Procedure 29 Spondylolysis Repair
Indications
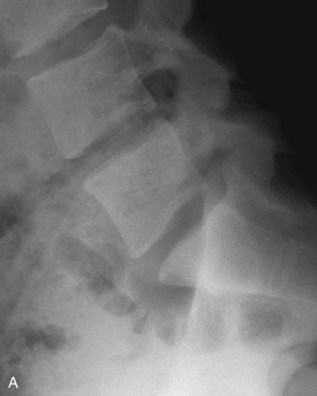
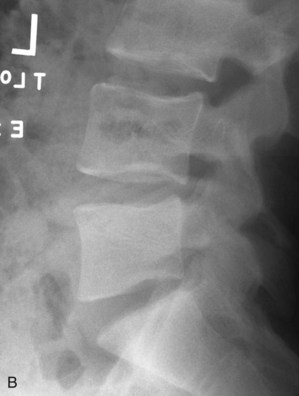
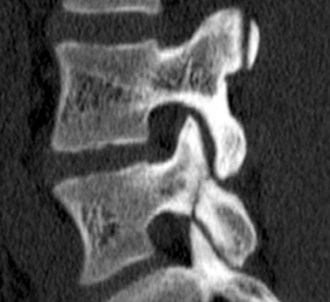
Examination/Imaging
Portals/Exposures
• A standard posterior lumbar exposure is used to access the affected vertebra. The lamina, facets, and proximal transverse process should be exposed (Buck, 1970; Askar, 2003; Chung, 2007; Debusscher, 2007).
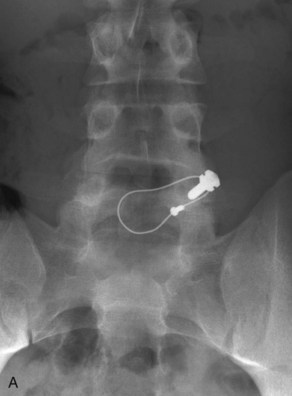
• Recently, minimally invasive techniques of repair have been described using percutaneous screws and of tubular retractors (Nichol, 1986; Morscher, 1988).
Procedure
Step 1
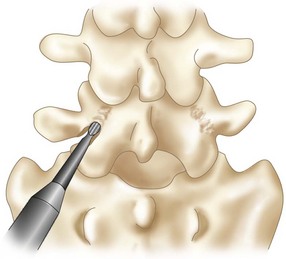
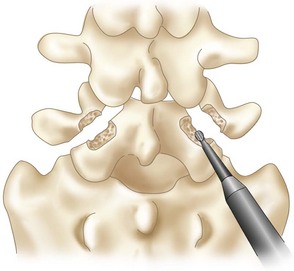
• Curettage of the pars defect is performed.
• A burr is used to freshen fracture surfaces (Figure 29-3). Note that the burr and exposure of the defect margins are enlarged in Figure 29-3 to illustrate the technique. The actual débridement should disrupt as little bone as possible.
• The soft tissue between the fracture surfaces is removed (Figure 29-4).
Step 2
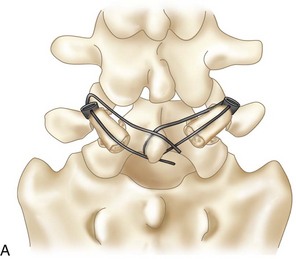
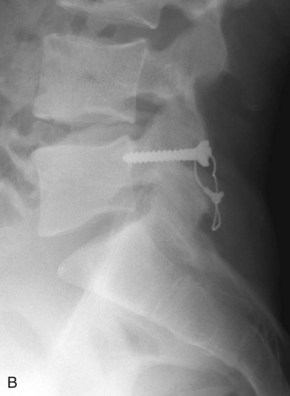
• A pedicle screw with a hole through its post is inserted using standard techniques.
• A cable is threaded through the hole in the pedicle screw post and around the spinous process (Figure 29-5, A and B).
Step 3
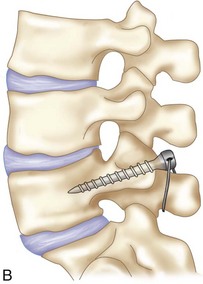
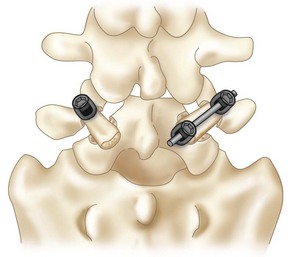
• An alternative technique uses a hook/rod construct (Figure 29-7).
• A pedicle screw is inserted using standard techniques.
• A sublaminar hook is placed, connected to the pedicle screw with a rod, and secured after compression force is applied.
• Minimal access techniques can be used to perform the same.
Askar Z, Wardlaw D, Koti M. Scott wiring for direct repair of lumbar spondylolysis. Spine. 2003;28:354-357.
Grade B description of the Scott wiring technique in 14 patients.
Buck JE. Direct repair of the defect in spondylolisthesis: preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970;52:432-437.
Grade B description of a direct screw fixation technique across the pars defect.
Chung CH, Chiu HM, Wang SJ, Hsu SY, Wei YS. Direct repair of multiple levels of lumbar spondylolysis by pedicle screw laminar hook and bone grafting: clinical, CT, and MRI-assessed study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20:399-402.
Debusscher F, Troussel S. Direct repair of defects in lumbar spondylolysis with a new pedicle screw hook fixation: clinical, functional and CT-assessed study. Eur Spine J. 2007;16:1650-1658.
Morscher E, Gerber B, Fasel J. Surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis by bone grafting and direct stabilization of spondylolysis by means of a hook screw. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1988;103:178-188.
Nichol RO, Scott JHS. Lytic spondylolysis repair by wiring. Spine. 1986;11:1027-1030.
Grade C retrospective review of a wiring technique.
Noggle JC, Sciubba DM, Samdani AF, et al. Minimally invasive direct repair of lumbar spondylolysis with a pedicle screw and hook construct. Neurosurg Focus. 2008;25:E15.
Grade B review of minimally invasive pedicle screw and hook-rod technique in five patients.
Sairyo K, Sakai T, Yasui N. Minimally invasive technique for direct repair of pars interarticularis defects in adults using a percutaneous pedicle screw and hook-rod system. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;10:492-495.
Grade C description of minimally invasive direct spondylolysis repair in two adults.
Songer MN, Rovin R. Repair of the pars interarticularis defect with a cable-screw construct: a preliminary report. Spine. 1998;23:263-269.
Tokuhasi Y, Matsuzaki H. Repair of defects in spondylolysis by segmental pedicular screw hook fixation: a preliminary report. Spine. 1996;21:2041-2045.
Grade B report of six patients treated with a screw-hook technique.