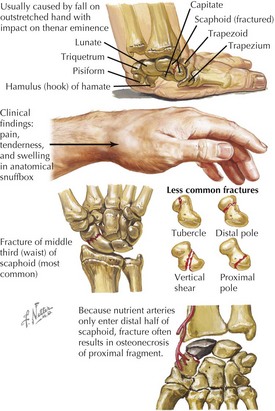
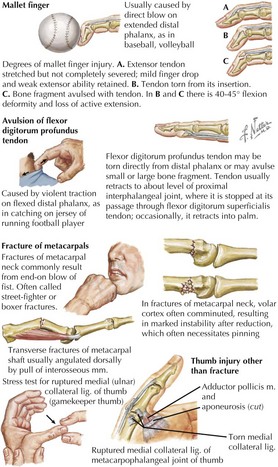
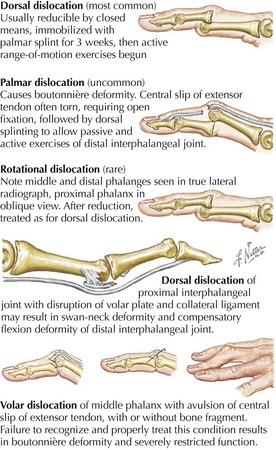
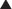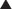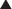23 Wrist and Hand Fractures
Anatomy of the Wrist and Hand
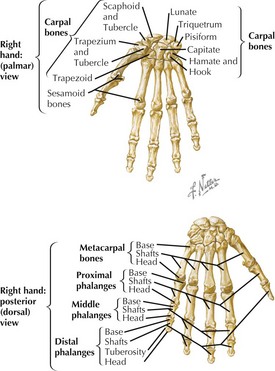
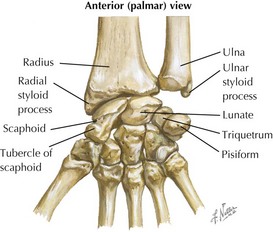
Joints of Wrist and Hand
• Radiocarpal (RC) joint
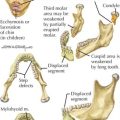
• Carpometacarpal (CM) joints
 Saddle joint between trapezium and thumb metatarsal more mobile than others: flex/extend, abduct/adduct, rotate, circumduct
Saddle joint between trapezium and thumb metatarsal more mobile than others: flex/extend, abduct/adduct, rotate, circumduct
 Saddle joint between trapezium and thumb metatarsal more mobile than others: flex/extend, abduct/adduct, rotate, circumduct
Saddle joint between trapezium and thumb metatarsal more mobile than others: flex/extend, abduct/adduct, rotate, circumductLigaments of Wrist and Hand
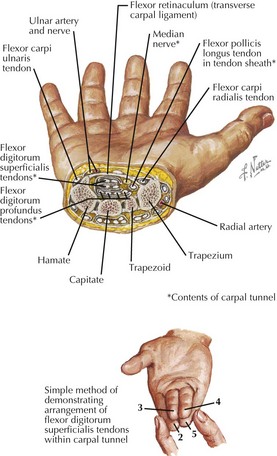
• Flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament) runs proximally between scaphoid (tubercle) and triquetrum and distally between trapezium (tubercle) and hamate (hook) and forms carpal tunnel.
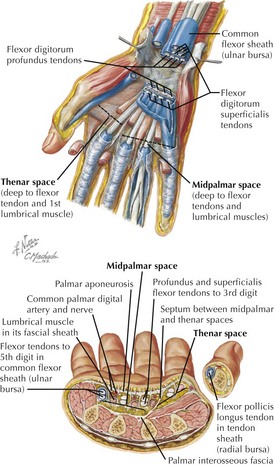
Wrist and Hand Compartments
• Forearm spaces around flexor digitorum tendons communicate with hand spaces and are pathways for forearm–hand compartment syndrome.
• Hypothenar compartment: defined by hypothenar muscle fascia (abductor, flexor brevis, opponens digiti minimi)
Vessels and Nerves
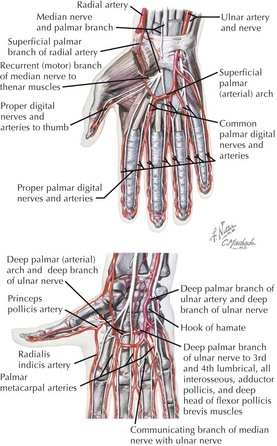
Arterial Supply
• Distal ulnar (medial) and radial (lateral) arteries contribute to anastomotic vascular arches in the palmar spaces.
Venous Drainage
Clinical Correlates
Compartment Syndrome
• Distal radius, ulnar, or carpal fractures and related tissue and vascular trauma can lead to increased compartment pressure(s), swelling, pain, and paresthesias.