History
Physical Examination
Laboratory Data
Postoperative Echocardiogram
Comments
Follow-Up
Postoperative 2 Weeks
Postoperative 4 Weeks
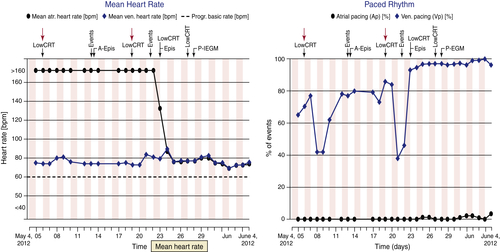
FIGURE 49-1 Remote monitoring website data. Two separate panels across identical 1-month time spans (May 4 to June 4) show separate graphic parameter trends. Low cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) events along the top of the panels represent alert notifications automatically delivered by the remote monitoring technology. Left panel, Persistent atrial fibrillation spontaneously terminates (May 23). Right panel, Episodic dips in CRT pacing percentage are noted, from baseline levels of approximately 80%. Atrial fibrillation terminates (May 23) and then CRT pacing percentage stabilizes at approximately 98%. Atrial pacing percentage remains negligible.
Postoperative 6 Weeks
Postoperative 8 Weeks
Focused Clinical Questions and Discussion Points
Question
Discussion
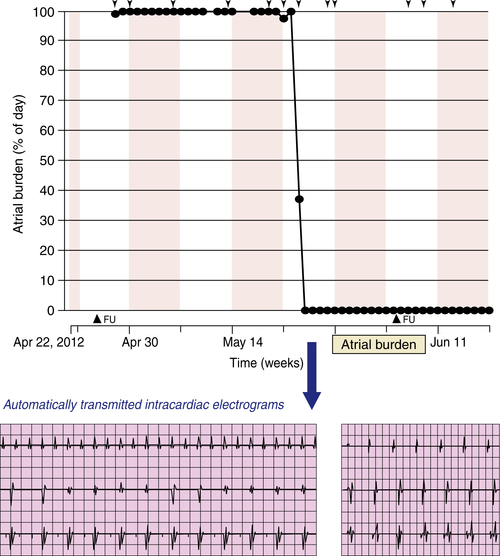
FIGURE 49-2
Question
Discussion
Question
Discussion
Question
Discussion
Final Diagnosis
Plan of Action
Intervention
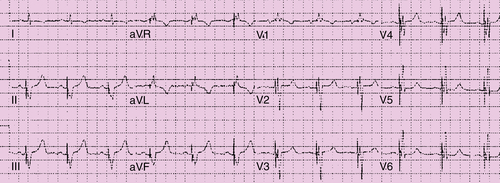
FIGURE 49-3
Outcome
Findings
Comments
Selected References
1. Boriani G., Santini M., Lunati M. et al. Improving thromboprophylaxis using atrial fibrillation diagnostic capabilities in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: the multicentre Italian ANGELS of AF Project. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5:182–188.
2. Camm A.J., Kirchhof P., Lip G.Y. et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2369–2429.
3. Ganesan A.N., Brooks A.G., Roberts-Thomson K.C. et al. Role of AV nodal ablation in cardiac resynchronization in patients with coexistent atrial fibrillation and heart failure: a systematic review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:719–726.
4. Healey J.S., Israel C.W., Connolly S.J. et al. Relevance of electrical remodeling in human atrial fibrillation: results of the asymptomatic atrial fibrillation and stroke evaluation in pacemaker patients and the atrial fibrillation reduction atrial pacing trial mechanisms of atrial fibrillation study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5:626–631.
5. Koplan B.A., Kaplan A.J., Weiner S. et al. Heart failure decompensation and all-cause mortality in relation to percent biventricular pacing in patients with heart failure: is a goal of 100% biventricular pacing necessary? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:355–360.
6. Varma N., Wilkoff B. Device features for managing patients with heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 2011;7:215–225 viii.
7. Santini M., Gasparini M., Landolina M. et al. Device-detected atrial tachyarrhythmias predict adverse outcome in real-world patients with implantable biventricular defibrillators. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:167–172.
8. Varma N., Stambler B., Chun S. Detection of atrial fibrillation by implanted devices with wireless data transmission capability. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2005;28(Suppl 1):S133–S136.
9. Varma N., Epstein A, Irimpen A. et al. TRUST Investigators. Efficacy and safety of automatic remote monitoring for ICD follow-up: the TRUST trial. Circulation. 2010;122:325–332.