Choroidal Melanoma
Clinical Features:
The most common appearance is a pigmented, elevated choroidal lesion that will enlarge without treatment (Fig. 21.2.1 and Fig. 21.2.2). Without documented growth, features such as overlying lipofuscin (orange pigment), associated subretinal fluid, larger size, and proximity to the optic nerve help to differentiate from benign lesions such as choroidal nevus. On a clinical basis, the diagnosis can be made with greater than 99% accuracy. Biopsy is rarely necessary, but can confirm the diagnosis. Radiation retinopathy can often develop after treatment with external radiation (Fig 21.2.3).
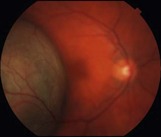
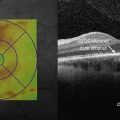
Figure 21.2.1 Color fundus photograph of a large, elevated pigmented choroidal melanoma. The lesion is so elevated that the neighboring macula and optic nerve are out of focus.
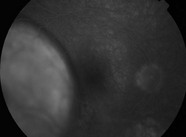
Figure 21.2.2 Late phase fluorescein angiogram (corresponding to Figure 21.2.1) shows an internal circulation of the choroidal melanoma.
OCT Features:
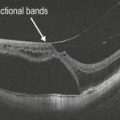
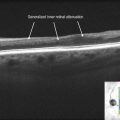
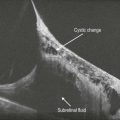
A large homogeneous hyporeflective, elevated area of choroidal infiltration is typically seen in association with overlying subretinal fluid (Figs. 21.2.4 and 21.2.5). Enhanced depth imaging OCT can assist the documentation of relatively small melanomas. Older lesions can exhibit cystoid retinal degeneration over the surface of the tumor. More acute lesions can show shaggy photoreceptors overlying subretinal fluid. Associated retinopathy can lead to severe cystoid macular edema and retinal atrophy (Fig. 21.2.6).

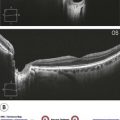
Figure 21.2.4 OCT (corresponding to Figure 21.2.1) shows a large hyporeflective cavity in the choroidal space corresponding to the melanoma with adjacent subretinal fluid. There is mirror artifact overlying the hyporeflective cavity on the left side of the image. There is shadowing underneath the melanoma blocking the choroid and sclera.

Figure 21.2.5 OCT of another choroidal melanoma with a large hyporeflective cavity in the choroidal space that is elevating the overlying retina. There is a cap of subretinal fluid overlying the lesion and additional hyper-reflective material in the subretinal space, which may represent shed photorecepters. The inner retina is abnormally hyper-reflective.

Figure 21.2.6 OCT (corresponding to Figure 21.2.2) shows severe cystoid macular edema (CME) with adjacent retinal atrophy. There is also generalized loss of photoreceptors.
Ancillary Testing:
B-scan ultrasonography can be useful in distinguishing choroidal melanoma from benign lesions, such as choroidal nevus. Fluorescein angiography can also be helpful by demonstrating a characteristic internal circulation within the melanoma (Fig. 21.2.2).