Small-Bore Feeding Tube Insertion Using an Electromagnetic Guidance System (CORTRAK®)
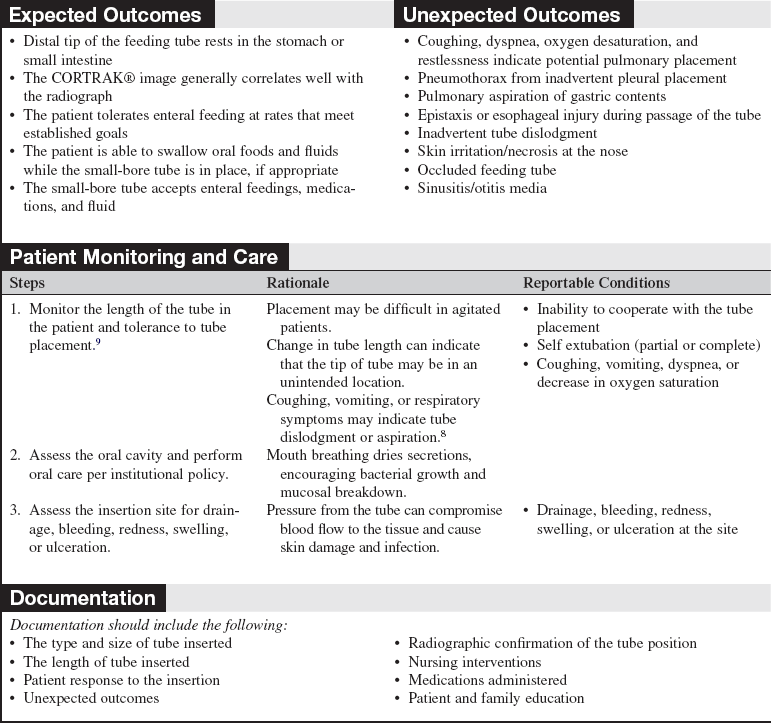
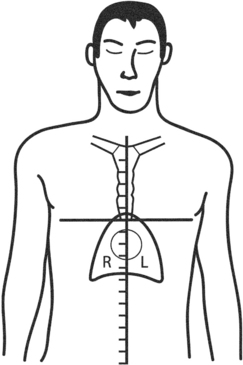
The CORTRAK® system uses electromagnetic technology to enhance the safety of bedside placement of small-bore nasoenteric feeding tubes. The guidance system directs feeding tube placement by tracking the relative location of the tube as it proceeds down the alimentary tract. This visual guidance aids in avoiding intubation of the pulmonary system and facilitates postpyloric placement of feeding tubes.1,5,8,12,15
PREREQUISITE NURSING KNOWLEDGE
• Knowledge of upper respiratory and gastrointestinal anatomy and physiology is necessary.
• Proficiency is needed in physical assessment skills for lungs and abdomen.
• Clinical and technical competence is necessary in placement of small-bore feeding tubes and in use of the CORTRAK® (Corpak MedSystems, Wheeling, IL) device, based on institutional policies.
• Recognition is needed of risk factors associated with placement errors during insertion of small-bore feeding tubes: endotracheal intubation, advanced age, altered level of consciousness, and diminished reflexes for airway protection.14
• The benefits of enteral nutrition for the critically ill, including indications for postpyloric placement, should be understood.6
EQUIPMENT
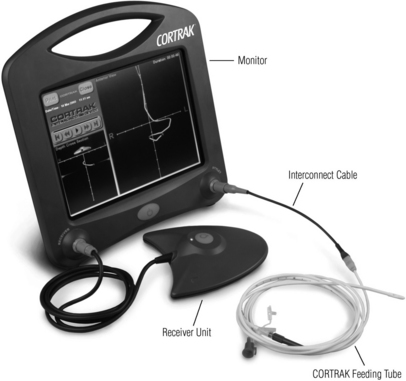
• CORTRAK® feeding tube placement device (Fig 132-1)
• CORTRAK® feeding tube with transmitting stylet
• 50-mL or larger catheter-tipped or Luer-Lok/slip syringe
• Water (tap water or sterile water based on institutional policy)
• Additional personal protective equipment, including gown and goggles
• Viscous lidocaine (optional)
PATIENT AND FAMILY EDUCATION
• Explain the essential role adequate nutritional status plays in promoting wound healing and recovery from illness.  Rationale: Explanation may elicit cooperation and allay patient anxiety.
Rationale: Explanation may elicit cooperation and allay patient anxiety.
• Explain why a feeding tube is needed to ensure adequate nutritional intake.  Rationale: Explanation may elicit cooperation and facilitate tube insertion.
Rationale: Explanation may elicit cooperation and facilitate tube insertion.
• Outline the steps in the procedure and the patient’s role during feeding tube insertion (e.g., position, swallowing as instructed).  Rationale: Patient cooperation may facilitate insertion.
Rationale: Patient cooperation may facilitate insertion.
• Describe the typical sensations experienced during feeding tube insertion.  Rationale: Explanation may alleviate anxiety and promote patient cooperation.
Rationale: Explanation may alleviate anxiety and promote patient cooperation.
• Inform patient and family of the need for postinsertion radiograph.  Rationale: Information may provide reassurance regarding expected course of events.
Rationale: Information may provide reassurance regarding expected course of events.
• Reinforce the importance of using care when changing position or getting out of bed once the tube is placed.  Rationale: Emphasis may aid in preventing inadvertent dislodgment of the tube.
Rationale: Emphasis may aid in preventing inadvertent dislodgment of the tube.
PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION
Patient Assessment
• Verify that the patient has no implanted medical devices that may be affected by electromagnetic fields.  Rationale: The CORTRAK® system is generally contraindicated for patients with implanted medical devices because of the potential for electromagnetic interference to impact the function of the implanted device or the CORTRAK®. However, no contraindication exists for defibrillators and pacemakers because extensive testing has shown that CORTRAK® does not affect the operation of these devices.4
Rationale: The CORTRAK® system is generally contraindicated for patients with implanted medical devices because of the potential for electromagnetic interference to impact the function of the implanted device or the CORTRAK®. However, no contraindication exists for defibrillators and pacemakers because extensive testing has shown that CORTRAK® does not affect the operation of these devices.4
• Assess the patient for the presence of absolute contraindications for nasal placement of small-bore feeding tubes, including basilar skull fracture; history of transsphenoidal surgery; facial, nasal, or sinus trauma; or severe clotting abnormalities.  Rationale: These conditions carry a high risk for complications from passage of the tube through the nasopharyngeal area. Intracranial placement of small-bore feeding tubes has occurred with the nasal approach in patients with basilar skull fracture. The orogastric route is a safer alternative in this situation.11
Rationale: These conditions carry a high risk for complications from passage of the tube through the nasopharyngeal area. Intracranial placement of small-bore feeding tubes has occurred with the nasal approach in patients with basilar skull fracture. The orogastric route is a safer alternative in this situation.11
• Evaluate the patient for relative contraindications for placement of either nasally or orally inserted small-bore feeding tubes, including esophageal varices with recent bleeding or ligation within 72 hours; esophageal stricture, tumor, recent esophageal surgery; history of gastrointestinal surgery with altered anatomic pathways; gastroesophageal reflux; and gastroparesis.  Rationale: These conditions may impede efforts to achieve optimal tip position for enteral nutrition.6
Rationale: These conditions may impede efforts to achieve optimal tip position for enteral nutrition.6
• Additional relative contraindications for nasal placement also include history of nasal polyps, septal abnormalities, sinusitis, and minor to moderate clotting abnormalities.  Rationale: These conditions carry a relative risk for complications from passage of the tube through the nasopharyngeal route. Placement of the tube may still be undertaken if the assessment of benefit outweighs risk.
Rationale: These conditions carry a relative risk for complications from passage of the tube through the nasopharyngeal route. Placement of the tube may still be undertaken if the assessment of benefit outweighs risk.
• Assess gastrointestinal function.  Rationale: A functional gastrointestinal tract is essential for safe and effective tube feeding. The integrity and function of the gastrointestinal tract also guide decisions regarding the optimal location for delivery of nutrients (gastric versus postpyloric tip position).
Rationale: A functional gastrointestinal tract is essential for safe and effective tube feeding. The integrity and function of the gastrointestinal tract also guide decisions regarding the optimal location for delivery of nutrients (gastric versus postpyloric tip position).
Patient Preparation
• Reinforce the information previously covered during patient and family education. Respond to any additional questions or concerns the patient may have.  Rationale: Emphasis may enhance patient cooperation by reducing anxiety.
Rationale: Emphasis may enhance patient cooperation by reducing anxiety.
• Assess the need to remove any existing large-bore feeding tube.  Rationale: In some cases, the large-bore tube may be kept in place to allow gastric decompression while delivery of enteral formula takes place in the small intestine. When the large-bore tube is to be replaced by a small-bore tube, the larger tube should be removed before the new tube is passed to avoid dislodging the small-bore tube during removal of the large-bore tube.
Rationale: In some cases, the large-bore tube may be kept in place to allow gastric decompression while delivery of enteral formula takes place in the small intestine. When the large-bore tube is to be replaced by a small-bore tube, the larger tube should be removed before the new tube is passed to avoid dislodging the small-bore tube during removal of the large-bore tube.
• Obtain an order from the physician or advanced practice nurse for the administration of metoclopramide 10 mg intravenously 10 minutes before the procedure (optional). Metoclopramide is used with caution because prolonged administration at higher doses is associated with the development of tardive dyskinesia.  Rationale: Enhanced gastric motility facilitates passage of the tube distal to the pylorus.3
Rationale: Enhanced gastric motility facilitates passage of the tube distal to the pylorus.3
References
1. Ackerman, M, Mick, DJ. Technologic approaches to -determining proper placement of enteral feeding tubes. AACN Adv Crit Care. 2006; 17:246–249.
2. Aguilar-Nescimento JE, Kudsk, KA, Use of small bore feeding tubes. success and failures. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2007; 10:226–291.
3. Bankhead, RR, Fang, JC, Enteral access devices Gottschlich MM, ed.. The A. S. P. E. N. Nutrition Support Core Curriculum. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Silver Spring, MD, 2007:233–245.
4. CORPAK MedSystems, CORTRAK® contraindication statement . CORPACK MedSystems, Wheeling, IL, 2008.
5. CORPAK Medsystems, CORTRAK® enteral access system operator’s guide . CORPAK Medsystems, Wheeling, IL, 2008.
6. Cresci, G. Trauma, surgery, burns. In: Gottschlich MM, et al, eds. The A. S. P. E. N. Nutrition Support Core Curriculum. Silver Spring, MD: American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition; 2007:455–476.
![]() 7. Ellett, ML, et al. Predicting the insertion distance for placing gastric tubes. Clin Nurs Res. 2005; 14:11–27.
7. Ellett, ML, et al. Predicting the insertion distance for placing gastric tubes. Clin Nurs Res. 2005; 14:11–27.
8. Gray, R, et al, Bedside electromagnetic-guided feeding tube placement. an improvement over traditional placement technique. Nutr Clin Pract 2007; 22:436–444.
![]() 9. Metheny, NA, et al. Indicators of tube site during feedings. J Neurosci Nurs. 2005; 37(6):320–325.
9. Metheny, NA, et al. Indicators of tube site during feedings. J Neurosci Nurs. 2005; 37(6):320–325.
10. Metheny, NA, Preventing respiratory complications of tube feedings. evidence based practice. Am J Crit Care. 2006; 15(4):360–369.
11. Metheny, NA, Meert, KL, Clouse, RE, Complications related to feeding tube placement. Curr Opin Gastroenterol . 2007; 23:178–182.
12. Phang, J, Marsh, W, Prager, R. Feeding tube placement with the aid of a new electromagnetic transmitter. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2006; 30:S48. [[abstract SO82]].
13. Roberts, S, Echeverria, P, Gabriel, SA. Devices and techniques for bedside enteral feeding tube placement. Nutr Clin Pract. 2007; 22:412–420.
14. Sorokin, R, Gottlieb, JE, Enhancing patient safety during feeding-tube insertion. a review of more than 2000 insertions. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2006; 30:440–445.
15. Stockdale, W, et al. Nasoenteric feeding tube insertion utilizing an electromagnetic tube placement system. Nutr Clin Pract. 2007; 22:118. [[abstract NP24]].