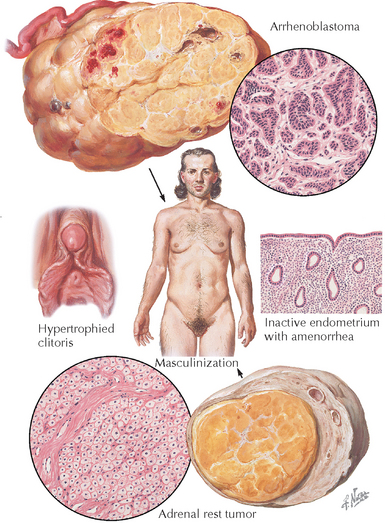
Chapter 179 Virilization
INTRODUCTION
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
Differential Diagnosis
Workup and Evaluation
MANAGEMENT AND THERAPY
Nonpharmacologic
FOLLOW-UP
MISCELLANEOUS
Azziz R, Ochoa TM, Bradley ELJr, et al. Leuprolide and estrogen versus oral contraceptive pills for the treatment of hirsutism: a prospective randomized study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:3406.
Moghetti P, Tosi F, Tosti A, et al. Comparison of spironolactone, flutamide, and finasteride efficacy in the treatment of hirsutism: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:89.
Coonrod DV, Rizkallah TH. Virilizing adrenal carcinoma in a woman of reproductive age: a case presentation and literature review. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172:1912.
Guido M, Romualdi D, Giuliani M, et al. Drospirenone for the treatment of hirsute women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a clinical, endocrinological, metabolic pilot study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2817.
Ibanez L, Potau N, Marcos MV, de Zegher F. Treatment of hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, oligomenorrhea, dyslipidemia, and hyperinsulinism in nonobese, adolescent girls: effect of flutamide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:3251.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Polycystic ovary syndrome. ACOG Practice Bulletin 41. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100:1389.
Azziz R. The evaluation and management of hirsutism. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:995.
Bailey-Pridham DD, Sanfilippo JS. Hirsutism in the adolescent female. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1989;36:581.
Bergfeld WF. Hirsutism in women. Effective therapy that is safe for long-term use. Postgrad Med. 2000;107:93. 99.
Chang RJ. A practical approach to the diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191:713.
Conn JJ, Jacobs HS. Managing hirsutism in gynaecological practice. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998;105:687.
Curran DR, Moore C, Huber T. Clinical inquiries. What is the best approach to the evaluation of hirsutism? J Fam Pract. 2005;54:465.
Ehrmann DA. Polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1223.
Ehrmann DA, Rosenfield RL. Clinical review 10: an endocrinologic approach to the patient with hirsutism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990;71:1.
Ginsburg J, White MC. Hirsutism and virilisation. Br Med J. 1980;280:369.
Gordon CM. Menstrual disorders in adolescents. Excess androgens and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1999;46:519.
Harborne L, Fleming R, Lyall H, et al. Metformin or antiandrogen in the treatment of hirsutism in polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:4116.
Karp L, Herrmann WL. Diagnosis and treatment of hirsutism in women. Obstet Gynecol. 1973;41:283.
Lobo RA. Hyperandrogenism. In: Katz VL, Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, editors. Comprehensive Gynecology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier; 2007:979.
Marshburn PB, Carr BR. Hirsutism and virilization. A systematic approach to benign and potentially serious causes. Postgrad Med. 1995;97:99. 105.
Rosenfield RL. Clinical practice. Hirsutism. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2578.
Tagatz GE, Kopher RA, Nagel TC, Okagaki T. The clitoral index: a bioassay of androgenic stimulation. Obstet Gynecol. 1979;54:562.