History
Current Medications
Physical Examination
Laboratory Data
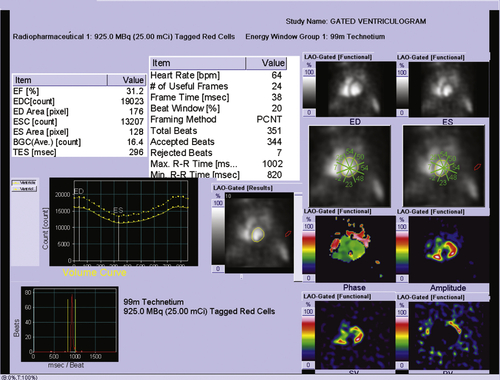
Electrocardiogram
Findings
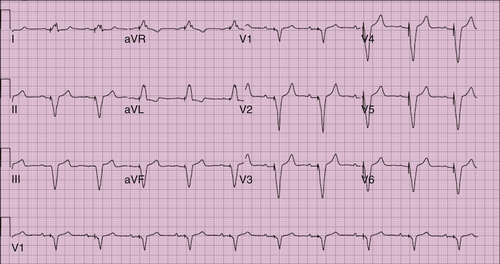
FIGURE 21-1 Electrocardiogram before the battery change. SVG-OM, Saphenous vein graft–obtuse margin.
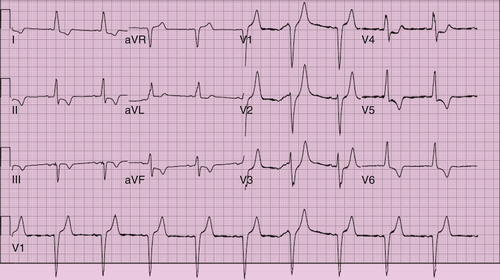
FIGURE 21-2 Unpaced postoperative electrocardiogram.
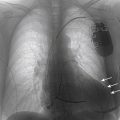
Chest Radiograph
Findings
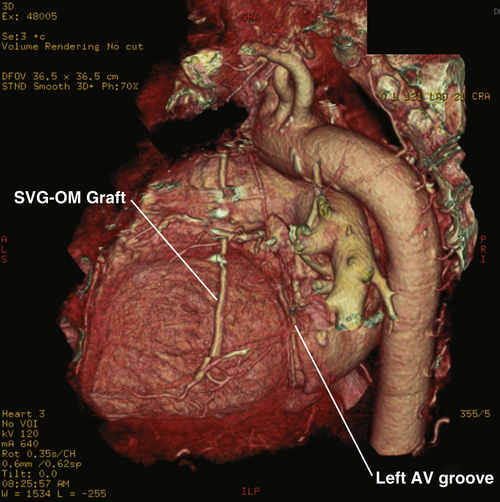
Computed Tomography
Findings
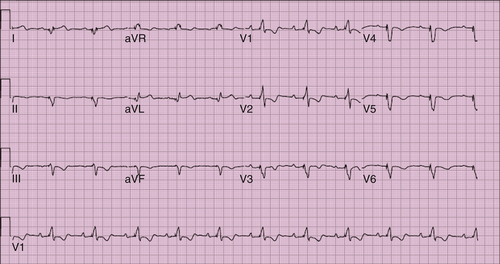
FIGURE 21-3 Postoperative paced electrocardiogram.
Focused Clinical Questions and Discussion Points
Question
Discussion
Question
Discussion
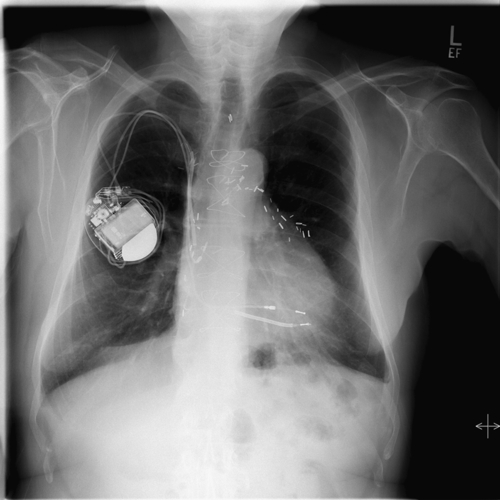
FIGURE 21-4 Chest radiograph on admission.
Question
Final Diagnosis
Plan of Action
Intervention
Outcome
Findings
Comments
Selected References
1. Choset H., Zenati M., Ota T. et al. Enabling medical robotics for the next generation of minimally invasive procedures: minimally invasive cardiac surgery with single port access. In: Rosen J., Hannaford B., Satava R.M., eds. Surgical robotics. New York: Springer; 2011:257–270.
2. DeRose J.J., Steinberg J.S. Surgical approaches to epicardial left ventricular lead implantation for biventricular pacing. In: Yu C., Hayes D.L., Auricchio A., eds. Cardiac resynchronization therapy. Blackwell: Malden, Massachusetts; 2006:227–236.
3. Derose Jr. J.J., Balaram S., Ro C. et al. Midterm follow-up of robotic biventricular pacing demonstrates excellent lead stability and improved response rates. Innovations (Phila). 2006;1:105–110.
4. Joshi S., Steinberg J.S., Ashton Jr. R.C. et al. Follow-up of robotically assisted left ventricular epicardial leads for cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:2358–2359.
5. Kamath G.S., Balaram S., Choi A. et al. Long-term outcome of leads and patients following robotic epicardial left ventricular lead placement for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2011;34:235–240.