Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prevention of Viral Diseases
I Laboratory Identification of Viruses
1. Bacterial or fungal etiology for an infection should be excluded before undertaking laboratory analysis for viral infection.
2. Appropriate specimens for analysis are determined by the site of infection and presumptive diagnosis based on symptoms.
B Microscopic examination of clinical specimens
1. Light microscopy can detect virus-induced histologic changes, called viral cytopathic effects (CPEs), in cells and tissues.
• Common CPEs include vacuolization, necrosis, syncytia formation, and various types of inclusion bodies.
2. Electron microscopy can visualize virions directly in cells or stool specimens.
1. Unlike bacteria or fungi, viruses replicate only within cells and must be isolated and grown in cells that support their replication.
2. Some viruses cannot be grown in the laboratory because no suitable culture system has been developed.
D Laboratory assays for detecting viral proteins
1. Hemagglutination: viral hemagglutinin (HA) protruding from the surface of some enveloped viruses binds to erythrocytes of specific species, causing them to clump.
• Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI): specific antibody blocking of hemagglutination can identify the virus strain causing HA. Patient serum that can block HA of a specific strain of virus indicates prior infection with that strain of virus (e.g., influenza A H1N1)
• Hemadsorption is the binding of certain erythrocytes to viral HA expressed in the membrane of infected cells.
• Virus-specific antibody is used to detect free virions and free or cell-associated viral proteins.
a. Antibody-antigen binding is detected by a probe such as a fluorescent marker, radiolabel, or enzyme (e.g., horseradish peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, and β-galactosidase) that produces a colored product on addition of substrate.
• Immunofluorescence (IF) and enzyme immunoassay (EIA) detect viral proteins expressed on the surface of infected cells (see Fig. 5-3).
• Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and radioimmunoassay (RIA) detect and quantitate free virions or viral proteins in a sample.
E Laboratory assays for detecting viral nucleic acids
• Assays for viral nucleic acids are particularly useful in identifying slowly replicating viruses or those that do not have obvious cytopathic effects.
1. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (DNA), reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) (RNA), and related technologies, which permit amplification of specific nucleic acid sequences, are especially helpful in rapid detection of viruses
2. Southern blotting for DNA and Northern blotting for RNA detect electrophoretically separated genome sequences.
3. In situ hybridization detects viral DNA or RNA within infected cells.
F Serology (history of the infection)
1. Serologic testing can determine the type and titer of antiviral antibodies in serum and the identity of viral antigens.
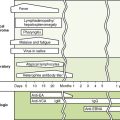
2. Titers of antibody to key viral antigens indicate the stage of infection with Epstein-Barr virus and hepatitis B virus.
1. Because viruses use much of the host cell biochemical machinery, they offer fewer targets than bacteria for drugs that are effective antiviral agents but nontoxic to host cells.
2. The primary potential targets of antiviral drugs are illustrated in Chapter 18, Fig. 18-5.
B Common viruses treatable with antiviral drugs
1. The mechanism of action and approved uses of the major types of antiviral drugs are summarized in Table 20-1.
TABLE 20-1

*Viruses against the indicated drugs have been approved for use. A more complete list of anti-HIV drugs is provided in Chapter 26.
2. The largest number of approved drugs are nucleoside analogues that disrupt replication of the viral genome in herpesviruses or HIV.
C Mechanisms of viral resistance to drugs
1. Mutation in target protein (e.g., polymerase) or activating enzyme (e.g., thymidine kinase of herpes simplex virus) of antiviral drug.
2. Rapid mutation rate of viruses can facilitate generation of resistance
3. Resistance is rare when multiple drugs with different mechanisms are used for HIV (highly active antiretroviral therapy [HAART]).
A Passive immunization by administration of immunoglobulin (Table 20-2)
TABLE 20-2
| Virus | Recipient |
| Hepatitis A | Contacts |
| Hepatitis B | Potentially infected individuals |
| Measles | Potentially infected individuals |
| Rabies | Potentially infected individuals |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | Premature newborns |
| Varicella-zoster virus | Immunocompromised children |
| Cytomegalovirus | Transplant recipients |
• Provides rapid, short-term protection
1. Rabies gammaglobulin immediately after infection to block progression of the virus
2. Varicella-zoster gammaglobulin for immunocompromised children (e.g., those with leukemia), postexposure for pregnant women up to 20 weeks, and newborns of mothers with active varicella-zoster virus infection
3. Hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus gammaglobulin to block infection of liver after exposure
4. Antibodies to respiratory syncytial virus protect early-term babies against life-threatening pneumonia
B Active immunization (Table 20-3)
TABLE 20-3
Frequently Used Viral Vaccines
| Virus | Type of Vaccine | Indications |
| Hepatitis A | Inactivated | Travelers |
| Hepatitis B | Subunit | Newborns, medical personnel, sexually promiscuous individuals, intravenous drug abusers |
| Human papilloma subunit virus | Young women aged 13-25 years (before sexual activity) | |
| Influenza | Inactivated | Adults, especially medical personnel and elderly patients |
| Influenza | Attenuated | Children (>2 yr) and adults (<60 yr) |
| Measles | Attenuated | Children |
| Mumps | Attenuated | Children |
| Polio | Inactivated (Salk vaccine) | Children (recommended) |
| Attenuated (Sabin vaccine) | Children | |
| Rotavirus | Attenuated or reassortant | Children |
| Rubella | Attenuated | Children |
| Varicella-zoster | Attenuated | Children (stronger form for adults [>60 yrs]) |
• Attenuated strains of virus, which will not cause serious disease in immunocompetent individuals
a. Common vaccines include measles, mumps, rubella, influenza, and varicella-zoster, all of which are recommended for routine administration to young children.
b. Live vaccines have a small probability of causing disease in immunocompromised individuals.
c. The live oral polio vaccine (Sabin) is not recommended because of potential for reversion to virulence and production of disease.
• Virus from another species that elicits a protective response in humans