Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration (Assist)
PREREQUISITE NURSING KNOWLEDGE
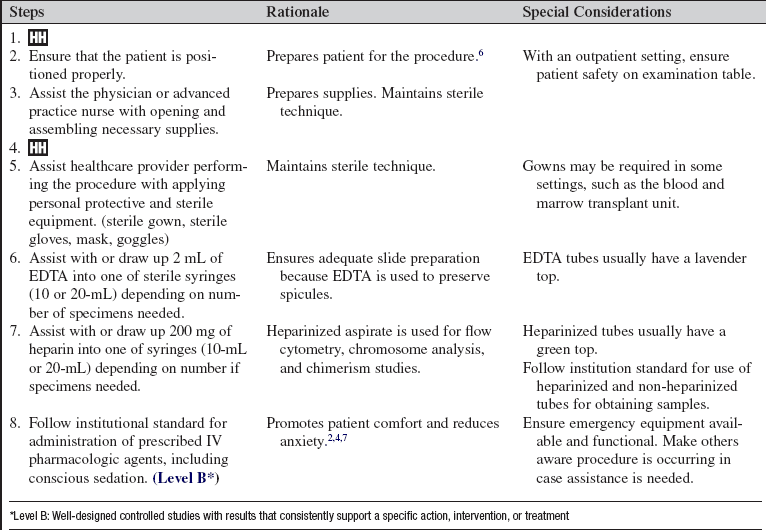
• A thorough understanding is needed of the anatomy and physiology of the posterior and anterior iliac crest and the sternum. The preferred site for a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy is the posterior iliac crest.1 The sternum may be used to aspirate marrow; however, a core biopsy cannot be obtained from the sternum because of risk of damage to underlying organs, most significantly the heart.6,8
• Clinical and technical competence in assisting with a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy is necessary.
• Clinical and technical competence in preparing slides and caring for a core biopsy is needed.
• Knowledge of sterile technique is necessary.
• Understanding is needed of institutional policies and procedures for administration of and monitoring of intravenous (IV) and oral pharmacologic agents, including conscious sedation (if indicated).
• Procedural care of the patient receiving IV conscious sedation or oral antianxiolytics or pain medication should be understood.
• Bone marrow aspirate is used in identification of normal and abnormal hematopoietic elements. The aspirate is also used to identify malignant clones with flow cytometry, to identify chromosomal abnormalities that occur in hematologic malignant disease, to perform molecular diagnostic studies of gene rearrangements and translocations, and to perform chimerism studies in patients after allogeniec transplant.
• The bone marrow biopsy is used for morphologic analysis of hematopoietic cells and for assessment of the architecture of the bone marrow that may be abnormal in certain disease states.
• Indications for bone marrow aspiration and biopsy include the following:
 To diagnosis a hematologic abnormality
To diagnosis a hematologic abnormality
 To monitor a hematologic disease state after initial diagnosis or therapy
To monitor a hematologic disease state after initial diagnosis or therapy
 To diagnose bone marrow involvement before stem cell collection and for staging of various malignant states
To diagnose bone marrow involvement before stem cell collection and for staging of various malignant states
 To assess the status of disease after autologous bone marrow or hematopoietic stem cell transplant
To assess the status of disease after autologous bone marrow or hematopoietic stem cell transplant
 To assess chimerism disease status and immune reconstitution after an allogeneic bone marrow or hematopoietic stem cell transplant
To assess chimerism disease status and immune reconstitution after an allogeneic bone marrow or hematopoietic stem cell transplant
 To evaluate immunodeficiency syndromes or to confirm an infectious disease process in the marrow
To evaluate immunodeficiency syndromes or to confirm an infectious disease process in the marrow
• Contraindications to bone marrow biopsy and aspirate are the presence of hemophilia, severe disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, or other related severe bleeding disorders. Thrombocytopenia alone is not a contraindication to bone marrow examination.3,5 The use of anticoagulant medications may pose serious bleeding risk; therefore, coagulation studies should be obtained in these patients. The decision on whether anticoagulation can be safely withheld prior to and restarted after the procedure is patient dependent.
EQUIPMENT
• Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy kit, which includes the following:
 Povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine-alcohol antiseptic preparation
Povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine-alcohol antiseptic preparation
 1 vial of lidocaine (1% or 2%; 5-10 mL)
1 vial of lidocaine (1% or 2%; 5-10 mL)
 5 or 10-mL syringe for drawing up lidocaine
5 or 10-mL syringe for drawing up lidocaine
 Needles of appropriate lengths to anesthetize both skin and periosteum
Needles of appropriate lengths to anesthetize both skin and periosteum
 Sterile 4 × 4 and 2 × 2 gauze pads
Sterile 4 × 4 and 2 × 2 gauze pads
 Bone marrow aspirate needle (Illinois needle)
Bone marrow aspirate needle (Illinois needle)
 Jamshidi bone biopsy needle (regular or extra long)
Jamshidi bone biopsy needle (regular or extra long)
 20-mL syringe for bone marrow aspirate
20-mL syringe for bone marrow aspirate
 10-mL syringes for marrow aspiration
10-mL syringes for marrow aspiration
 Edetate disodium (EDTA) sterile solution (15 mg/mL; 2 mL total)
Edetate disodium (EDTA) sterile solution (15 mg/mL; 2 mL total)
• Filtered needle (if lidocaine drawn from glass vial)
• Fluid shield face mask or goggles
• Required tubes for specimen processing: two EDTA (lavender top) and two sodium heparin (green top) tubes (follow institution standard)
• Glass slides and cover plate
• 2½- to 6-inch spinal needle (may be required for anesthetizing periosteum in the obese patient)
• Container for bone biopsy specimen including appropriate fixative (10% formalin or sterile saline solution–soaked sterile gauze)
• 1 additional vial of lidocaine (1% or 2%)
• 1 vial of 100 unit/mL heparin (follow institution standard)
Additional equipment for patients receiving conscious sedation:
PATIENT AND FAMILY EDUCATION
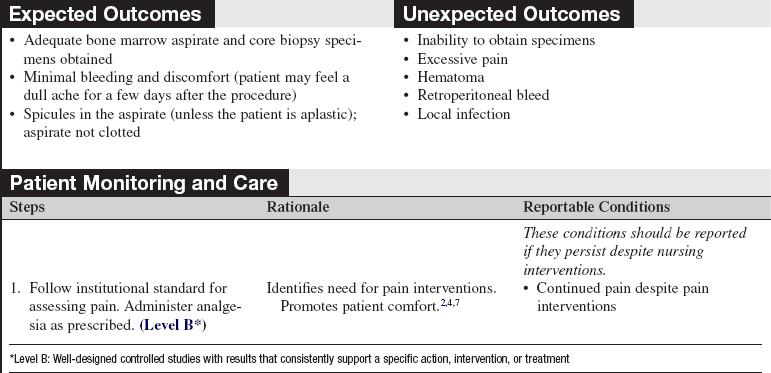
• Assess patient and family understanding of the bone marrow aspiration and biopsy procedure and the reason for it.  Rationale: Clarification of the procedure and reinforcement of information may reduce patient and family anxiety and stress.
Rationale: Clarification of the procedure and reinforcement of information may reduce patient and family anxiety and stress.
• Inform the patient and family (if permitted by patient) that the results will be shared with them as soon as they are available.  Rationale: The patient and family are usually anxious about the results.
Rationale: The patient and family are usually anxious about the results.
• Explain the actual procedure to the patient and family.  Rationale: The patient and family are prepared for what to expect. Anxiety is decreased. The patient is involved in care.
Rationale: The patient and family are prepared for what to expect. Anxiety is decreased. The patient is involved in care.
• Review safety requirements for patients who will receive pharmacologic agents for sedation (i.e., must have transportation and escort home and may not drive until the following day).  Rationale: Review ensures patient safety and healthcare provider’s accountability for patients receiving sedation.
Rationale: Review ensures patient safety and healthcare provider’s accountability for patients receiving sedation.
• Encourage the patient to verbalize any pain experienced during the procedure.  Rationale: Additional lidocaine, pain medication, or sedation medication can be administered. Patient becomes a participant in care.
Rationale: Additional lidocaine, pain medication, or sedation medication can be administered. Patient becomes a participant in care.
• Instruct patient and family to keep pressure dressing clean, dry, and in place for 24 hours after the procedure. Ask patient or family to assess for bruising or hematoma. Advise the use of ice pack to site to reduce pain and hematoma.  Rationale: Proper dressing care reduces chance of bleeding and minimizes chance of infection at the site.
Rationale: Proper dressing care reduces chance of bleeding and minimizes chance of infection at the site.
• Avoid applying heat to the procedure site.  Rationale: Heat could exacerbate bleeding.
Rationale: Heat could exacerbate bleeding.
• Advise against non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin for 24 hours after biopsy.  Rationale: This measure reduces the chance of bleeding or hematoma at site.
Rationale: This measure reduces the chance of bleeding or hematoma at site.
• Advise use of acetaminophen for pain relief, if not contraindicated.  Rationale: Acetaminophen relieves pain and does not promote bleeding.
Rationale: Acetaminophen relieves pain and does not promote bleeding.
PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION
Patient Assessment
• Assess patient’s home medications, including over-the-counter medications that can increase clotting time.  Rationale: Assessment decreases risk of bleeding and hematoma.
Rationale: Assessment decreases risk of bleeding and hematoma.
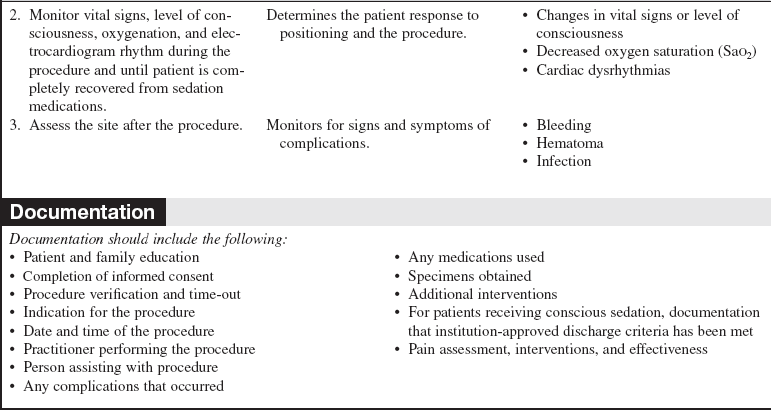
• Assess the need for antianxiety or analgesic medication or conscious sedation.  Rationale: If the patient is very anxious before the procedure or has had severe pain with previous bone marrow procedures, small doses of analgesia or sedation promote patient comfort. Relaxation of surrounding muscles makes procedure easier on patient and provider.
Rationale: If the patient is very anxious before the procedure or has had severe pain with previous bone marrow procedures, small doses of analgesia or sedation promote patient comfort. Relaxation of surrounding muscles makes procedure easier on patient and provider.
• Assess coagulation studies in patients who are taking anticoagulant medications.  Rationale: Patients at risk for bleeding complications are identified.
Rationale: Patients at risk for bleeding complications are identified.
• Assess the ability of the patient to lie on his or her stomach or side, with the head of the bed at no greater than a 25-degree elevation.  Rationale: Access to and control of the posterior iliac crest is best obtained with the patient lying flat, or with the head of the bed only slightly raised, in a side-lying or prone position.
Rationale: Access to and control of the posterior iliac crest is best obtained with the patient lying flat, or with the head of the bed only slightly raised, in a side-lying or prone position.
• Assess vital signs and oxygenation status.  Rationale: Baseline data are provided. Assessment ensures that the blood pressure and oxygenation status can be maintained if the patient is placed on his or her side or prone.
Rationale: Baseline data are provided. Assessment ensures that the blood pressure and oxygenation status can be maintained if the patient is placed on his or her side or prone.
• Assess for recent bone marrow aspiration and biopsy sites.  Rationale: The patient may have a painful experience if an additional biopsy is performed at a site that has not yet healed from a previous procedure. Penetration of scar tissue from areas of previous biopsies also may be difficult.
Rationale: The patient may have a painful experience if an additional biopsy is performed at a site that has not yet healed from a previous procedure. Penetration of scar tissue from areas of previous biopsies also may be difficult.
Patient Preparation
• Ensure that the patient and family understand pre- and postprocedural teachings and discharge instructions. Answer questions as they arise, and reinforce information as needed.  Rationale: Understanding of previously taught information is evaluated and reinforced. The patient and family understand postprocedure care. The patient is made a participant in care.
Rationale: Understanding of previously taught information is evaluated and reinforced. The patient and family understand postprocedure care. The patient is made a participant in care.
• Verify correct patient with two identifiers.  Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
• Obtain informed consent for bone marrow aspiration and biopsy and, if indicated, conscious sedation.  Rationale: Informed consent protects the rights of the patient and makes a competent decision possible for the patient.
Rationale: Informed consent protects the rights of the patient and makes a competent decision possible for the patient.
• Perform a pre-procedure verification and time out, if non-emergent.  Rationale: Ensures patient safety.
Rationale: Ensures patient safety.
• Administer analgesia or sedation as prescribed.  Rationale: Patient may need analgesia or sedation to ensure adequate cooperation and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
Rationale: Patient may need analgesia or sedation to ensure adequate cooperation and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
• Follow institution standard for a patient receving conscious sedation.  Rationale: Preparation ensures that appropriate emergency equipment and medical staff are available.
Rationale: Preparation ensures that appropriate emergency equipment and medical staff are available.
• Obtain IV access for patients receiving sedation.  Rationale: A secure patent IV line is necessary for administration of IV pharmacologic agents and, if necessary, emergency antagonist agents.
Rationale: A secure patent IV line is necessary for administration of IV pharmacologic agents and, if necessary, emergency antagonist agents.
• Obtain a complete blood count and differential via venipuncture.  Rationale: Many pathologists prefer to review a peripheral blood sample in conjunction with the marrow to make a complete and accurate diagnostic evaluation.
Rationale: Many pathologists prefer to review a peripheral blood sample in conjunction with the marrow to make a complete and accurate diagnostic evaluation.
• Confirm availability of personnel who will assist with the procedure.  Rationale: Slide preparation, specimen processing, and obtaining additional supplies require an appropriately trained assistant for the procedure.
Rationale: Slide preparation, specimen processing, and obtaining additional supplies require an appropriately trained assistant for the procedure.
• Assist the patient to an appropriate position depending on the patient’s comfort and the practitioner’s preference.  Rationale: Positioning ensures good visualization and control of the posterior iliac crest.
Rationale: Positioning ensures good visualization and control of the posterior iliac crest.
References
![]() 1. Bain, BJ. Bone marrow aspiration. J Clin Pathol. 2001; 54:657–663.
1. Bain, BJ. Bone marrow aspiration. J Clin Pathol. 2001; 54:657–663.
![]() 2. Burkle, CM, et al. Morbidity and mortality of deep sadation in outpatient bone marrow biopsy. Am J Hematol. 2004; 77:250–256.
2. Burkle, CM, et al. Morbidity and mortality of deep sadation in outpatient bone marrow biopsy. Am J Hematol. 2004; 77:250–256.
![]() 3. Ellis, LD, Jensen, WN, Westerman, MP, Needle biopsy of bone and marrow. an experience with 1,445 biopsies. Arch Intern Med 1964; 114:213–221.
3. Ellis, LD, Jensen, WN, Westerman, MP, Needle biopsy of bone and marrow. an experience with 1,445 biopsies. Arch Intern Med 1964; 114:213–221.
4. Gudgin, EJ, Besser, MW, Craig, JIO. Entonox as a sedative for bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. Int J Lab Hematol. 2008; 30:65–67.
![]() 5. Hyun, BH, Gulati, GL, Ashton, JK, Bone marrow examination. techniques and interpretation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 1988; 2:513–523.
5. Hyun, BH, Gulati, GL, Ashton, JK, Bone marrow examination. techniques and interpretation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 1988; 2:513–523.
![]() 6. Riley, RS, et al, A pathologist’s perspective on bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. 1performing a bone marrow examination. J Clin Lab Anal 2004; 18:70–90.
6. Riley, RS, et al, A pathologist’s perspective on bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. 1performing a bone marrow examination. J Clin Lab Anal 2004; 18:70–90.
![]() 7. Vanhelleputte, P, et al, Pain during bone marrow aspiration. prevalence and prevention. J Pain Symptom Manage 2003; 26:860–866.
7. Vanhelleputte, P, et al, Pain during bone marrow aspiration. prevalence and prevention. J Pain Symptom Manage 2003; 26:860–866.
![]() 8. Van Marum RJ, Te Velde L. Cardiac tamponade following sternal puncture in two patients. Netherlands J Med. 2001; 59:39–40.
8. Van Marum RJ, Te Velde L. Cardiac tamponade following sternal puncture in two patients. Netherlands J Med. 2001; 59:39–40.
Aboul-Nasr, R, et al. Comparison of touch imprints with aspirate smears for evaluating bone marrow specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1999; III(6):753–758.
Burke, JM, Dx/Rx. leukemia,. Jones and Bartlett, Boston, 2006.
Bain, BJ. Bone marrow trephine biopsy. J Clin Pathol. 2001; 54:737–742.
DeVita, VT, et al. Cancer principles and practice,, ed 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
Huyn, BH, Stevenson, AJ, Hanua, CA. Fundamentals of bone marrow examination. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1994; 8:651–663.
Lawson, S, et al. Trained nurses can obtain satisfactory bone marrow aspirates and trephine biopsies. J Clin Pathol. 1999; 52:154–156.
Lin, EM, Advanced practice in oncology nursing. case studies and review,. Saunders, Philadelphia, 2001.
Litwack, K. Core curriculum for perianesthesia nursing,, ed 4. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1999.
Quinn, DMD, Schick, L, Perianesthesia nursing core curriculum. preoperative, phase I and phase II PACU nursing,. Saunders, Philadelphia, 2004.
Ryan, DH, Cohen, HJ. Bone marrow aspiration and morphology, hematology basic principles and practice,, ed 3. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2000.
Trewhitt, KG. Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy collection and interpretation. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2001; 28:1409–1415.
Watson, M, et al. Oncology,, ed 2. New York: Oxford Press; 2006.