Vasculitis and the reactive erythemas
Vasculitis and the reactive erythemas are characterized by inflammation within or around blood vessels. This may result from a type III hypersensitivity response, with circulating immune complexes, but other mechanisms are also possible.
Vasculitis
Aetiopathogenesis
The CICs, which may be associated with several conditions (Table 1), lodge in the vessel wall where they activate complement and cytokine release, attract polymorphs and damage tissue. Inflammatory cells infiltrate vessels. Endothelial cells may show swelling, fibrinoid change or necrosis.
| Group | Example |
|---|---|
| Idiopathic | 50% of cases (no cause found) |
| Blood disease | Cryoglobulinaemia |
| Connective tissue disease | Systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis |
| Drugs | Antibiotics, diuretics, non-steroidals, anticonvulsants, allopurinol, cocaine |
| Infections | Hepatitis B, streptococci, Mycobacterium leprae, Rickettsia |
| Neoplasia | Lymphoma, leukaemia |
| Other | Wegener’s granulomatosis, giant cell arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa |
Clinical presentation
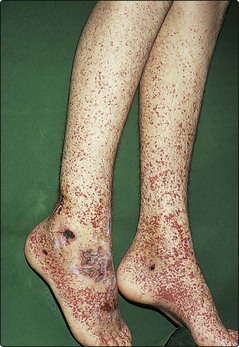
This depends on the size and site of the vessels involved. Vasculitis may be confined to the skin, or may be systemic and involve the joints, kidneys, lungs, heart, gut and nervous system. The skin signs are of palpable purpura, often painful and usually on the lower legs or buttocks (Fig. 1). Specific types are as follows:
 Henoch–Schönlein purpura describes these signs, with arthritis, abdominal pain and haematuria. Direct immunofluorescence studies on a skin biopsy will show the small vessel immunoglobulin (Ig) A–CIC vasculitis, which can be helpful diagnostically. Mainly affects children and often follows a streptococcal infection.
Henoch–Schönlein purpura describes these signs, with arthritis, abdominal pain and haematuria. Direct immunofluorescence studies on a skin biopsy will show the small vessel immunoglobulin (Ig) A–CIC vasculitis, which can be helpful diagnostically. Mainly affects children and often follows a streptococcal infection.
 Nodular vasculitis, characterized by tender subcutaneous nodules on the lower legs, results when deeper dermal vessels are involved.
Nodular vasculitis, characterized by tender subcutaneous nodules on the lower legs, results when deeper dermal vessels are involved.
 Polyarteritis nodosa is characterized by a necrotizing vasculitis in medium-sized arteries. It is uncommon and afflicts middle-aged men who, in addition to tender subcutaneous nodules along the line of arteries, may develop hypertension, renal failure and neuropathy.
Polyarteritis nodosa is characterized by a necrotizing vasculitis in medium-sized arteries. It is uncommon and afflicts middle-aged men who, in addition to tender subcutaneous nodules along the line of arteries, may develop hypertension, renal failure and neuropathy.
 Wegener’s granulomatosis is a rare but potentially fatal granulomatous vasculitis of unknown cause. Malaise, upper and lower respiratory tract necrosis, glomerulonephritis and, in 40% of cases, a cutaneous vasculitis are found. Classical antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies (c-ANCA) directed at proteinase 3 (PR3) are present.
Wegener’s granulomatosis is a rare but potentially fatal granulomatous vasculitis of unknown cause. Malaise, upper and lower respiratory tract necrosis, glomerulonephritis and, in 40% of cases, a cutaneous vasculitis are found. Classical antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies (c-ANCA) directed at proteinase 3 (PR3) are present.
 Giant cell arteritis affects medium-sized arteries in the elderly. Visual loss may result if prednisolone is withheld. Patients present with scalp tenderness due to temporal artery involvement that can progress to scalp necrosis.
Giant cell arteritis affects medium-sized arteries in the elderly. Visual loss may result if prednisolone is withheld. Patients present with scalp tenderness due to temporal artery involvement that can progress to scalp necrosis.
Erythema multiforme
Erythema multiforme is an immune-mediated disease, characterized by target lesions on the hands and feet. It has a variety of causes (Table 2).
| Group | Cause |
|---|---|
| Idiopathic | 50% of cases (no cause found) |
| Viral | Herpes simplex, hepatitis B, orf, adenovirus, mumps, Mycoplasma |
| Bacterial | Streptococci, Rickettsia |
| Fungal | Coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis |
| Drugs | Antibiotics, phenytoin, non-steroidals |
| Other | Lupus erythematosus (p. 80), pregnancy, malignancy |
Clinical presentation
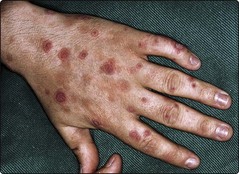
Typical target lesions, seen on the hands and feet, consist of red rings with central pale or purple areas, which may blister (Fig. 2). Involvement of the oral, conjunctival and genital mucosae is not uncommon and, if extensive, is known as erythema multiforme major. Crops of new lesions appear for 2–3 weeks. The differential diagnosis includes toxic erythema (p. 86), Stevens–Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Sweet’s disease, urticaria and pemphigoid. A biopsy is often helpful. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (p. 87) may sometimes represent erythema multiforme in a severe form.
Erythema nodosum
Erythema nodosum is a panniculitis (i.e. an inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) that usually presents as painful red nodules on the lower legs. It is believed to result from CIC deposition in vessels of the subcutis. Infection, drugs and some systemic diseases are underlying causes (Table 3).
| Group | Cause |
|---|---|
| Idiopathic | About 20% of cases |
| Bacterial | Streptococci, TB, leprosy, Yersinia, Mycoplasma, Salmonella |
| Fungal | Coccidioidomycosis, Trichophyton |
| Viral | Cat-scratch fever, chlamydiae |
| Drugs | Sulphonamides, oral contraceptives |
| Systemic disease | Inflammatory bowel disease, sarcoidosis, Behçet’s disease, malignancy (rare) |
Clinical presentation
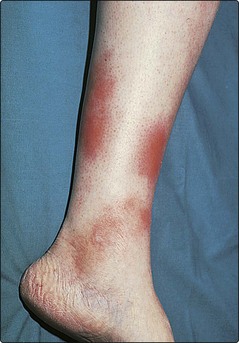
Deep, firm and tender reddish–blue nodules, 1–5 cm in diameter, develop on the calves (Fig. 3), shins and occasionally on the forearms. Joint pains and fever are common. Spontaneous resolution usually occurs within 8 weeks. Women are affected more than men (F : M ratio 3 : 1). Other causes of panniculitis (e.g. pancreatic disease, cold, trauma and lupus erythematosus), cellulitis and phlebitis need to be excluded. A skin biopsy is helpful. If tuberculosis or sarcoidosis is suspected, a chest radiograph and Mantoux test are indicated.
Sweet’s disease
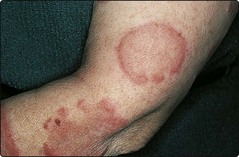
Sweet’s disease (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) occurs as raised plum-coloured plaques on the face or limbs (Fig. 4), typically with fever and a raised neutrophil count. It is not a true vasculitis but results from polymorph infiltration of the dermis. Leukaemia, ulcerative colitis and other disorders may be associated and must be excluded. Drugs are another cause. Treatment with prednisolone is usually required.
Graft-versus-host (GVH) disease
GVH disease occurs when immunologically competent donor lymphocytes react against host tissues, principally the skin and gut. It is mostly associated with bone marrow transplantation, e.g. given for leukaemia or aplastic anaemia. Fever, malaise and a morbilliform eruption (Fig. 5), which may progress to toxic epidermal necrolysis, typify the acute GVH reaction. The acute type may be difficult to differentiate from a drug eruption, a viral infection or a cutaneous reaction to radiation therapy. Chronic GVH disease may resemble lichen planus or systemic sclerosis. A skin biopsy often helps, and treatment with systemic steroids is usually needed.
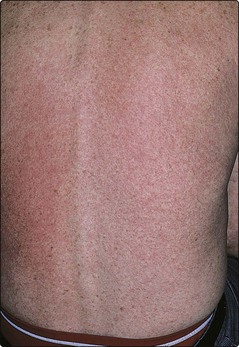
Fig. 5 Graft-versus-host disease.
An acute eruption is shown in a patient following bone marrow transplant.
Vasculitis and the reactive erythemas
 Vasculitis is a circulating immune complex (CIC) disorder showing palpable purpura, sometimes with internal organ involvement. Investigations may reveal the underlying cause. Treatment with dapsone, prednisolone or other immunosuppressive drugs is often indicated.
Vasculitis is a circulating immune complex (CIC) disorder showing palpable purpura, sometimes with internal organ involvement. Investigations may reveal the underlying cause. Treatment with dapsone, prednisolone or other immunosuppressive drugs is often indicated.
 Erythema multiforme is an immune-mediated reaction with target and mucosal lesions, often due to infection, commonly herpes simplex, or drugs. The underlying cause should be sought.
Erythema multiforme is an immune-mediated reaction with target and mucosal lesions, often due to infection, commonly herpes simplex, or drugs. The underlying cause should be sought.
 Erythema nodosum presents as painful red nodules on the lower legs and is regarded as a CIC response to infection (e.g. streptococcal), drugs or internal disease (e.g. sarcoidosis).
Erythema nodosum presents as painful red nodules on the lower legs and is regarded as a CIC response to infection (e.g. streptococcal), drugs or internal disease (e.g. sarcoidosis).
 Sweet’s disease is characterized by plum-coloured plaques on the face and limbs. Leukaemia or a systemic disorder may be associated. A course of prednisolone is often required.
Sweet’s disease is characterized by plum-coloured plaques on the face and limbs. Leukaemia or a systemic disorder may be associated. A course of prednisolone is often required.