Hypervascular pancreatic mass with multiple peptic ulcers and thickened folds
 of the stomach.
of the stomach.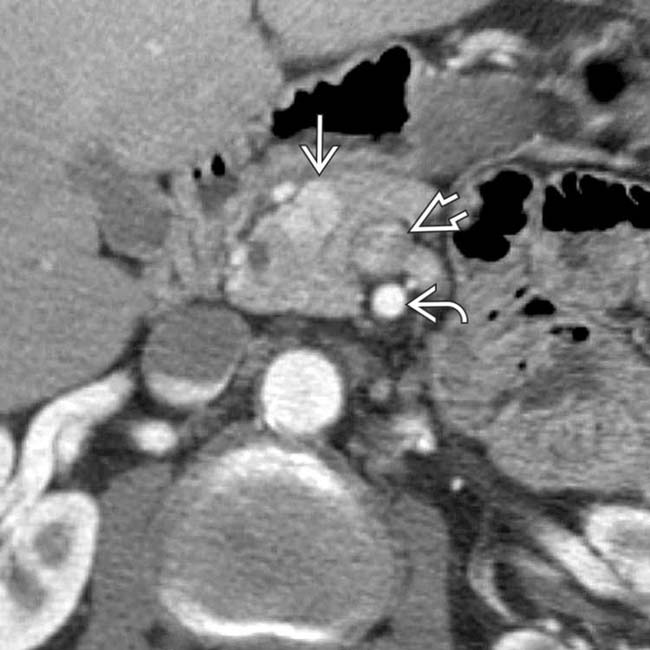
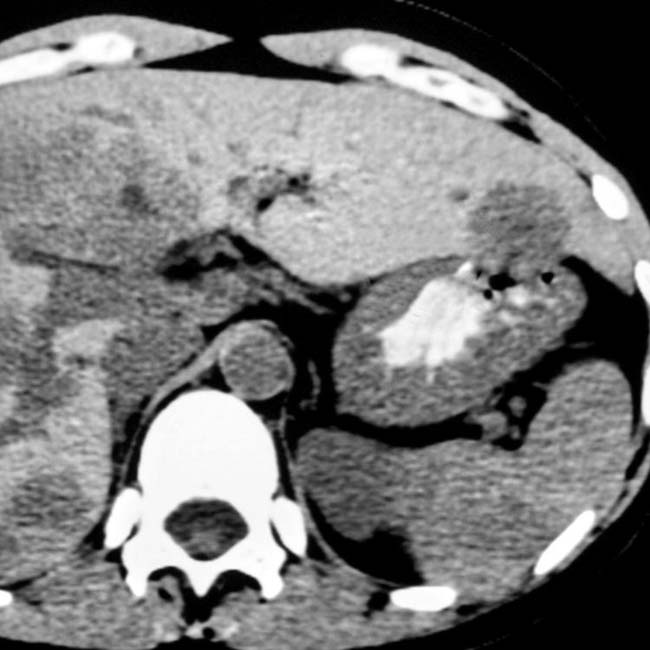
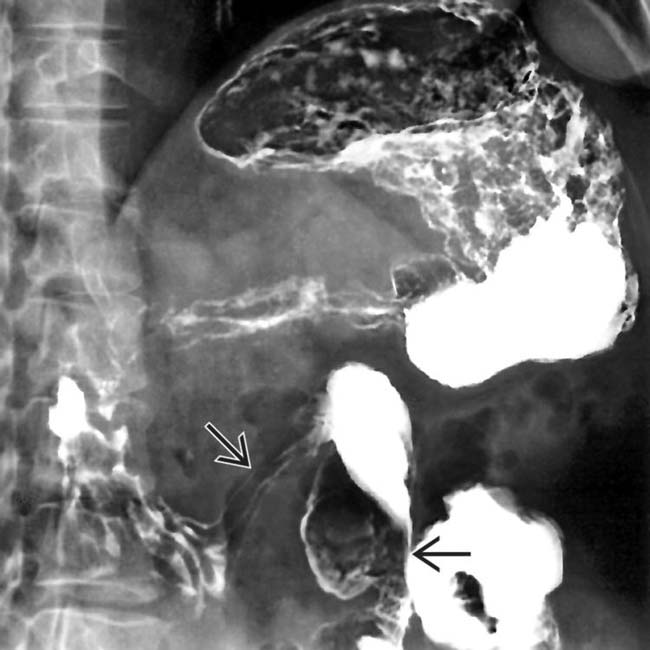
 in the pancreatic head. It is important to distinguish this from the superior mesenteric artery
in the pancreatic head. It is important to distinguish this from the superior mesenteric artery  and superior mesenteric vein
and superior mesenteric vein  .
.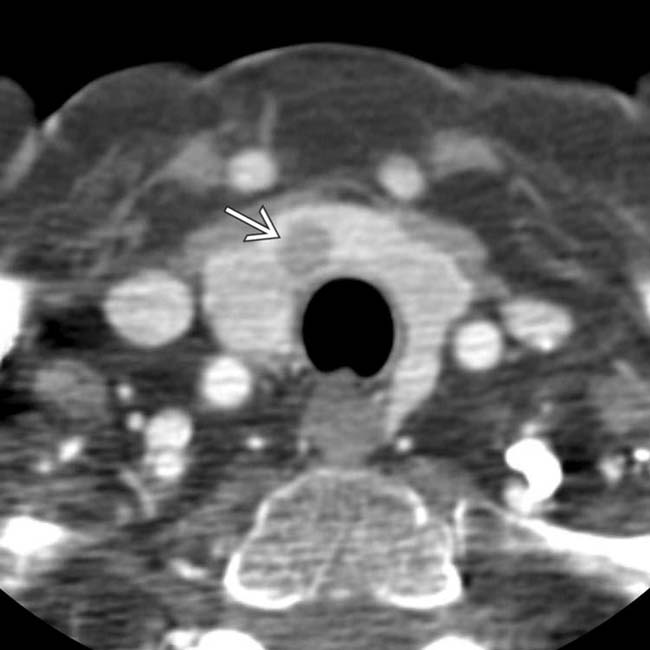
 , representing parathyroid adenomas or hyperplasia.
, representing parathyroid adenomas or hyperplasia.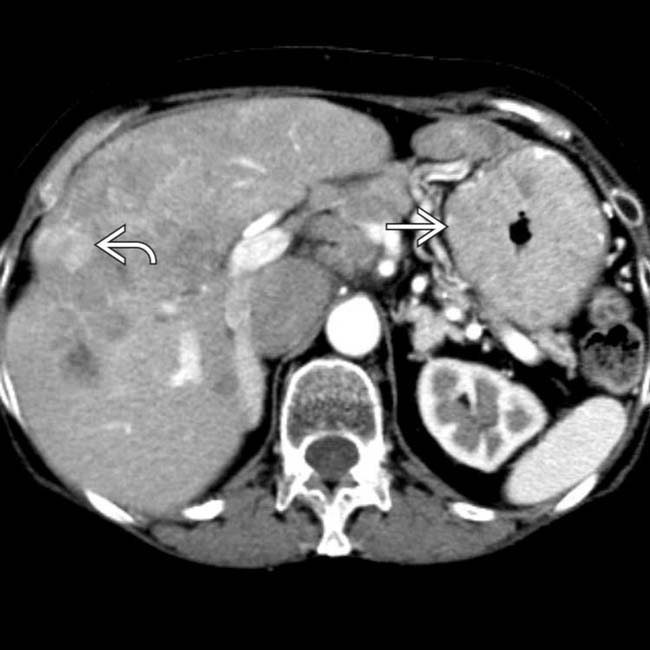
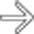
 . Multiple liver metastases are present
. Multiple liver metastases are present 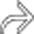 . The serum gastrin levels were strikingly elevated, confirming ZES, though the gastrinoma was not identified on CT.
. The serum gastrin levels were strikingly elevated, confirming ZES, though the gastrinoma was not identified on CT.IMAGING
General Features
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Gastritis
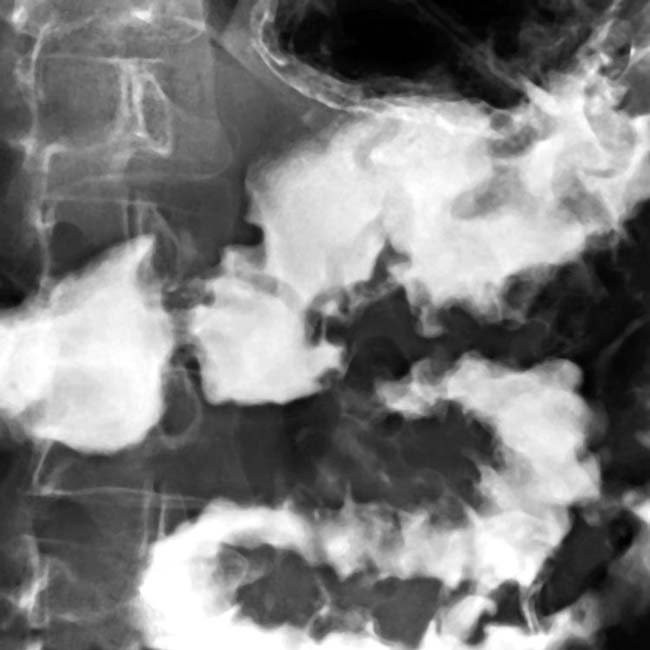
 resulting in a dilated duodenum due to spasm and edema. Gastric folds are thickened and the barium within the stomach is diluted and poorly adherent due to increased secretions. These are classic fluoroscopic features of ZES.
resulting in a dilated duodenum due to spasm and edema. Gastric folds are thickened and the barium within the stomach is diluted and poorly adherent due to increased secretions. These are classic fluoroscopic features of ZES.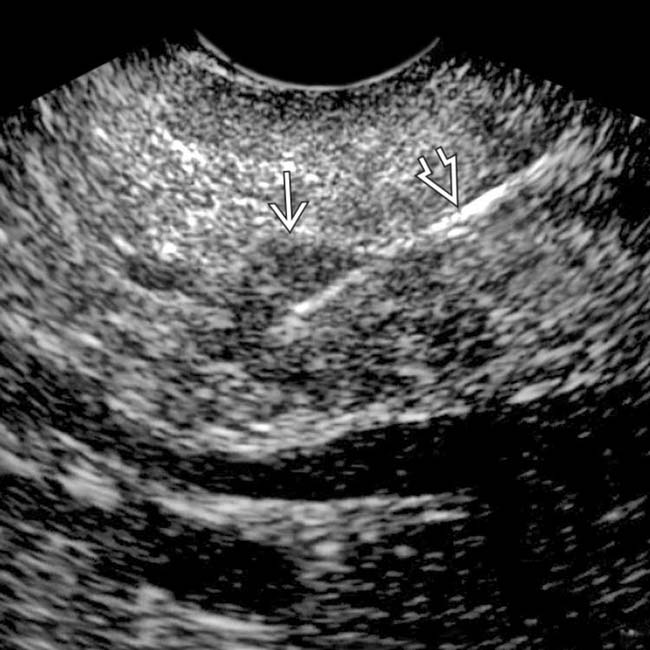
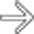
 that was biopsied during the same procedure. The biopsy needle is evident
that was biopsied during the same procedure. The biopsy needle is evident  . This documented a gastrinoma, accounting for the patient’s signs and symptoms.
. This documented a gastrinoma, accounting for the patient’s signs and symptoms.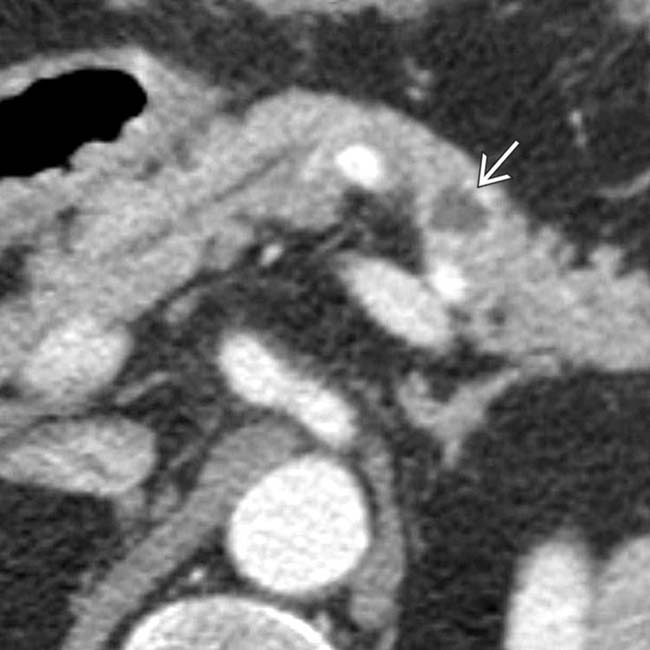
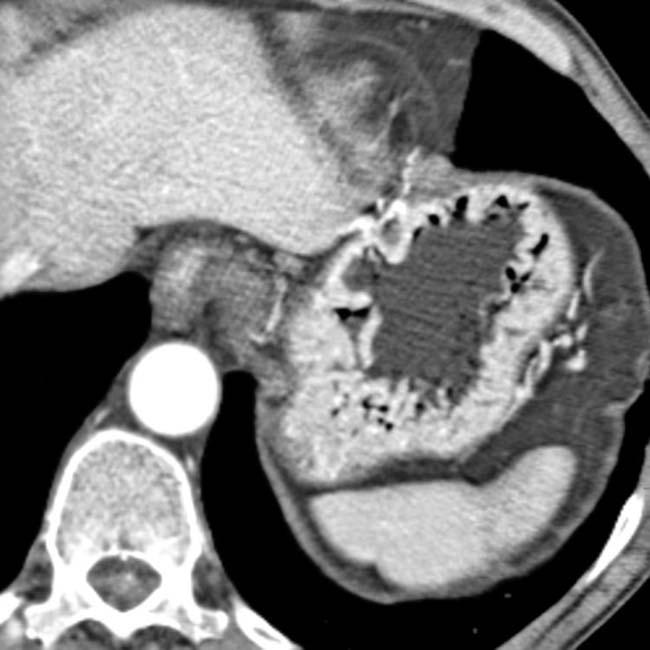
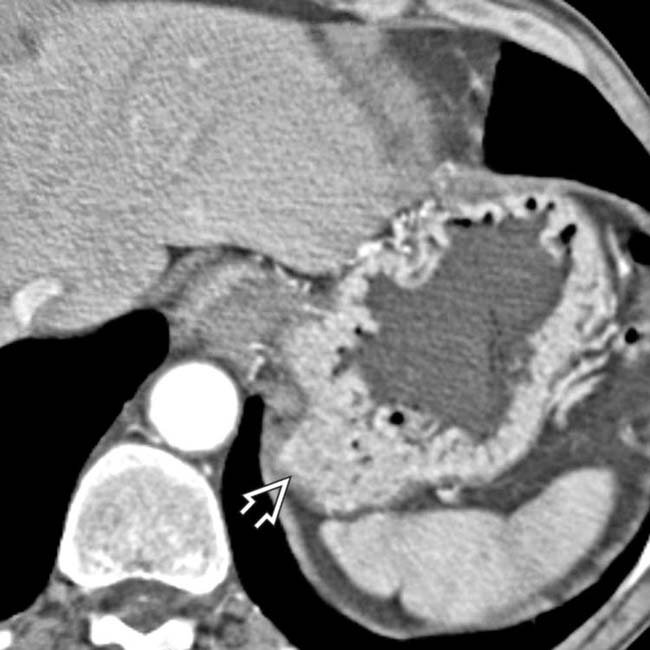
 with an enhancing, solid periphery and a cystic or necrotic center.
with an enhancing, solid periphery and a cystic or necrotic center.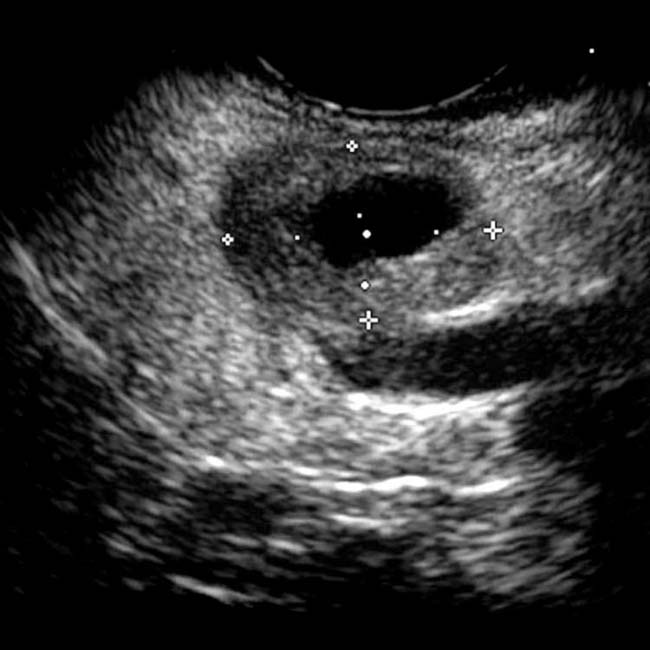
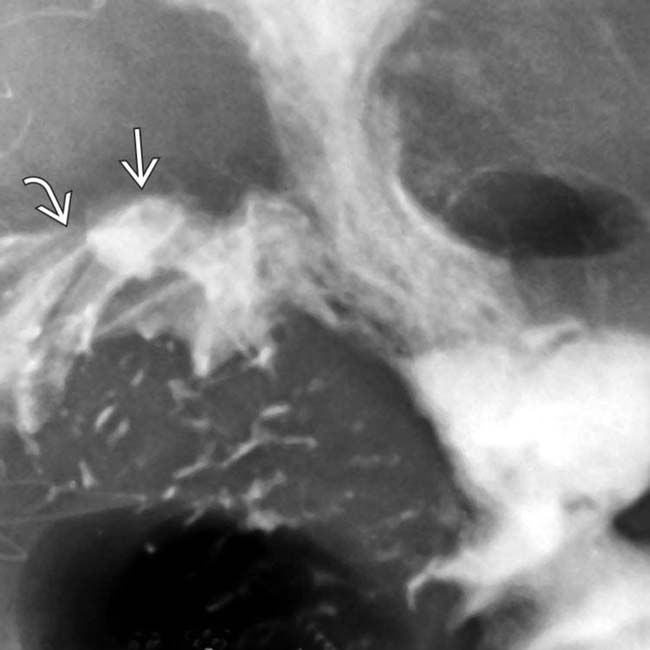
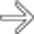 at the site of the gastroenteric anastomosis. Note the radiating folds
at the site of the gastroenteric anastomosis. Note the radiating folds 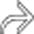 leading to the ulcer crater.
leading to the ulcer crater.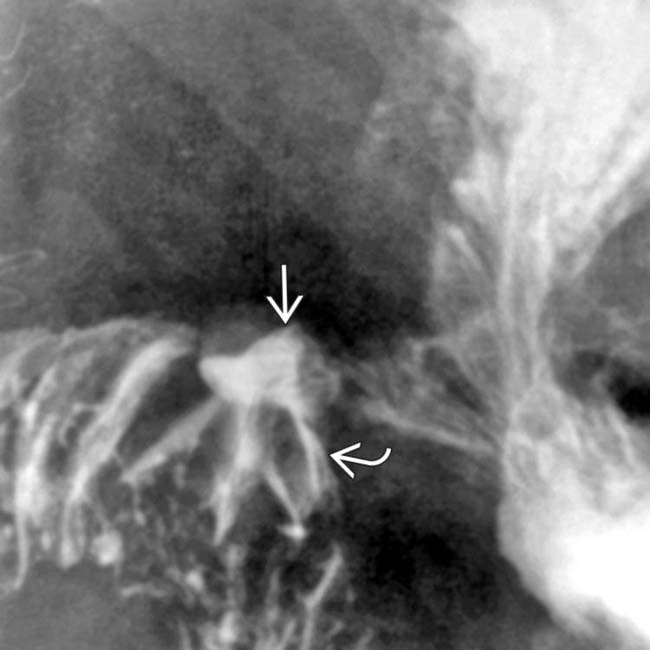
 and the radiating folds
and the radiating folds  leading to the ulcer crater.
leading to the ulcer crater.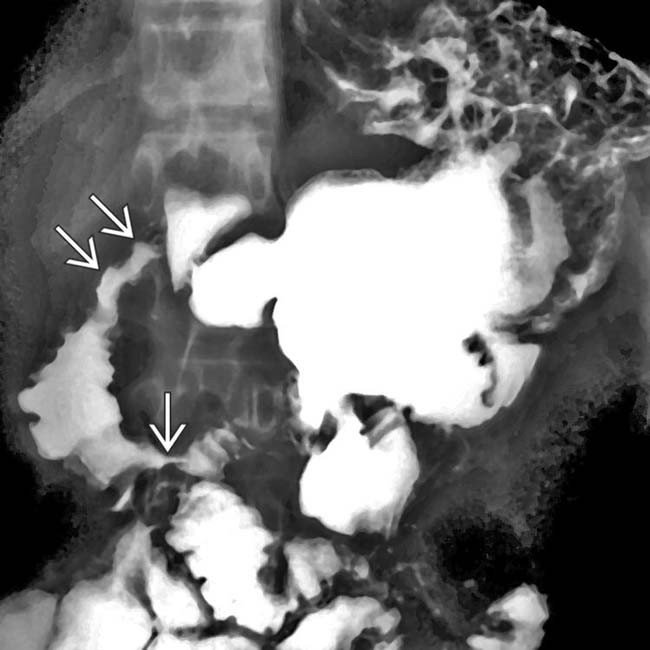
 .
.
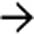 , probably from prior ulceration.
, probably from prior ulceration.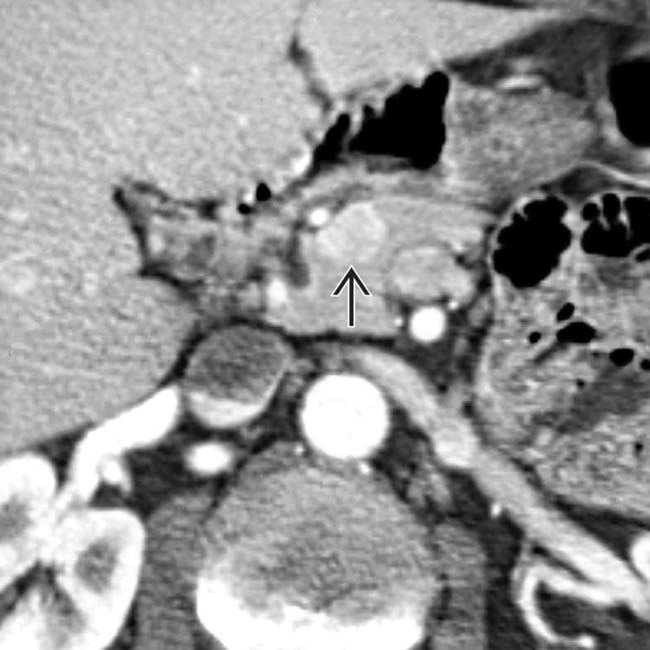
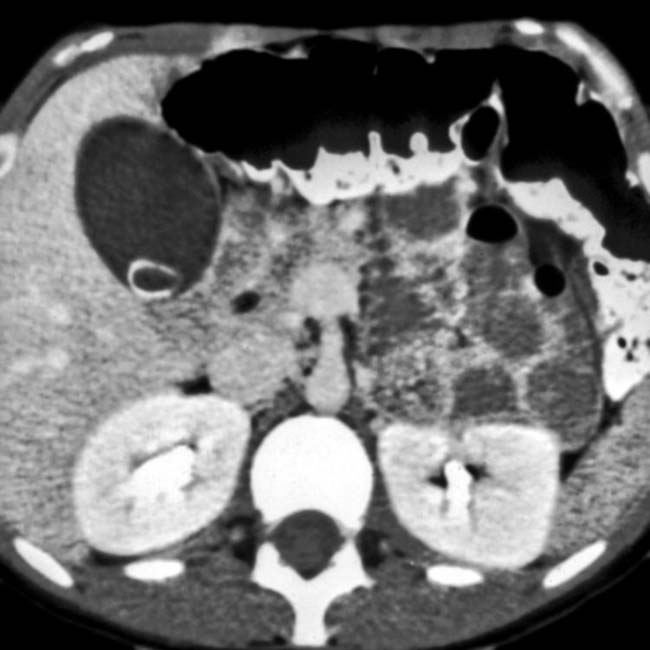
 in the pancreatic head which proved to be a gastrinoma at resection.
in the pancreatic head which proved to be a gastrinoma at resection.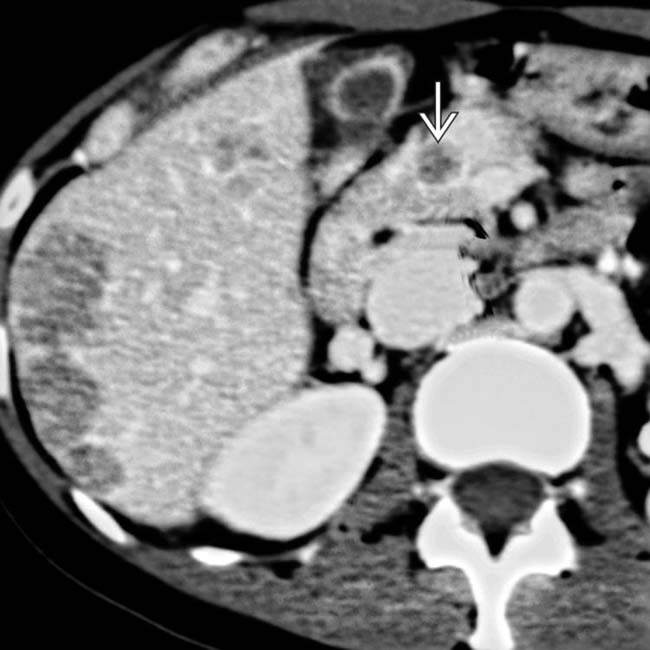
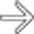 in the pancreatic head and multiple subtle liver metastases.
in the pancreatic head and multiple subtle liver metastases.