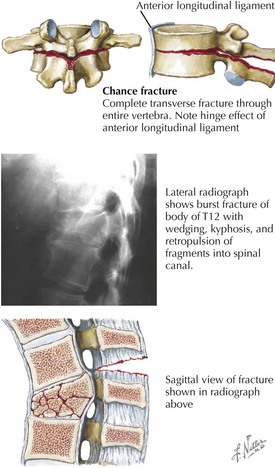
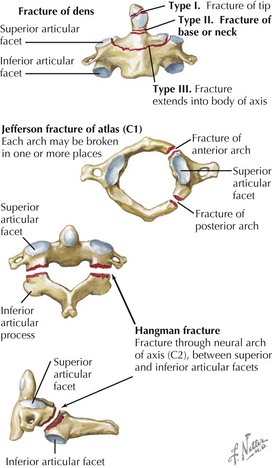
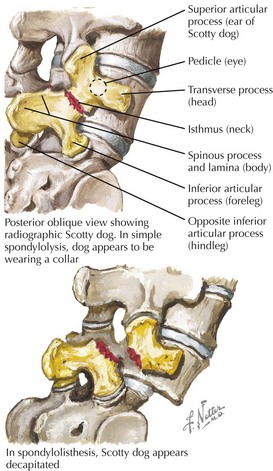
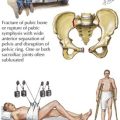
3 Vertebral Fractures
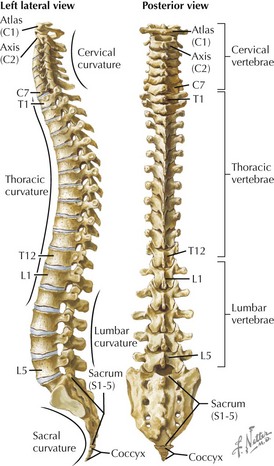
Anatomy of the Vertebral Column
Articulated Vertebrae and Spine
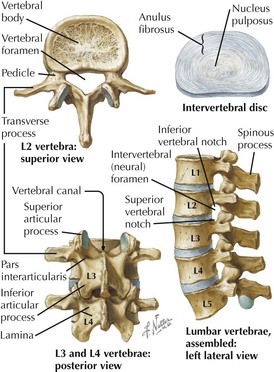
Typical Vertebrae
Cervical Vertebrae
• C2, axis
Sacral Vertebrae
• Fusion of sacral bodies typically occurs in adulthood, though disc remnants can remain visible on imaging.
Joints and Ligaments of the Spine
• Vertebral body joints: discs, symphyses
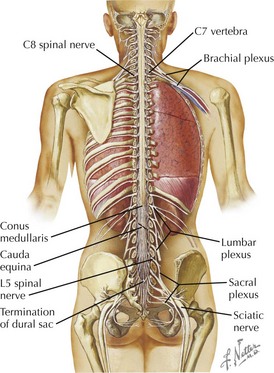
Nerves and Vessels of Spine and Cord
Spinal Cord and Nerves
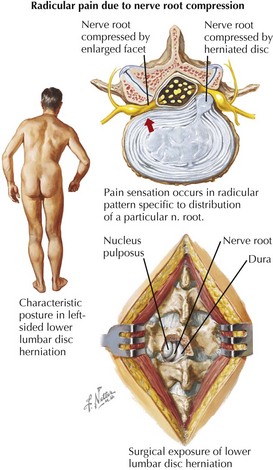
• Spinal cord and meningeal sheaths adjoin inner bone of bodies, pedicles, laminae in vertebral canal and are susceptible to trauma with fractures.
• Because the cord is shorter than the length of vertebral canal, cervical roots exit more laterally than those below.
Vessels
Arteries of the Spine and Cord
• Vertebrae are supplied by periosteal and equatorial branches of major cervical and thoracoabdominal arteries.
• Spinal cord is supplied by longitudinal anterior (1) and posterior spinal (2) arteries, arising superiorly from vertebral arteries.
• Spinal arteries receive segmental input from segmental spinal and radicular branches of cervical and thoracoabdominal arteries (e.g., aorta).