W
wafer A very thin lens to be cemented on a larger lens to make a bifocal lens.
Wagner’s disease See syndrome, Wagner’s.
warpage, corneal See corneal warpage.
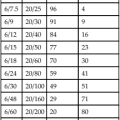
water content Water in a contact lens expressed as a percentage of the total mass of the lens in its hydrated state under equilibrium conditions with physiological saline solution containing 9 g/l sodium chloride at a temperature of 20 ± 0.5°C and with a stated pH value.
< ?xml:namespace prefix = "mml" />
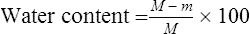
where M is the mass of hydrated lens, m is the mass of dry lens.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has categorized hydrogel contact lenses into four groups according to their water content and their surface reactivity (referred to as ionic if it contains more than 0.2% ionic material, and nonionic otherwise). Group 1: water content less than 50% and non-ionic. Group 2: water content greater than 50% and non-ionic. Group 3: water content less than 50% and ionic. Group 4: water content greater than 50% and ionic.
water-drinking test See test, provocative.
waterfall after-effect; illusion See after-effect, waterfall.
watery eye See epiphora.
wave, alpha See alpha waves.
wave number See wavelength.
wavefront A virtual surface emanating from an object or an optical system, perpendicular throughout to a bundle of rays.
See aberration, wavefront.
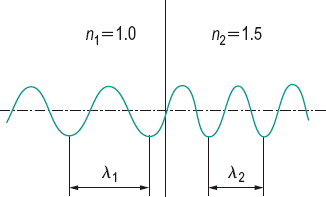
wavelength Distance in the direction of propagation of a periodic wave between two successive points at the same position in the wave (e.g. the distance between two crests). Symbol: λ. Note 1: The wavelength in a medium is equal to the wavelength in vacuum divided by the refractive index of the medium. Unless otherwise stated, values of wavelength are generally those in air. The refractive index of standard air (15°C, 101 325 N/m2) lies between 1.00027 and 1.00029 for visible radiations. Note 2: The reciprocal of the wavelength is called the wave number. Note 3: The wavelength is longer for red light than for blue light. Wavelength λ is equal to
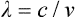
where c is the velocity of light and v is the frequency of light. (Fig. W1)
See fluorescence; infrared; interferometer; light; phase; phenomenon, Bezold–Brücke; spectrum, electromagnetic; ultraviolet; theory, wave.
wavelength, complementary See colour, complementary.
wavelength, dominant (of a colour stimulus, not purple) Wavelength of the monochromatic light stimulus that, when combined in suitable proportions with the specified achromatic light stimulus, yields a match with the colour stimulus considered. Note: When the dominant wavelength cannot be given (this applies to purples), its place is taken by the complementary wavelength (CIE).
See colour, complementary.
Weber’s fraction; law See law, Weber’s.
Weber’s syndrome See syndrome, Weber’s.
Weber–Fechner law See law, Weber’s.
wedge, optical A filter in which the transmittance varies continuously along a path (straight or curved) on its surface. If the filter transmits all the wavelengths more or less equally, it is called a neutral wedge.
See phenomenon, Bielschowsky’s.
weeping Excessive lacrimation. See epiphora; lacrimal apparatus; lacrimation.
weeping reflex See reflex, lacrimal.
Wegener’s granulomatosis See keratitis, peripheral ulcerative; scleritis.
Weill–Marchesani syndrome See syndrome, Weill–Marchesani.
Welland’s test See test, bar reading.
Wernicke’s disease See disease, Wernicke’s.
Wernicke’s hemianopic pupil; pupillary reaction; pupillary reflex; sign See reflex, hemianopic pupillary.
Wessley ring See ring, Wessley.
Wesson Fixation Disparity Card See disparity, retinal.
wettability See angle, contact.
wetting angle See angle, contact.
wetting solution A solution that (1) transforms a hydrophobic surface into a hydrophilic one; (2) acts as a lubricant; (3) helps to clean the surface; (4) helps to prevent contamination of the lens while being inserted. It is spread on both surfaces of a rigid contact lens prior to insertion. However, the effect of a wetting solution only lasts a short time because it is quickly removed by the tear layer. A common wetting agent is polyvinyl alcohol, which also has viscosity building properties.
See enzyme; tears, artificial.
‘what’ system See system, parvocellular visual.
Wheatstone amblyopia See amblyoscope, Wheatstone.
‘where’ system See system, magnocellular visual.
white See colour, achromatic; colour, complementary; light, white.
white pupil; pupillary reflex See leukocoria.
Whitnall’s tubercle See tubercle, lateral orbital.
wide-angle lens See lens, wide-angle.
Wieger, ligament of See ligament of Wieger.
Wilbrand’s knee That portion of the decussating optic nerve fibres from the inferior nasal retina which loop forward into the contralateral optic nerve for a distance of up to 3 mm from the anterior part of the optic chiasma and then pass backward into the optic tract. The existence of Wilbrand’s knee in normal subjects has been questioned.
See scotoma, junction.
Willis, circle of See circle of Willis.
Wilson’s disease See disease, Wilson’s.
Wilson three-mirror fundus lens See slit-lamp.
wing cells See corneal epithelium.
wink The rapid, voluntary closure and opening of one eye.
See blink.
with movement See retinoscope.
with the rule astigmatism See astigmatism, with the rule.
Wolfring, glands of See glands of Wolfring.
Wollaston ellipse See ellipse, Tscherning.
Wollaston lens See lens, Wollaston.
Wollaston polarizer; prism See prism, Wollaston.
Wood’s light See light, Wood’s.
word blindness See alexia.
working distance See distance, working.
Worth amblyoscope See amblyoscope, Worth.
Worth’s classification of binocular vision See vision, Worth’s classification of binocular.
Worth’s four dot test See test, Worth’s four dot.
Wundt’s visual illusion See illusion, Wundt’s visual.