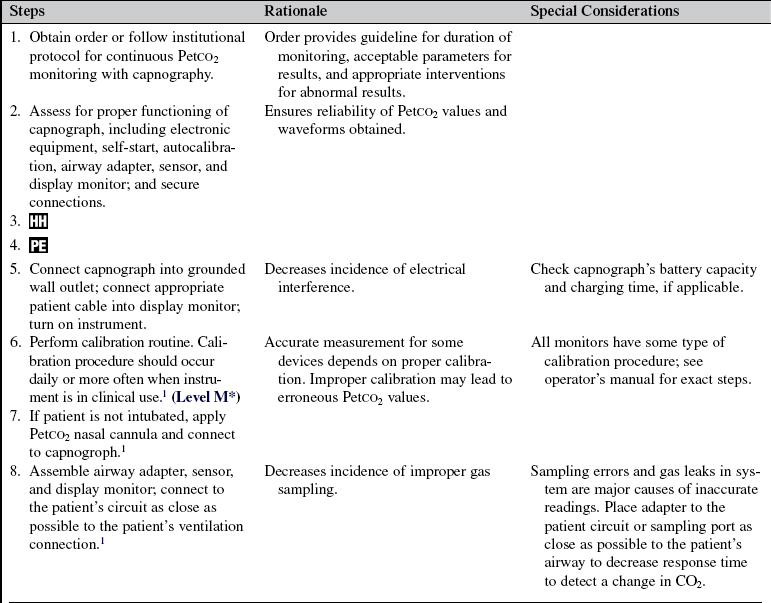
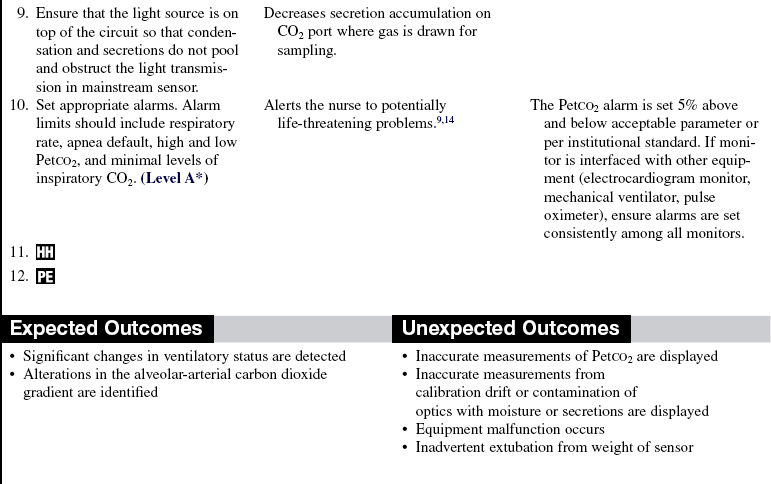
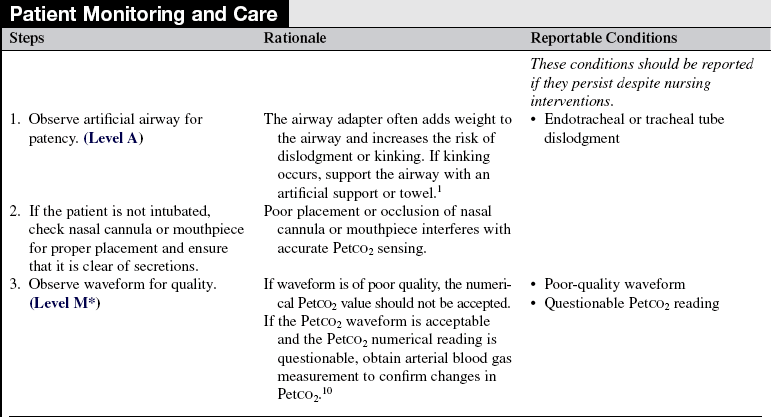
Continuous End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring
End-tidal carbon dioxide provides a noninvasive continuous measurement of ventilation12 or inhaled and exhaled carbon dioxide concentration commonly referred to as capnography. A capnograph depicts this measurement as a graphic picture or waveform tracing of each respiratory cycle. The partial pressure of end-tidal CO2 is assumed to represent alveolar gas, which under normal ventilation/perfusion matching in the lungs closely parallels arterial levels of CO2.
PREREQUISITE NURSING KNOWLEDGE
• Capnography provides the clinician with a calculation of airway respiratory rate (RR), and the combination of both end-tidal carbon dioxide (PetCO2) and RR can provide clinicians with one of the earliest indications that ventilation is hindered. The carbon dioxide waveform changes immediately on any degradation in quality of breathing and some of the most pertinent real-time information provided to give the caregiver an immediate alert to respiratory compromise, such as hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or cessation of breathing.6 PetCO2 monitoring is the earliest indicator of airway compromise, and in the aforementioned study, abnormal PetCO2 findings were observed with many acute respiratory events. In another study, acute respiratory events were found to cause PetCO2 abnormalities seen before oxygenation desaturation or observed hypoventilation.3
• Capnography can be thought of as the “ventilation vital sign” because it provides breath-to-breath feedback and generates a respiratory rate that is measured at the airway. The clinician now has the ability to measure respiratory frequency and detection of respiratory depression in patients who are not intubated sooner than with traditional monitoring techniques, which allows for safer titration of medications.6
• Ventilation is the bulk movement of gases into and out of the lung and is composed of two distinct processes: inspiration and expiration.
 During inspiration, gas is delivered to the alveoli, at which time it participates in gas exchange. Oxygenation occurs when the oxygen diffuses across the alveolar membrane into the blood. CO2 exchange occurs during this time as it diffuses across the alveolar membrane into the alveoli. Oxygenated blood is then distributed to and metabolized by the cells of muscles and organs. Oxygen saturation can be evaluated with a blood gas machine (oxygen saturation [SaO2]) or pulse oximetry (SpO2).
During inspiration, gas is delivered to the alveoli, at which time it participates in gas exchange. Oxygenation occurs when the oxygen diffuses across the alveolar membrane into the blood. CO2 exchange occurs during this time as it diffuses across the alveolar membrane into the alveoli. Oxygenated blood is then distributed to and metabolized by the cells of muscles and organs. Oxygen saturation can be evaluated with a blood gas machine (oxygen saturation [SaO2]) or pulse oximetry (SpO2).
 During expiration, alveolar gas is exhaled, which results in the elimination of CO2. Cells produce carbon dioxide (CO2) as a by-product of metabolism; this CO2 is transported by the vascular system to the lungs where it is eliminated through exhalation. For exhaled CO2 to be detected, adequate circulation must carry CO2-laden blood from the peripheral tissues to the lungs and adequate ventilation must carry CO2 from the lungs to the mouth.6 CO2 elimination can also be evaluated with a blood gas machine (SaO2) PetCO2 monitor/capnography.
During expiration, alveolar gas is exhaled, which results in the elimination of CO2. Cells produce carbon dioxide (CO2) as a by-product of metabolism; this CO2 is transported by the vascular system to the lungs where it is eliminated through exhalation. For exhaled CO2 to be detected, adequate circulation must carry CO2-laden blood from the peripheral tissues to the lungs and adequate ventilation must carry CO2 from the lungs to the mouth.6 CO2 elimination can also be evaluated with a blood gas machine (SaO2) PetCO2 monitor/capnography.
• Just as capnography cannot measure oxygenation, pulse oximetry cannot directly measure ventilation or alveolar ventilation (but SpO2 can provide some directional reflection of ventilation changes if the patient is breathing room air). To assist in the complete monitoring of the patient’s respiratory status, the two parameters must be used together: pulse oximetry to assess how well oxygen has moved across the alveolar capillary membrane into the blood to be transported to the tissues, and capnography to determine how well the patient is ventilating through the process of moving air in and out of the lungs and exhaling carbon dioxide.6
• For a patient who is not intubated who needs capnography, a specialized nasal cannula delivers supplemental oxygen and measures PetCO2, apneic events, and respiratory rate. Placing the capnography cannula is the same as initiating a nasal cannula for supplemental oxygen. Breath samples are obtained through both nostrils, and oxygen is delivered through the nasal prongs (design depends on manufacturer). An extension in the front of the mouth can be used for patients who breathe by mouth.6 PetCO2 can be monitored in patients who are intubated; the sensor is directly connected to the ventilator circuit.
• The principles of arterial blood gas sampling (see Procedure 64) and interpretation should be understood.
• Indications for continuous end-tidal CO2 monitoring include the following:
 Determine a baseline CO2 waveform and PetCO2.1,15
Determine a baseline CO2 waveform and PetCO2.1,15
 Continuously monitor the patency of the airway and the presence of breathing.
Continuously monitor the patency of the airway and the presence of breathing.
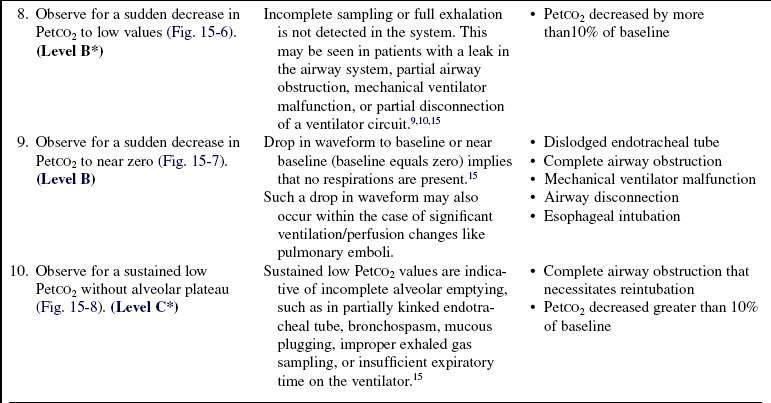
 Provide mechanism for early detection of changes in waveform pattern or PetCO2 value that may accompany a sudden or gradual change in CO2 production or elimination (permissive hypercapnia, hyperthermia, hypoventilation [extubation], hyperventilation therapy), or reduction in circulation (pulmonary blood flow).1,4,11,13,15
Provide mechanism for early detection of changes in waveform pattern or PetCO2 value that may accompany a sudden or gradual change in CO2 production or elimination (permissive hypercapnia, hyperthermia, hypoventilation [extubation], hyperventilation therapy), or reduction in circulation (pulmonary blood flow).1,4,11,13,15
• Basic principles of PetCO2 monitoring should be understood. The end-tidal CO2 monitor may be a stand-alone system, a module incorporated into the patient’s bedside physiologic monitor or incorporated into a mechanical ventilator. An infrared capnograph passes light through an expiratory gas sample and, with a photodetector, measures absorption of that light by the gas. The capnograph determines the amount of CO2 in the gas sample based on the absorption properties of CO2. The capnograph also visually graphs the pattern in which CO2 is exhaled and provides a display called a capnogram or PetCO2 waveform.1
• The capnograph samples exhaled CO2 by one of two methods: aspiration (side stream) or nonaspiration (mainstream) sampling. In the side stream method, a sample of gas is transported via small-bore tubing to the bedside monitor for analysis. In the mainstream system, analysis occurs directly at the patient-ventilator circuit.1
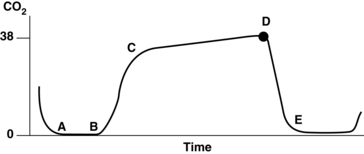
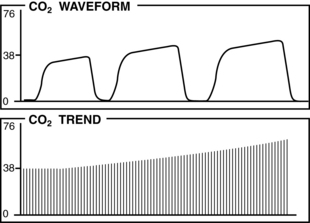
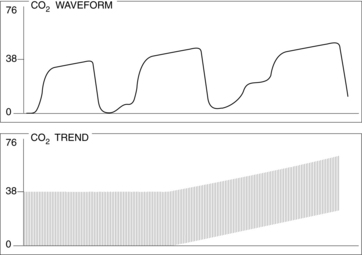
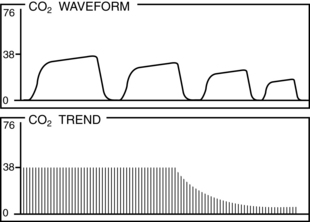
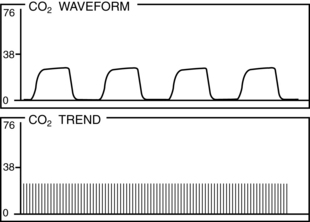
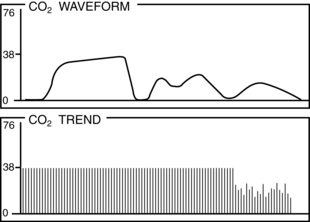
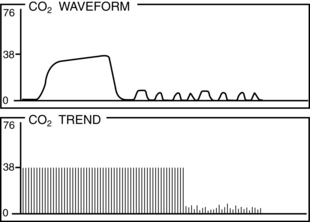
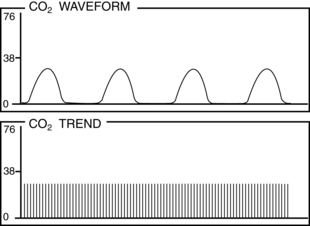
• Normal PetCO2 concentration in a patient with healthy lungs and airway conditions is 30 to 43 mm Hg. As the patient breathes, a characteristic waveform is created that can be divided into two segments: inspiration and expiration. Indications for PetCO2 monitoring include verification of endotracheal tube (ETT) placement, CPR, procedural sedation, gastric tube placement, and endoscopic procedures.8 The normal capnographic waveform has the following characteristics (Fig. 15-1):
 A zero baseline represents the completion of inspiration and the beginning of exhalation of CO2-free gas from anatomic dead space. This gas comes from the large airways, oropharynx, and nasopharynx (see Fig. 15-1, A-B).
A zero baseline represents the completion of inspiration and the beginning of exhalation of CO2-free gas from anatomic dead space. This gas comes from the large airways, oropharynx, and nasopharynx (see Fig. 15-1, A-B).
 A rapid sharp upstroke occurs as the gas from the intermediate airways, containing a mixture of fresh gas and CO2, begins to be exhaled from the lungs (see Fig. 15-1, B-C).
A rapid sharp upstroke occurs as the gas from the intermediate airways, containing a mixture of fresh gas and CO2, begins to be exhaled from the lungs (see Fig. 15-1, B-C).
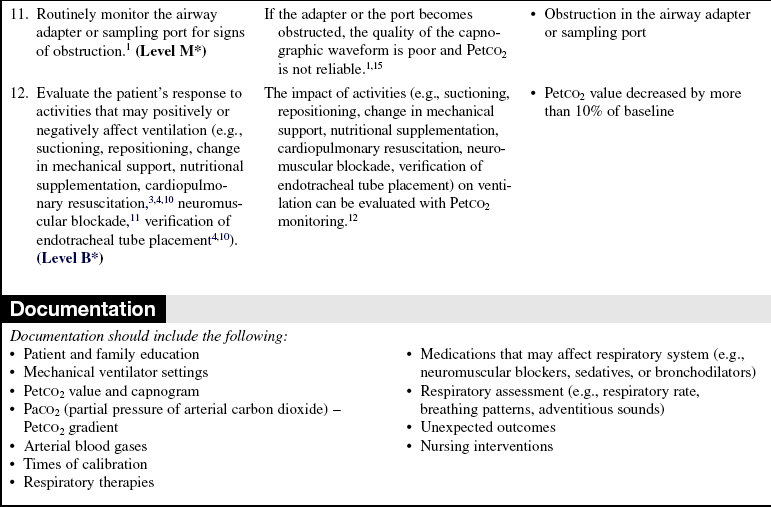
 A nearly flat alveolar plateau occurs as exhaled flow velocity slows and mixed gas is displaced by alveolar gas (Fig. 15-1, C-D). Alveolar exhalation of CO2 is nearing completion.
A nearly flat alveolar plateau occurs as exhaled flow velocity slows and mixed gas is displaced by alveolar gas (Fig. 15-1, C-D). Alveolar exhalation of CO2 is nearing completion.
 A distance end-tidal point most closely reflects the maximal concentration of exhaled CO2 and the end of exhalation (Fig. 15-1, D).
A distance end-tidal point most closely reflects the maximal concentration of exhaled CO2 and the end of exhalation (Fig. 15-1, D).
 A rapid down stroke occurs as the patient begins the inspiration of gas that is essentially devoid of CO2 (see Fig. 15-1, D-E).
A rapid down stroke occurs as the patient begins the inspiration of gas that is essentially devoid of CO2 (see Fig. 15-1, D-E).
 The positively deflected limb occurs with exhalation, whereas the negatively deflected limb occurs with inhalation. This is opposite from other respiratory waveforms, including the respirogram, spirogram, and flow-volume loop. The capnogram deviates from normal whenever physiologic or mechanical disruption of the breath occurs.
The positively deflected limb occurs with exhalation, whereas the negatively deflected limb occurs with inhalation. This is opposite from other respiratory waveforms, including the respirogram, spirogram, and flow-volume loop. The capnogram deviates from normal whenever physiologic or mechanical disruption of the breath occurs.
PATIENT AND FAMILY EDUCATION
• Discuss the reason for implementation of capnography.  Rationale: Discussion reduces anxiety for the patient and family associated with an additional monitor, related interventions, and unfamiliar procedures.
Rationale: Discussion reduces anxiety for the patient and family associated with an additional monitor, related interventions, and unfamiliar procedures.
• If the patient is alert, explain the procedure to the patient; if the patient is not alert, explain the procedure to the family.  Rationale: This communication informs the patient and family of the purpose of monitoring, improves cooperation with interventions, and reduces anxiety.
Rationale: This communication informs the patient and family of the purpose of monitoring, improves cooperation with interventions, and reduces anxiety.
PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION
Patient Assessment
• Assess indications for PetCO2 monitoring1,4,11,13,15:
•  Rationale: Assessment for initiation of PetCO2 monitoring ensures that patients at risk for inadequate ventilation and gas exchange receive monitoring for such occurrences, allowing for early institution of appropriate interventions.
Rationale: Assessment for initiation of PetCO2 monitoring ensures that patients at risk for inadequate ventilation and gas exchange receive monitoring for such occurrences, allowing for early institution of appropriate interventions.
Patient Preparation
• Verify correct patient with two identifiers.  Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
• Ensure that the patient understands preprocedural teachings. Answer questions as they arise, and reinforce information as needed.  Rationale: Understanding of previously taught information is evaluated and reinforced.
Rationale: Understanding of previously taught information is evaluated and reinforced.
References
![]() 1. AARC, AARC clinical practice guideline. capnography/capnometry during mechanical ventilation—2003 revision and update. Respir Care 2003; 48:534–538.
1. AARC, AARC clinical practice guideline. capnography/capnometry during mechanical ventilation—2003 revision and update. Respir Care 2003; 48:534–538.
![]() 2. Ahrens, T, et al. End-tidal carbon dioxide measurements as a prognostic indicator of outcome in cardiac arrest. Am J Crit Care. 2001; 10:391–398.
2. Ahrens, T, et al. End-tidal carbon dioxide measurements as a prognostic indicator of outcome in cardiac arrest. Am J Crit Care. 2001; 10:391–398.
3. Burton, JH, Harrah, JD, Germann, CA, et al. Does end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring detect respiratory events prior to current sedation montoring practices. Acad Emerg Med. 2006; 13(5):500–504.
![]() 4. Davis, DP, et al, The use of quantitative end-tidal capnometry to avoid inadvertent severe hyperventilation in patients with head injury after paramedic rapid sequence intubation . J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care. 2004; 56(4):808–814.
4. Davis, DP, et al, The use of quantitative end-tidal capnometry to avoid inadvertent severe hyperventilation in patients with head injury after paramedic rapid sequence intubation . J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care. 2004; 56(4):808–814.
5. Delorio, NM. Continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring for confirmation of endotracheal tube placement is neither widely available nor consistently applied by emergency physicians. Emerg Med J. 2005; 22:490–493.
6. Eisenbacher, S, Heard, L. Capnography in the gastroenterology lab. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2005; 28(2):99–106.
![]() 7. Erasmus, PD. The use of end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring to confirm endotracheal tube placement in adult and paedratic intensive care units in Australia and New Zealand. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004; 32(5):672–675.
7. Erasmus, PD. The use of end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring to confirm endotracheal tube placement in adult and paedratic intensive care units in Australia and New Zealand. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004; 32(5):672–675.
8. Hutchison, R, Rodriguez, L. Capnography and respiratory depression. Am J Nursing. 2008; 108(2):35–39.
![]() 9. La-Valle TL, Perry, AG, Capnography. assessing end-tidal CO2 levels. Dimensions Crit Care Nurs 1995; 14:70–77.
9. La-Valle TL, Perry, AG, Capnography. assessing end-tidal CO2 levels. Dimensions Crit Care Nurs 1995; 14:70–77.
![]() 10. Martin, S, Wilson, M, Monitoring gaseous exchange. implications for nursing care. Aust Crit Care 2002; 15:8–13.
10. Martin, S, Wilson, M, Monitoring gaseous exchange. implications for nursing care. Aust Crit Care 2002; 15:8–13.
![]() 11. Maslow, A, et al. Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass in patients without significant lung disease. Anesth Analg. 2001; 92:306–313.
11. Maslow, A, et al. Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass in patients without significant lung disease. Anesth Analg. 2001; 92:306–313.
12. Miner, JR, Krauss, B, Procedural sedation and analgesia research. state of the art. Acad Emerg Med. 2007; 14(2):170–178.
13. Rose, L, Presneill, JJ, Cade, JF. Update in computer-driven weaning from mechanical ventilation. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007; 35(2):213–221.
14. Silvestri, S, et al. The effectiveness of out-of-hospital use of continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring on the rate of unrecognized misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services system. Ann Emerg Med. 2005; 45(5):497–503.
![]() 15. St John R. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring. Crit Care Nurse. 2003; 23:83–88.
15. St John R. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring. Crit Care Nurse. 2003; 23:83–88.