118 Wilson’s disease
Salient features
Advanced-level questions
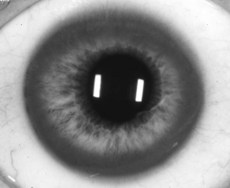
What is Kayser–Fleischer ring?
Deposition of copper in Descemet’s membrane (Fig. 118.1). The ring is most marked at the superior and inferior poles of the cornea. It is often apparent only on slit-lamp examination. It may be absent in patients with only hepatic manifestations, but it is present in those with neuropsychiatric disease.
How would you treat such a patient?
What are the radiographic features of Wilson’s disease?
• Osteopenia: most apparent in the hands, feet, and spine
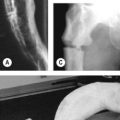
• Articular abnormalities: subchondral bone fragmentation, cyst formation and cortical irregularities, most commonly identified in the wrist, hand, foot, hip, shoulder, elbow and knee. Irregularity and indistinctness of the subchondral bone may form a characteristic ‘paintbrush’ appearance (Fig. 118.2)
• Osteomalacia and rickets have been reported. Radiologic signs of rickets, retardation of skeletal maturation and pseudofractures may be observed
• Additional characteristic radiographic findings are small, distinctly corticated ossicles around the affected joint and periosteal bone formation at the attachment sites of tendons and ligaments
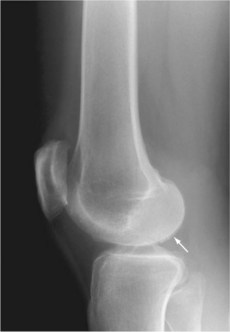
Fig. 118.2 Brushlike calcifications (arrow) along the articular surface.
(With permission from Firestein et al. 2008.)