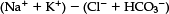12 Water, electrolytes and acid-base balance
Questions
Is an osmotic diuresis, due to hyperglycaemia for instance, a cause of both hyponatraemia and hypernatraemia. Please explain how this can be the case.
I have read the part concerning acid-base imbalances and I would like to ask about two things:
β2-adrenergic receptors increase the activity of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in the cell membrane. This is followed by the excretion of excess potassium in the urine.
Calcium ions protect the cell membrane from the effects of hyperkalaemia although they don’t alter the potassium concentration. The correction of this acute hyperkalaemia is shown in Box 12.1.
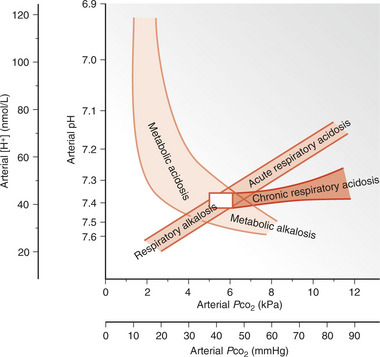
Initially, there is stimulation of the respiratory centre with hyperventilation leading to respiratory alkalosis. Metabolic acidosis ensues because of compensatory mechanisms including the renal excretion of bicarbonate and potassium as well as the accumulation of lactate, pyruvate and ketone bodies.