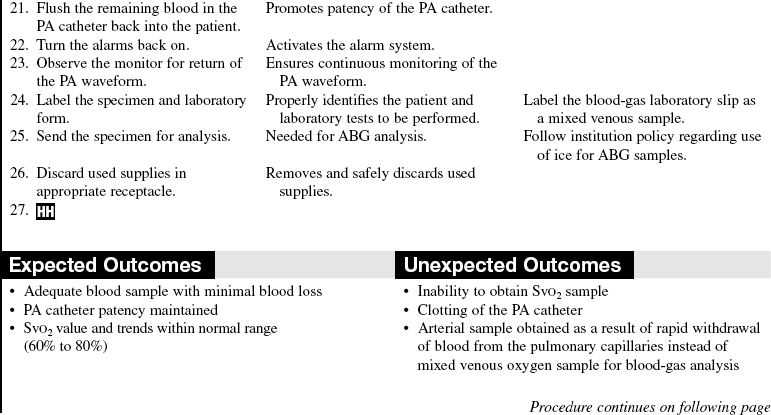
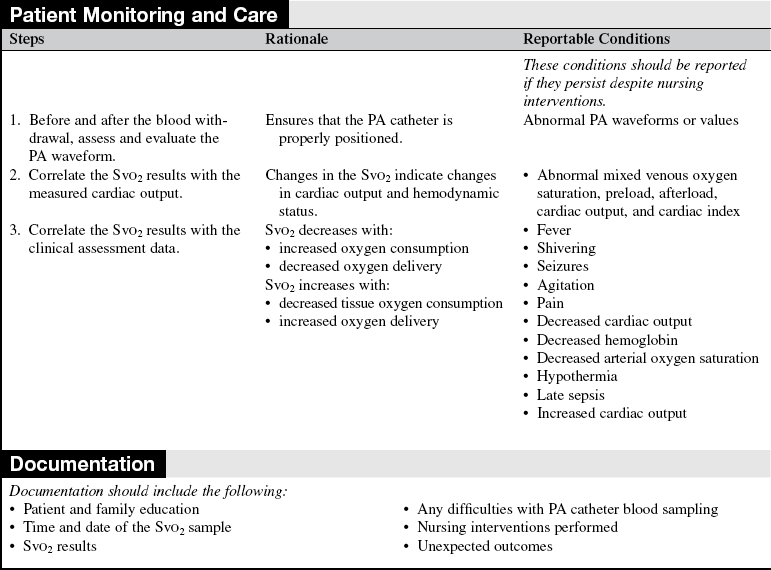
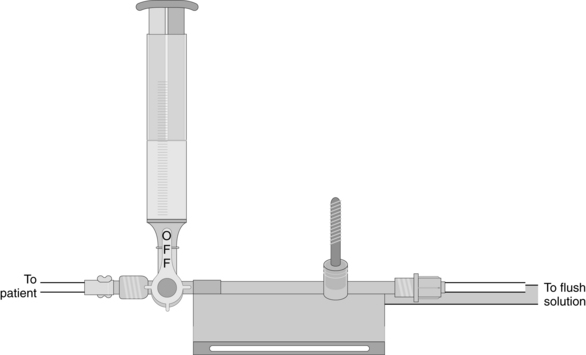
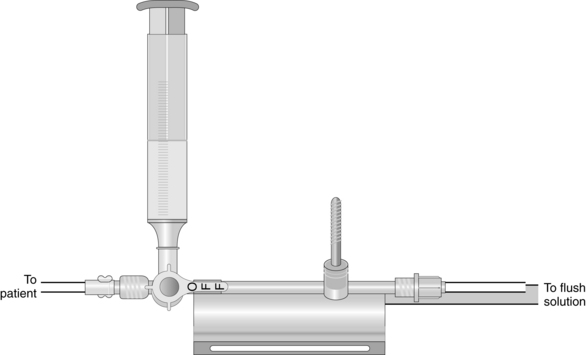
Blood Sampling from a Pulmonary Artery Catheter
PREREQUISITE NURSING KNOWLEDGE
• Knowledge of sterile technique is needed.
• Knowledge of cardiovascular and pulmonary anatomy and physiology is necessary.
• Gas exchange and acid-base balance should be understood.
• Technique for specimen collection and labeling should be known.
• Principles of hemodynamic monitoring need to be understood.
• Knowledge about the care of patients with pulmonary artery catheters (see Procedure 73) and stopcock manipulation (see Procedure 76) is needed.
• The most frequent blood specimen obtained from the pulmonary artery is one for mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) analysis.
• SvO2 measures the oxygen saturation of the venous blood in the pulmonary artery (see Procedure 16).
• SvO2 samples are obtained to calibrate the equipment when continuously monitoring SvO2 values.
• Routine blood sampling from the pulmonary artery catheter is not recommended because entry into the sterile system may increase the incidence of catheter-related infection.
EQUIPMENT
• Goggles or fluid shield face mask
• Needleless blood sampling access device
Additional equipment to have available as needed includes the following:
PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION
Patient Assessment
• Assess the patient’s cardiopulmonary and hemodynamic status, including abnormal lung sounds, respiratory distress, dysrhythmias, decreased mentation, agitation, and skin color changes.  Rationale: These signs and symptoms could necessitate blood sampling for venous oxygenation.
Rationale: These signs and symptoms could necessitate blood sampling for venous oxygenation.
• Assess for a decrease in cardiac output related to changes in preload, afterload, or contractility.  Rationale: Mixed venous blood samples are used to evaluate changes in cardiopulmonary function.
Rationale: Mixed venous blood samples are used to evaluate changes in cardiopulmonary function.
Patient Preparation
• Verify correct patient with two identifiers.  Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
• Ensure that the patient understands preprocedural teaching. Answer questions as they arise, and reinforce information as needed.  Rationale: Understanding of previously taught information is evaluated and reinforced.
Rationale: Understanding of previously taught information is evaluated and reinforced.
• Position the patient so that the stopcock for blood sampling is exposed.  Rationale: This positioning improves the ease of obtaining the blood sample and minimizes the contamination of the stopcock.
Rationale: This positioning improves the ease of obtaining the blood sample and minimizes the contamination of the stopcock.
References
![]() 1. Carlson, KK, et al. Obtaining reliable plasma sodium and glucose determinations from pulmonary artery catheters. Heart Lung. 1990; 19:613–619.
1. Carlson, KK, et al. Obtaining reliable plasma sodium and glucose determinations from pulmonary artery catheters. Heart Lung. 1990; 19:613–619.
![]() 2. Casey, AL, et al. A randomized, prospective clinical trial to assess the potential infection risk associated with the PosiFlow needleless connector. J Hosp Infection. 2003; 54:288–293.
2. Casey, AL, et al. A randomized, prospective clinical trial to assess the potential infection risk associated with the PosiFlow needleless connector. J Hosp Infection. 2003; 54:288–293.
![]() 3. Krueger, KE, et al. The reliability of laboratory data from blood samples collected through pulmonary artery catheters. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1981; 105:343–344.
3. Krueger, KE, et al. The reliability of laboratory data from blood samples collected through pulmonary artery catheters. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1981; 105:343–344.
![]() 4. O’Grady, NP, et al, Guidelines for the prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections . Am J Infect Control. 2002; 30(8):476–489.
4. O’Grady, NP, et al, Guidelines for the prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections . Am J Infect Control. 2002; 30(8):476–489.
![]() 5. Palermo, LM, Andrews, RW, Ellison, N. Avoidance of heparin contamination in coagulation studies drawn from indwelling lines. Anesth Analg. 1980; 59:222–224.
5. Palermo, LM, Andrews, RW, Ellison, N. Avoidance of heparin contamination in coagulation studies drawn from indwelling lines. Anesth Analg. 1980; 59:222–224.

 Rationale: Teaching provides information and may reduce anxiety and fear.
Rationale: Teaching provides information and may reduce anxiety and fear. Rationale: This explanation encourages patient assistance.
Rationale: This explanation encourages patient assistance.