Z
Zeis, glands of See glands of Zeis.
zinc sulphate An astringent and antiseptic agent sometimes used topically in solution 0.2% or 0.25%, to clear mucus from the outer surface of the eye (by precipitating proteins), to give temporary relief of minor eye infections, and to treat some types of bacterial conjunctivitis.
Zinn, annulus of See annulus of Zinn.
Zinn, circle of See circle of Zinn.
Zinn, zonule of A series of fibres passing from the ciliary body to the capsule of the lens at or near its equator, holding the lens in position and enabling the ciliary muscles to act upon it. The lens and zonule form a diaphragm that divides the eye into a small anterior area, which contains aqueous humour, and a larger posterior area, which contains vitreous humour. The zonule forms a ring that is roughly triangular in a meridional section. It is made up of fibres that are transparent and straight for the most part. The tension of these fibres varies with the state of contraction of the ciliary muscle and thus affects the convexity of the lens. The zonule of Zinn is made up of many non-cellular fibres, the fibrils of which consist of a cysteine-rich microfibrillar component of the elastic system, fibrillin. The fibres have been classified as follows: (1) The hyaloid zonule (orbiculo-posterior capsular fibres) which originate from the pars plana of the ciliary body and insert into the capsule just posterior to the equator at the edge of the patellar fossa. (2) The anterior zonule (orbiculo-anterior capsular fibres or anterior zonular sheet), which originate from the pars plana of the ciliary body and insert into the capsule just anterior to the equator. These are the strongest and thickest of the zonular fibres. (3) The posterior zonule (cilio-posterior capsular fibres or posterior zonular sheet), which originate from the pars plicata of the ciliary body and insert into the lens capsule posterior to the equator. These are the most numerous. (4) The equatorial zonule (cilio-equatorial fibres) which originate from the pars plicata of the ciliary body and insert into the lens capsule at the equator. Syn. suspensory apparatus of the lens; suspensory ligament; zonular fibres.
See canal, Hannover’s; canal of Petit; ciliary processes; ora serrata.
Zollner’s visual illusion See illusion, Zollner’s visual.
zone, ciliary See iris.
zone of comfort See criterion, Percival.
zone of the cornea, optical See optical zone of the cornea.
zone, optic See optic zone.
zone, pupillary See iris.
zone, scleral See scleral zone.
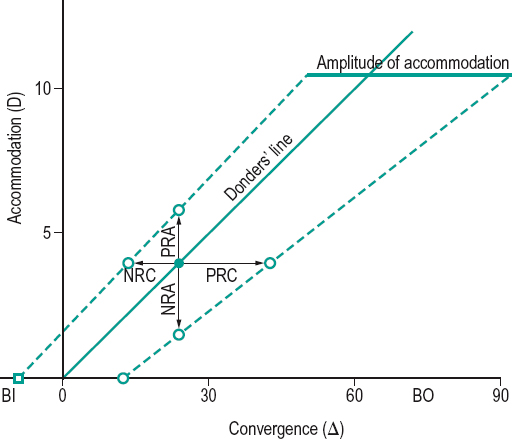
zone of clear, single, binocular vision In Donders’ diagram it is the region determined by the extremes of accommodation and convergence that can be evoked while retaining a clear, single image. Clinically, this is determined by measuring the limits of negative and positive relative convergence by using base-in and base-out prisms to blur, or by measuring relative accommodation by binocularly adding concave or convex lenses, for various binocularly fixated distances (Fig. Z1).
See accommodation, relative amplitude of; convergence, relative; Donders’ diagram; prism, rotary; vision, binocular.
zonula occludentes See tight junction.
zonular fibres See Zinn, zonule of.
zonule of Zinn See Zinn, zonule of.
zoster, herpes See herpes zoster ophthalmicus.
zygomatic bone See orbit.
zygomatic foramen See Table O4.
zygomycosis See phycomycosis.