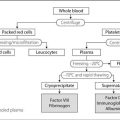
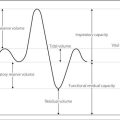
X
Xanthines (Methylxanthines). Derivatives of dioxypurine; they include caffeine and theophylline. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors, with wide spectra of activity, including CNS stimulation, diuresis, increased myocardial contractility and smooth muscle relaxation. May also inhibit adenosine and reduce noradrenaline release.
Xenon. Inert gas, making up less than 0.00001% of air. Shown to have analgesic and anaesthetic properties with a blood/gas partition coefficient of 0.14, resulting in extremely rapid uptake and excretion regardless of duration of use. Oil/gas partition coefficient is 1.9, with an MAC of 71%. Has respiratory depressant effects but little effect on cardiovascular stability. Increases cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure but may have neuroprotective properties through its inhibition of NMDA receptors. These features, plus its lack of adverse environmental properties (unlike N2O), have led to investigations into its use as an anaesthetic agent, despite its high cost.
Xylometazoline. Vasoconstrictor sympathomimetic drug, acting via α-adrenergic receptor agonism. Used as a nasal decongestant and to reduce bleeding during nasal intubation, including awake intubation. Instilled into each nostril as either drops or a spray of a 0.1% solution. Hypertension may rarely occur in susceptible patients, e.g. those taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Should be avoided in closed-angle glaucoma.